Содержание
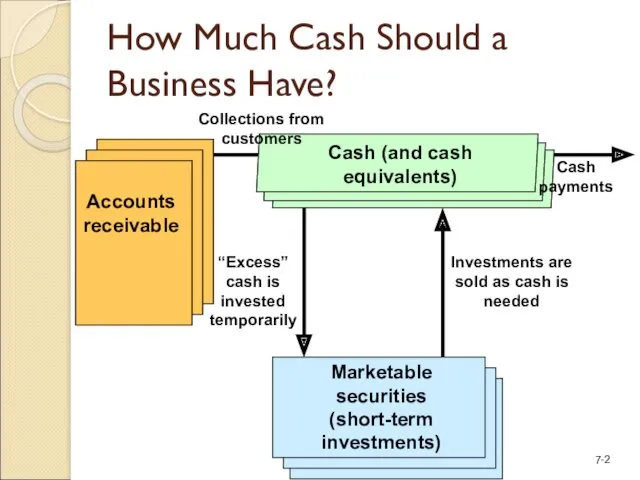
- 2. How Much Cash Should a Business Have?
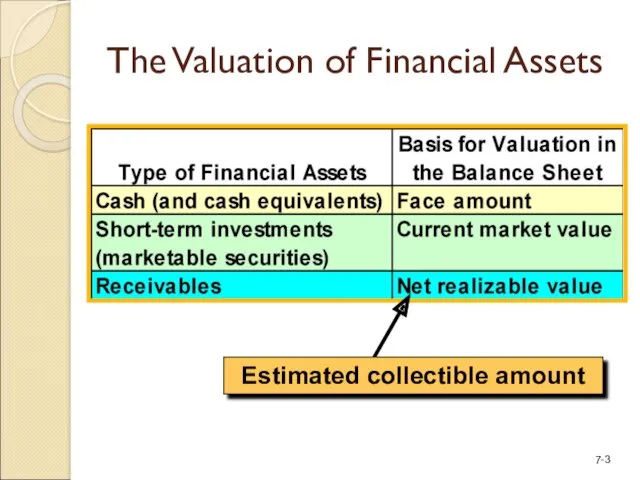
- 3. The Valuation of Financial Assets Estimated collectible amount
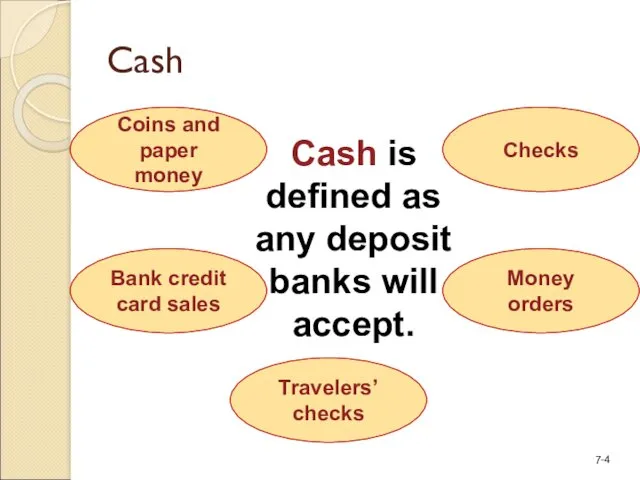
- 4. Cash Coins and paper money Checks Money orders Travelers’ checks Bank credit card sales Cash is
- 5. Reporting Cash in the Balance Sheet
- 6. Cash Management Accurately account for cash. Prevent theft and fraud. Assure the availability of adequate amounts
- 7. Internal Control Over Cash Segregate authorization, custody and recording of cash. Prepare a cash budget (or
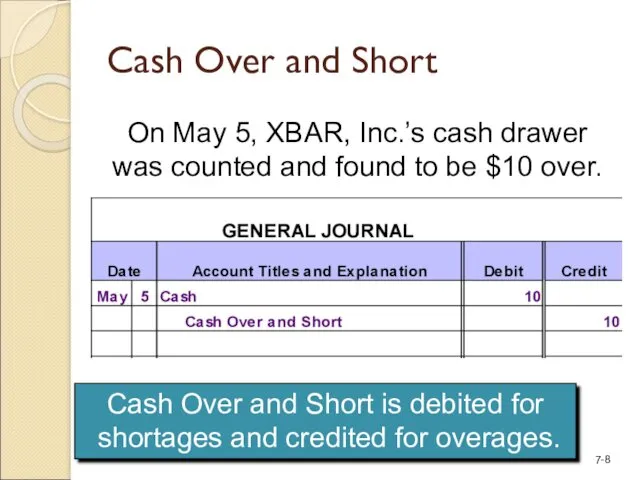
- 8. Cash Over and Short Cash Over and Short is debited for shortages and credited for overages.
