Содержание
- 2. Topics Covered 75 Years of Capital Market History Measuring Risk Portfolio Risk Beta and Unique Risk
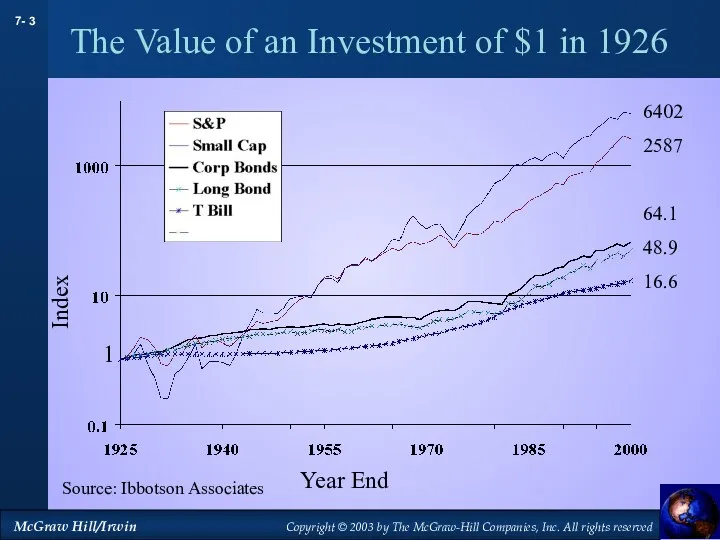
- 3. The Value of an Investment of $1 in 1926 Source: Ibbotson Associates Index Year End 1
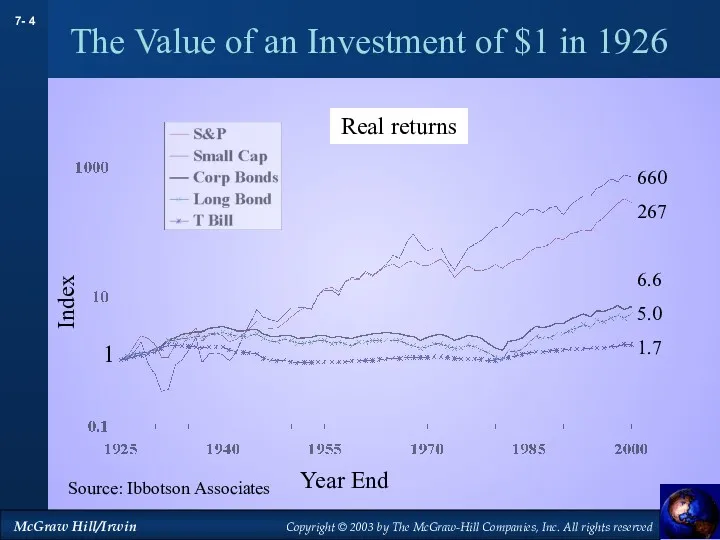
- 4. Source: Ibbotson Associates Index Year End 1 660 267 6.6 5.0 1.7 Real returns The Value
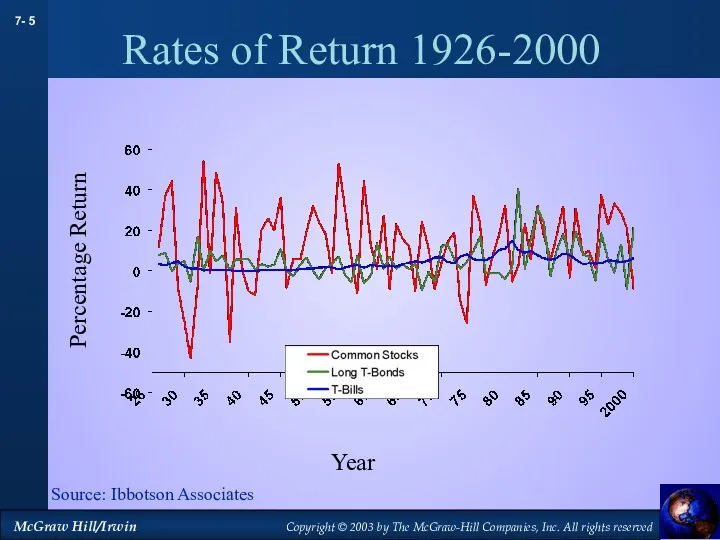
- 5. Rates of Return 1926-2000 Source: Ibbotson Associates Year Percentage Return
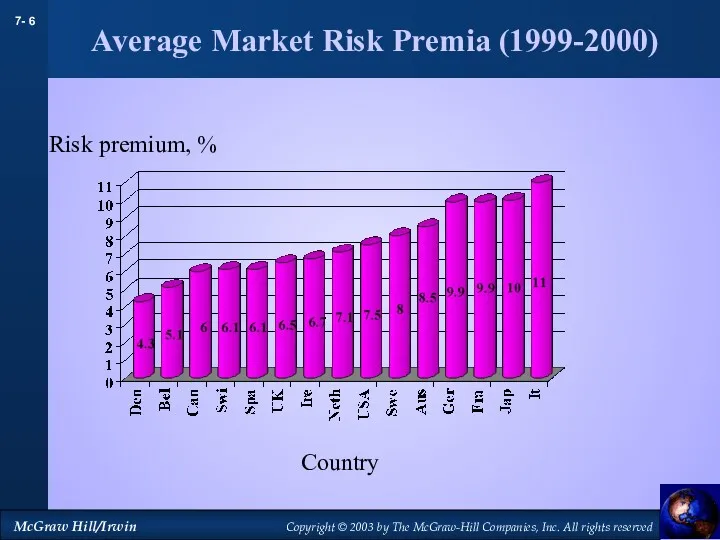
- 6. Average Market Risk Premia (1999-2000) Risk premium, % Country
- 7. Measuring Risk Variance - Average value of squared deviations from mean. A measure of volatility. Standard
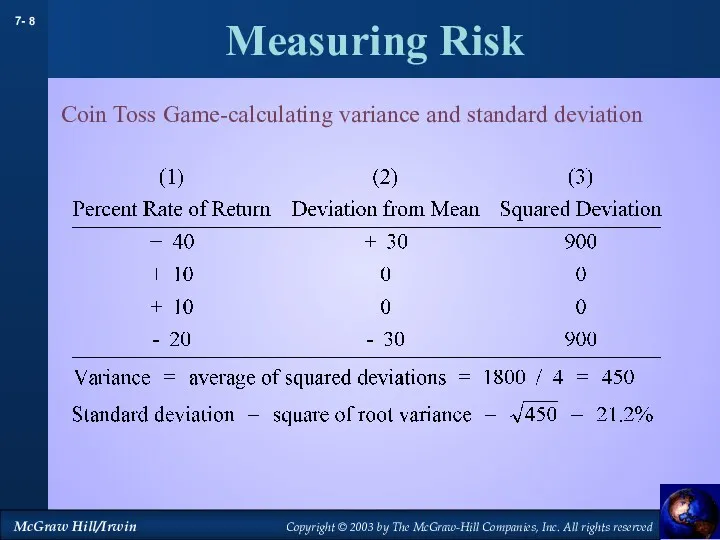
- 8. Measuring Risk Coin Toss Game-calculating variance and standard deviation
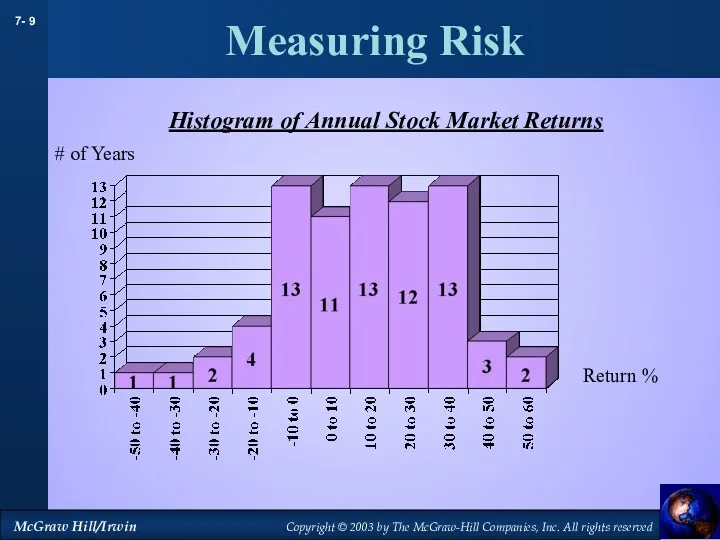
- 9. Measuring Risk Return % # of Years Histogram of Annual Stock Market Returns
