Содержание
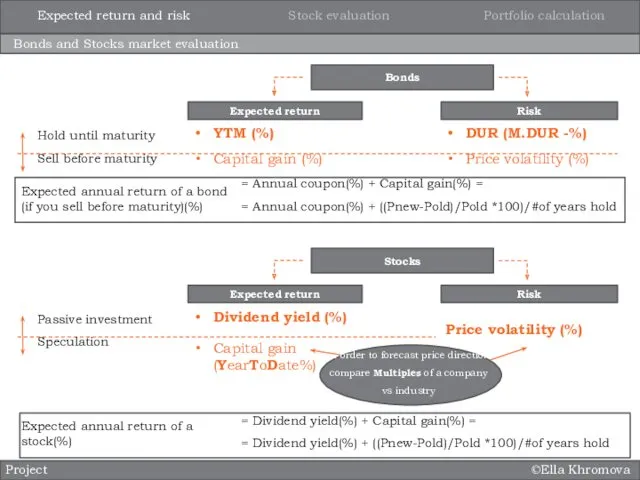
- 2. ©Ella Khromova Bonds and Stocks market evaluation Project Bonds Expected return Risk YTM (%) Capital gain
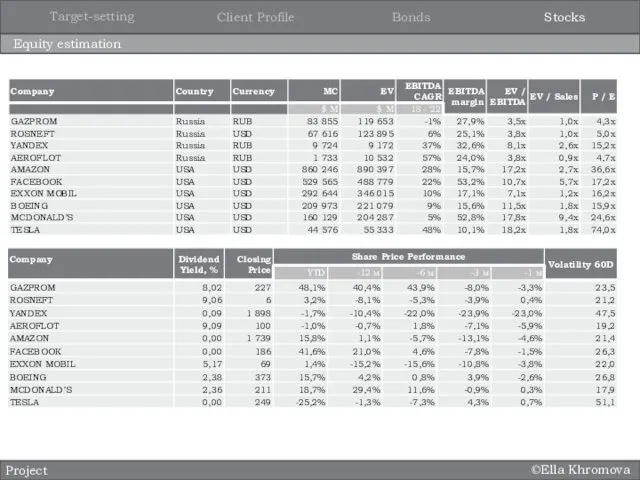
- 3. ©Ella Khromova Equity estimation Stocks Bonds Client Profile Target-setting Project
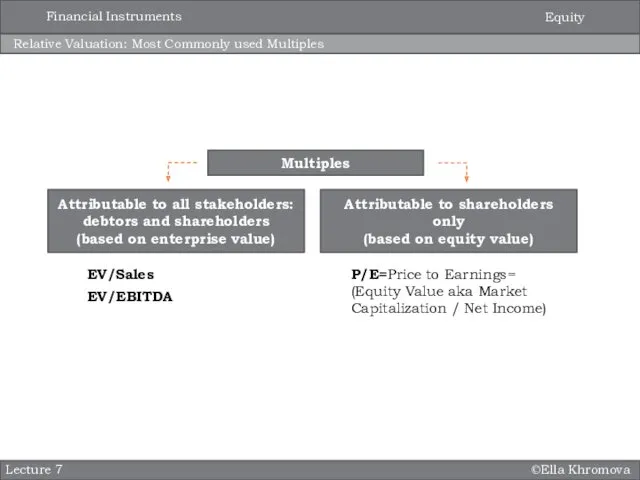
- 4. ©Ella Khromova Relative Valuation: Most Commonly used Multiples Lecture 7 Multiples Attributable to all stakeholders: debtors
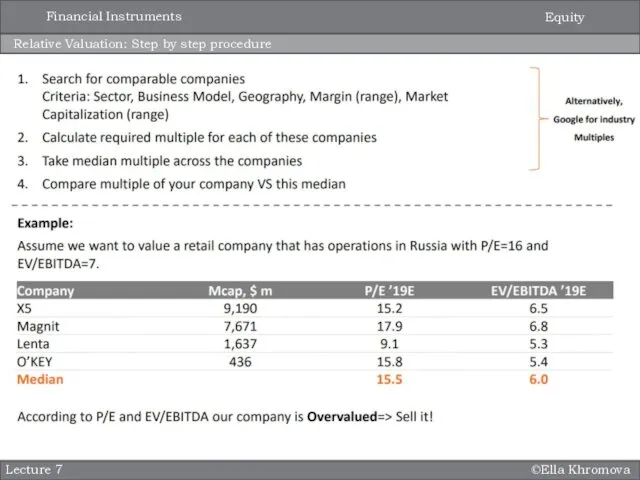
- 5. ©Ella Khromova Relative Valuation: Step by step procedure Lecture 7 Equity Financial Instruments