- 9. Reconciling the Bank Statement Согласование выписки с банковского счета Explains the difference between cash reported on
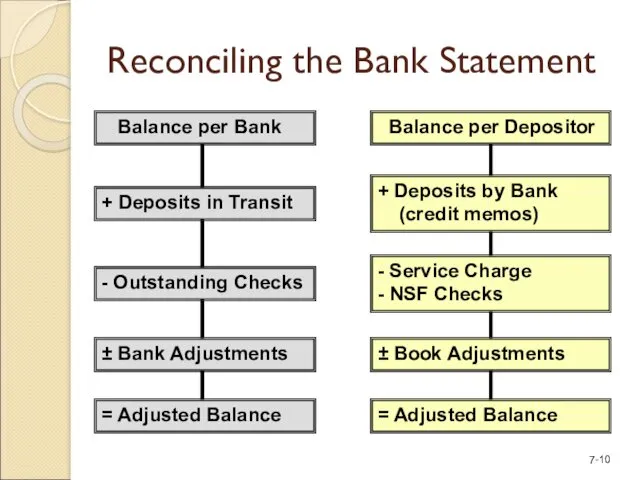
- 10. Reconciling the Bank Statement Balance per Bank + Deposits in Transit - Outstanding Checks ± Bank
- 11. Reconciling the Bank Statement The July 31 bank statement for Simmons Company indicated a cash balance
- 12. Reconciling the Bank Statement
- 13. Reconciling the Bank Statement
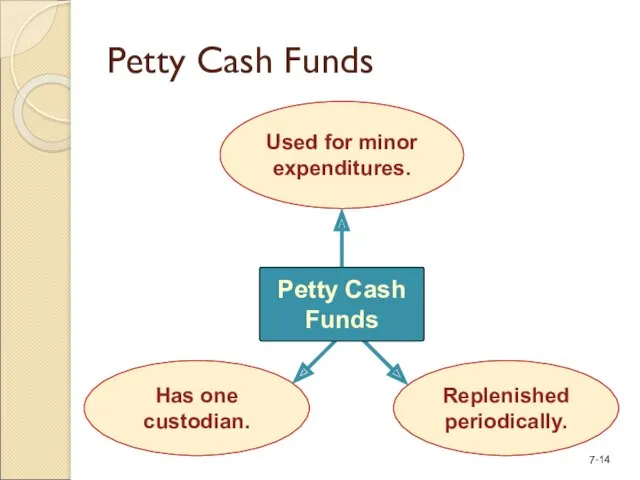
- 14. Used for minor expenditures. Petty Cash Funds Has one custodian. Replenished periodically. Petty Cash Funds
- 15. Short-Term Investments Bond Investments Capital Stock Investments Current Assets Almost As Liquid As Cash Readily Marketable
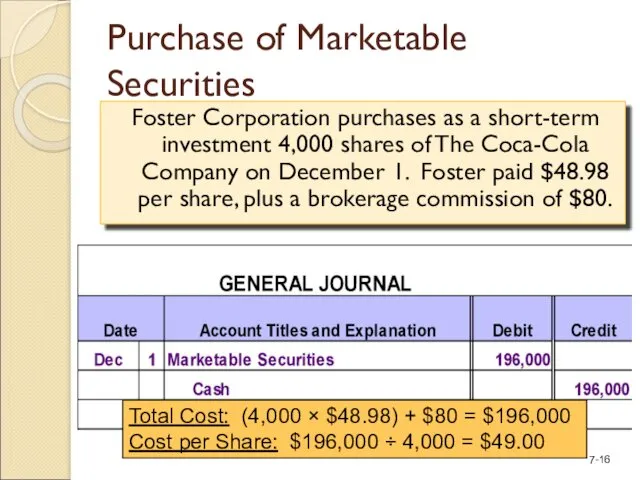
- 16. Purchase of Marketable Securities Foster Corporation purchases as a short-term investment 4,000 shares of The Coca-Cola