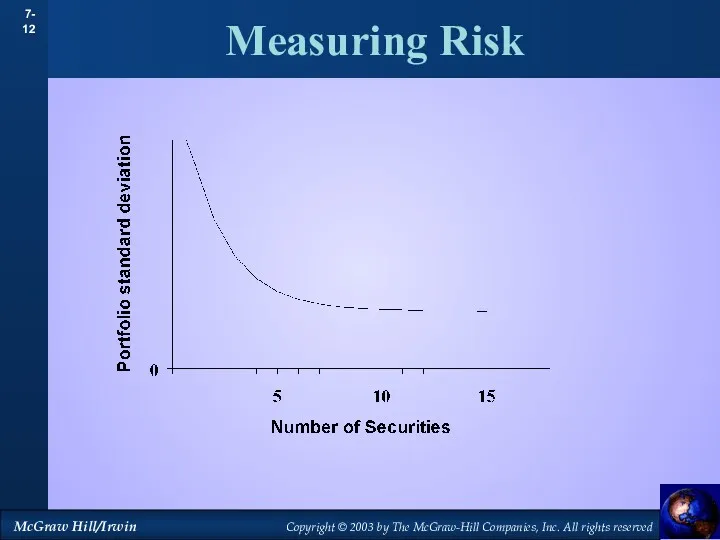
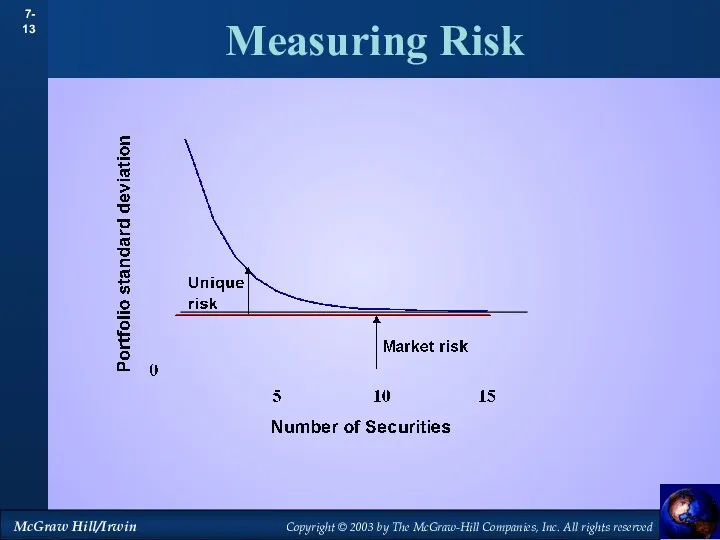
- 10. Measuring Risk Diversification - Strategy designed to reduce risk by spreading the portfolio across many investments.
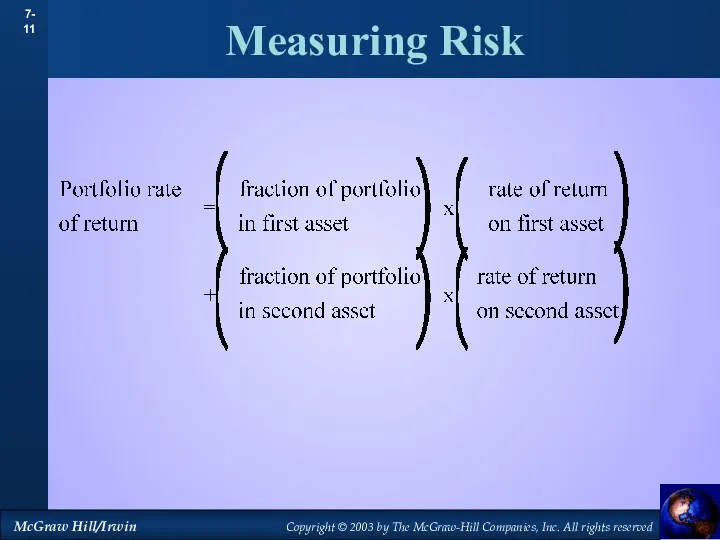
- 11. Measuring Risk
- 12. Measuring Risk
- 13. Measuring Risk
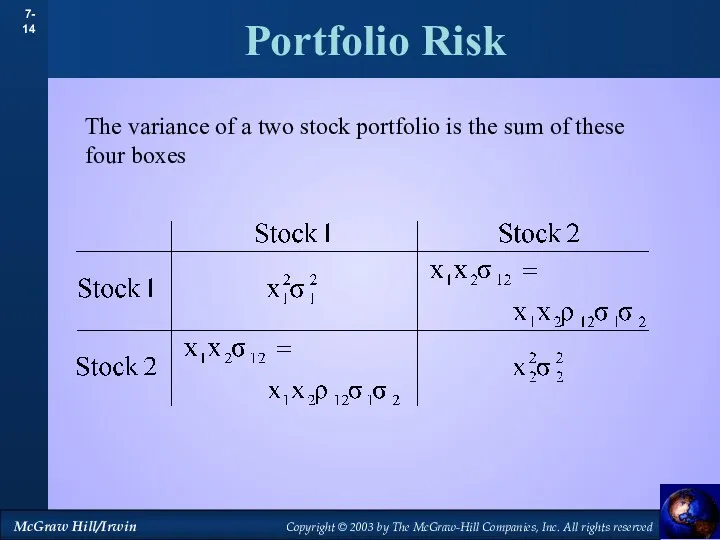
- 14. Portfolio Risk The variance of a two stock portfolio is the sum of these four boxes
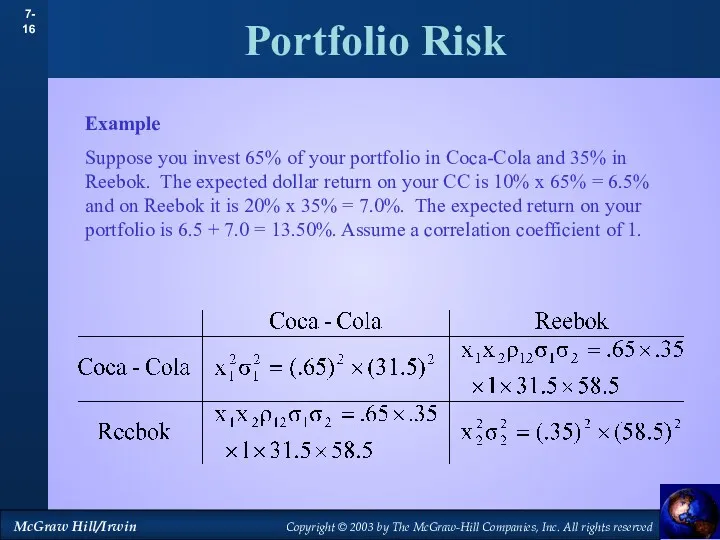
- 15. Portfolio Risk Example Suppose you invest 65% of your portfolio in Coca-Cola and 35% in Reebok.
- 16. Portfolio Risk Example Suppose you invest 65% of your portfolio in Coca-Cola and 35% in Reebok.
- 17. Portfolio Risk Example Suppose you invest 65% of your portfolio in Coca-Cola and 35% in Reebok.
- 18. Portfolio Risk
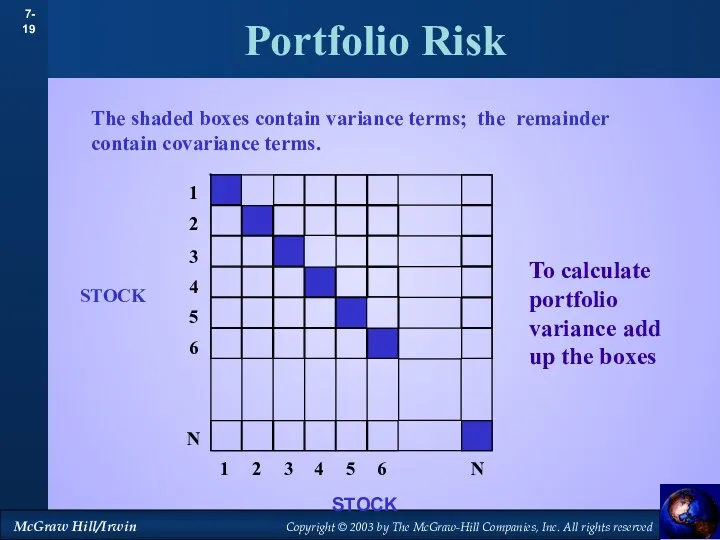
- 19. Portfolio Risk The shaded boxes contain variance terms; the remainder contain covariance terms. STOCK STOCK To
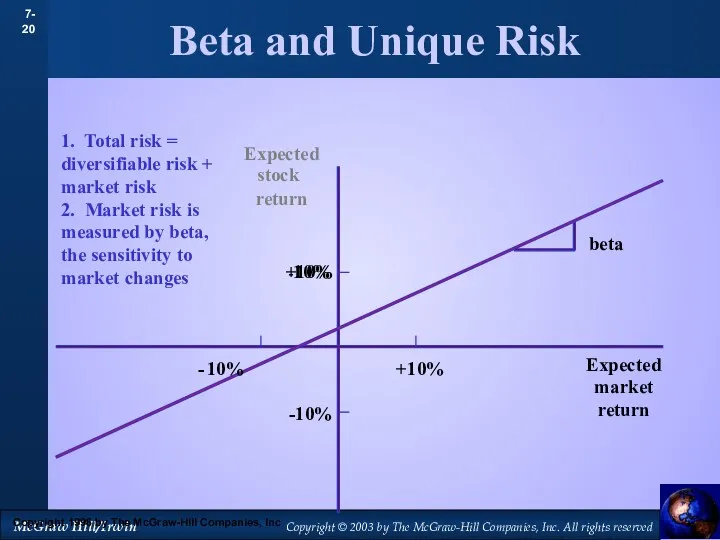