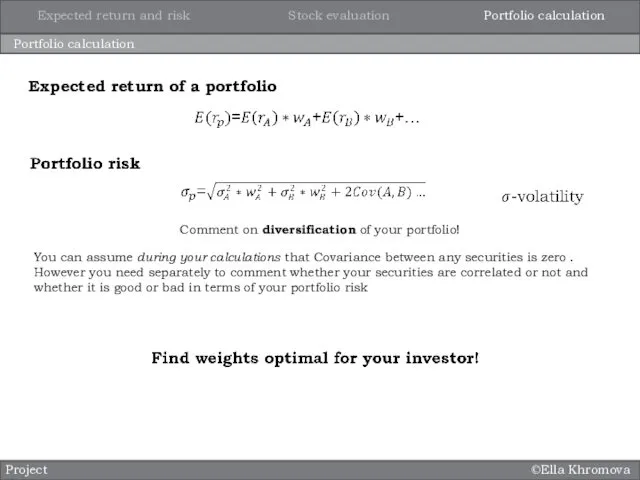
- 6. ©Ella Khromova Portfolio calculation Project Comment on diversification of your portfolio! Expected return of a portfolio
- 7. Lecture 9. Financial markets: Derivatives ©Ella Khromova Lecture 9 International finance and globalization Options Securities Futures
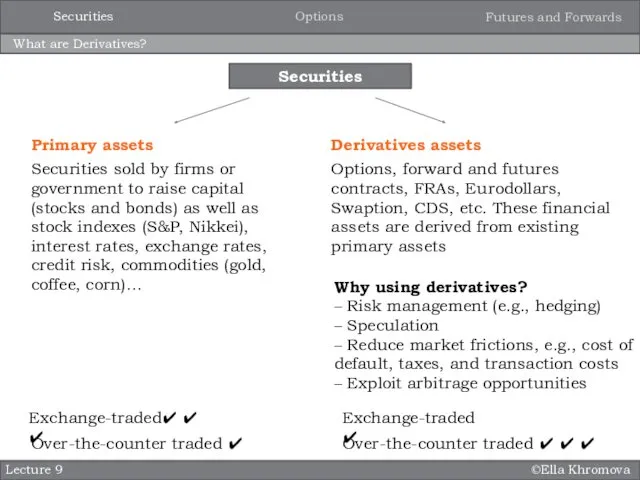
- 8. ©Ella Khromova What are Derivatives? Lecture 9 Primary assets Securities sold by firms or government to
- 9. ©Ella Khromova Options Lecture 9 Options: • Call - option to buy underlying asset • Put
- 10. ©Ella Khromova Long Call Lecture 9 Long Call Option example Payoff = Max [0, spot price