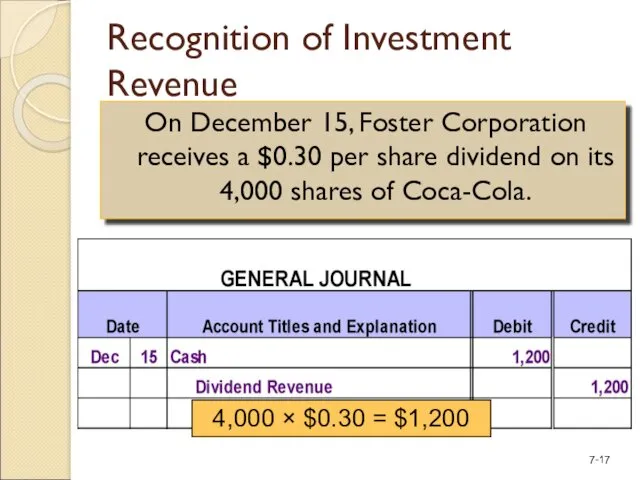
- 17. Recognition of Investment Revenue On December 15, Foster Corporation receives a $0.30 per share dividend on
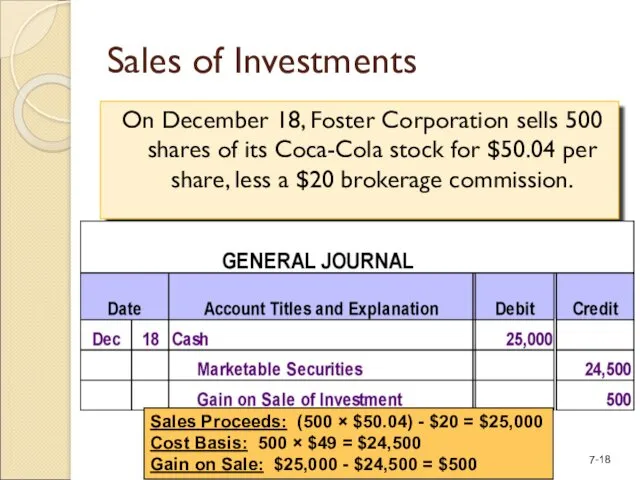
- 18. Sales of Investments On December 18, Foster Corporation sells 500 shares of its Coca-Cola stock for
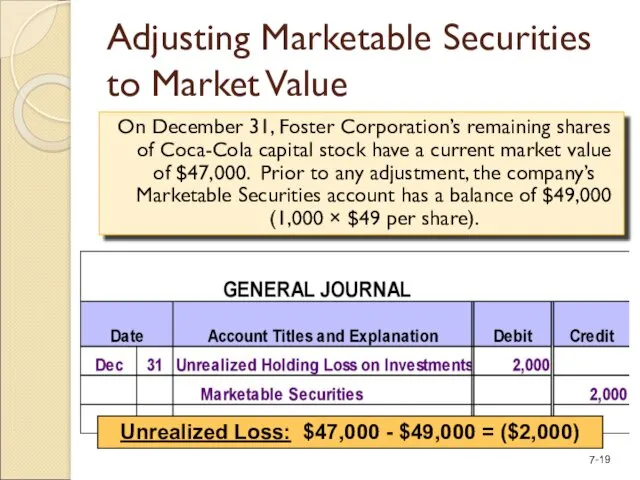
- 19. Adjusting Marketable Securities to Market Value On December 31, Foster Corporation’s remaining shares of Coca-Cola capital
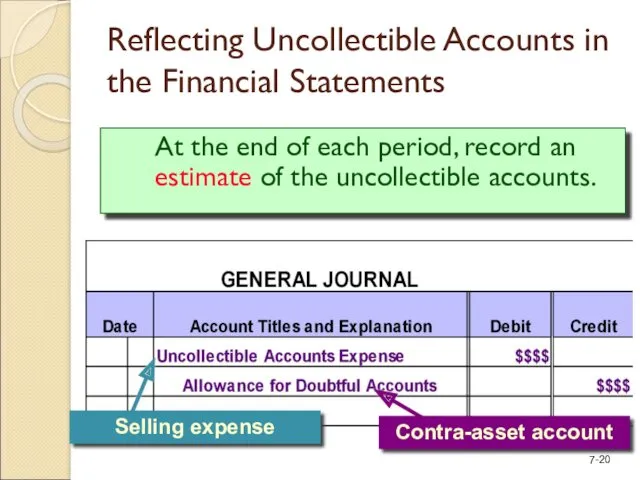
- 20. Reflecting Uncollectible Accounts in the Financial Statements At the end of each period, record an estimate
- 21. The Allowance for Doubtful Accounts The net realizable value is the amount of accounts receivable that
- 22. Writing Off an Uncollectible Account Receivable When an account is determined to be uncollectible, it no