- 20. Beta and Unique Risk 1. Total risk = diversifiable risk + market risk 2. Market risk
- 21. Beta and Unique Risk Market Portfolio - Portfolio of all assets in the economy. In practice
- 22. Beta and Unique Risk
- 24. Скачать презентацию








 Банківська система
Банківська система Қазіргі жағдайда коммерциялық банктердің қаржылық тұрақтылығын жүйелі талдау
Қазіргі жағдайда коммерциялық банктердің қаржылық тұрақтылығын жүйелі талдау Учет материалов организации
Учет материалов организации Бюджетные кредиты
Бюджетные кредиты Финансовая среда предпринимательства и предпринимательские риски
Финансовая среда предпринимательства и предпринимательские риски Новый механизм оказания адресной социальной помощи с 1 января 2020 года
Новый механизм оказания адресной социальной помощи с 1 января 2020 года Финансовый анализ положения компании Вимм-БильДанн
Финансовый анализ положения компании Вимм-БильДанн Себестоимость продукции
Себестоимость продукции Государственный бюджет
Государственный бюджет Финансовое планирование и прогнозирование. Бюджетирование
Финансовое планирование и прогнозирование. Бюджетирование Тема 2. Инвестиционный климат предприятия и его оценка
Тема 2. Инвестиционный климат предприятия и его оценка Принципы международного налогообложения
Принципы международного налогообложения Инструменты и методы бережливого производства
Инструменты и методы бережливого производства Решение задач распознавания образов нейросетями
Решение задач распознавания образов нейросетями Фондовый рынок и биржевые инструменты
Фондовый рынок и биржевые инструменты Қысқа мерзімдегі фирманың шығындар
Қысқа мерзімдегі фирманың шығындар Как найти средства на научное исследование: гранты, субсидии и спонсоры
Как найти средства на научное исследование: гранты, субсидии и спонсоры Нематериальные активы
Нематериальные активы Электрические сети и передача электрической энергии. Государственное регулирование в сфере электроэнергетики. Лекция 7-8
Электрические сети и передача электрической энергии. Государственное регулирование в сфере электроэнергетики. Лекция 7-8 Правовые основы социальной защиты и социального обеспечения
Правовые основы социальной защиты и социального обеспечения Державне регулювання ринків фінансових послуг. Фінансові компанії
Державне регулювання ринків фінансових послуг. Фінансові компанії Прогноз значения курса доллара США по состоянию на 20 мая
Прогноз значения курса доллара США по состоянию на 20 мая Банковские услуги и отношения людей с банками
Банковские услуги и отношения людей с банками Оборотный капитал корпорации и краткосрочное финансирование
Оборотный капитал корпорации и краткосрочное финансирование Бухгалтерский учет материалов
Бухгалтерский учет материалов Понятие монополистической деятельности на товарных рынках
Понятие монополистической деятельности на товарных рынках Vērtspapīri
Vērtspapīri Крупнейшие инвестиционные проекты России в сфере туризма
Крупнейшие инвестиционные проекты России в сфере туризма