- 23. Notice that the $500 write-off did not change the net realizable value nor did it affect
- 24. Monthly Estimates of Credit Losses At the end of each month, management should estimate the probable
- 25. Estimating Credit Losses — The Balance Sheet Approach Year-end Accounts Receivable is broken down into age
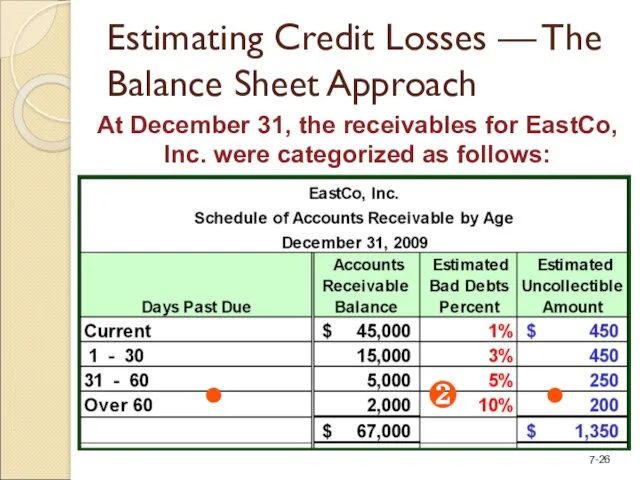
- 26. Estimating Credit Losses — The Balance Sheet Approach At December 31, the receivables for EastCo, Inc.
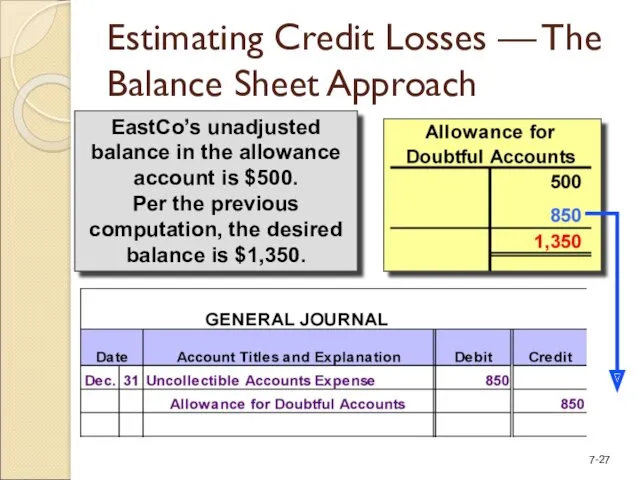
- 27. EastCo’s unadjusted balance in the allowance account is $500. Per the previous computation, the desired balance
- 28. Estimating Credit Losses — The Income Statement Approach Uncollectible accounts’ percentage is based on actual uncollectible
- 29. Estimating Credit Losses — The Income Statement Approach In 2009, EastCo had credit sales of $60,000.
- 30. Recovery of an Account Receivable Previously Written Off Subsequent collections require that the original write-off entry
- 31. Direct Write-Off Method This method makes no attempt to match revenues with the expense of uncollectible
- 32. Internal Controls for Receivables Maintenance of the accounts receivable subsidiary ledger. Custody of cash receipts. Authorization
- 33. Management of Accounts Receivable Extending credit encourages customers to buy from us but it ties up
- 34. A promissory note is an unconditional promise in writing to pay on demand or at a
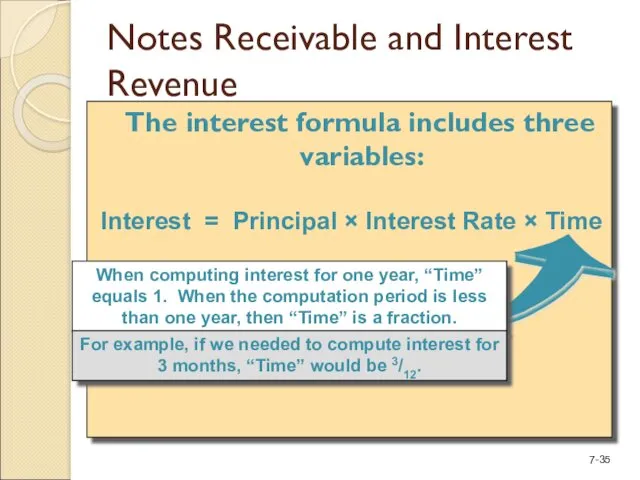
- 35. Notes Receivable and Interest Revenue The interest formula includes three variables: Interest = Principal × Interest
- 36. On November 1, Hall Company loans $10,000 to Porter Company on a 90-day note earning 12
- 37. What entry would Hall Company make on the maturity date? Notes Receivable and Interest Revenue $10,000
- 38. Financial Analysis and Decision Making Accounts Receivable Turnover Rate This ratio provides useful information for evaluating
- 39. Financial Analysis and Decision Making Avg. Number of Days to Collect A/R This ratio helps judge
- 41. Скачать презентацию




















 Банковские и страховые продукты
Банковские и страховые продукты Нововведения в сфере недвижимости в 2020 году
Нововведения в сфере недвижимости в 2020 году Методика SIGMA
Методика SIGMA Личные и семейные доходы
Личные и семейные доходы Инвестиционный проект в коммерческую недвижимость
Инвестиционный проект в коммерческую недвижимость Порядок открытия лицевых счетов. Лицевой счет с кодом 71
Порядок открытия лицевых счетов. Лицевой счет с кодом 71 Фьючерсы и опционы Биржи РТС (FORTS)
Фьючерсы и опционы Биржи РТС (FORTS) Подготовка к взрослой жизни. Повышение финансовой грамотности
Подготовка к взрослой жизни. Повышение финансовой грамотности 6-НДФЛ и уведомления
6-НДФЛ и уведомления Бюджет семьи
Бюджет семьи Гражданско-правовые отношения в бухгалтерском учете и налогообложении
Гражданско-правовые отношения в бухгалтерском учете и налогообложении Фінансові інвестиції
Фінансові інвестиції Финансирование проекта и управление затратами
Финансирование проекта и управление затратами Налоги. Системы и принципы налогообложения
Налоги. Системы и принципы налогообложения Концептуальные основы финансовой отчетности по МСФО. Цель финансовой отчетности
Концептуальные основы финансовой отчетности по МСФО. Цель финансовой отчетности Инвентаризация основных средств и нематериальных активов
Инвентаризация основных средств и нематериальных активов Банковская система в России. Виды и функции банков
Банковская система в России. Виды и функции банков Отчет об исполнении бюджета Бардымского муниципального района за 2019 год
Отчет об исполнении бюджета Бардымского муниципального района за 2019 год Оплата труда в здравоохранении
Оплата труда в здравоохранении Организация бухгалтерского учета кассовых операций
Организация бухгалтерского учета кассовых операций Директ-страхование
Директ-страхование Оценка риска на рынке ценных бумаг
Оценка риска на рынке ценных бумаг Державний борг
Державний борг Основы технического анализа
Основы технического анализа Спрос. Закон спроса
Спрос. Закон спроса Дивидендная политика различных компаний (4). Microsoft
Дивидендная политика различных компаний (4). Microsoft Електронне декларування 2020
Електронне декларування 2020 Деньги и денежный рынок
Деньги и денежный рынок