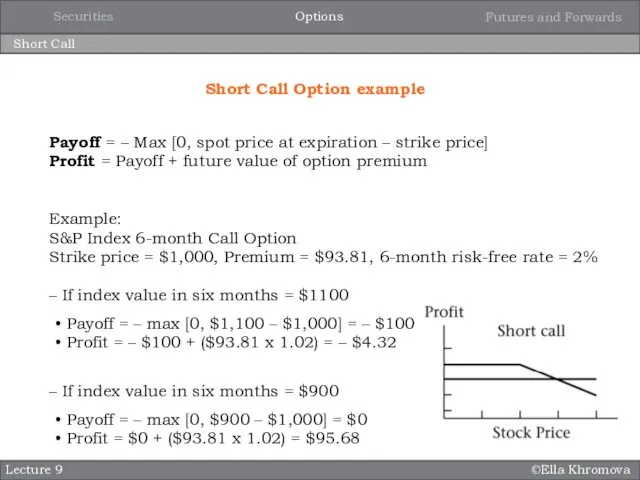
- 11. ©Ella Khromova Short Call Lecture 9 Short Call Option example Payoff = – Max [0, spot
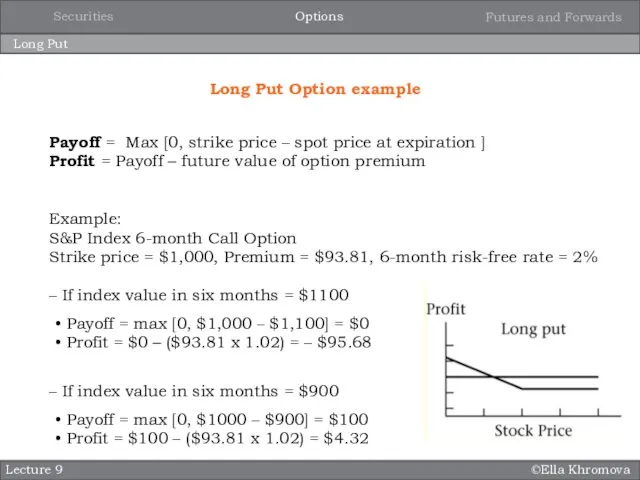
- 12. ©Ella Khromova Long Put Lecture 9 Long Put Option example Payoff = Max [0, strike price
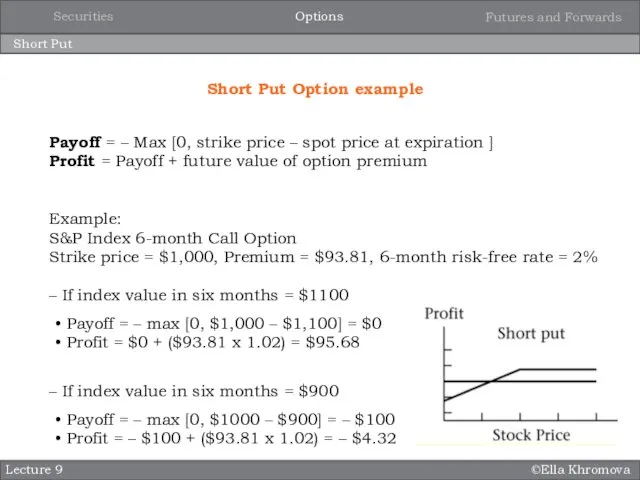
- 13. ©Ella Khromova Short Put Lecture 9 Short Put Option example Payoff = – Max [0, strike
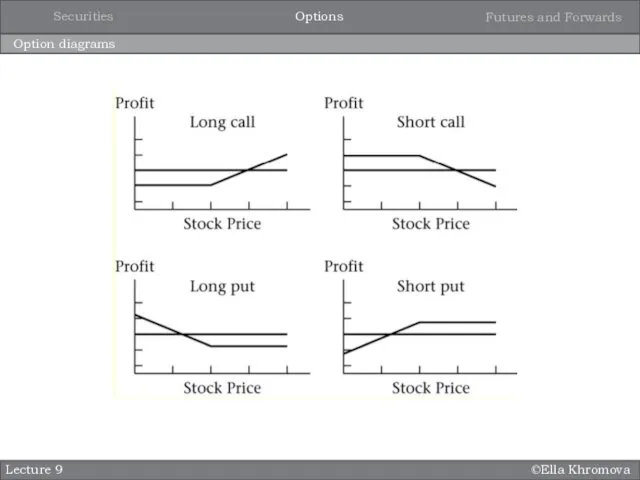
- 14. ©Ella Khromova Option diagrams Lecture 9 Options Securities Futures and Forwards
- 15. ©Ella Khromova Moneyness Lecture 9 In the Money - exercise of the option would be profitable
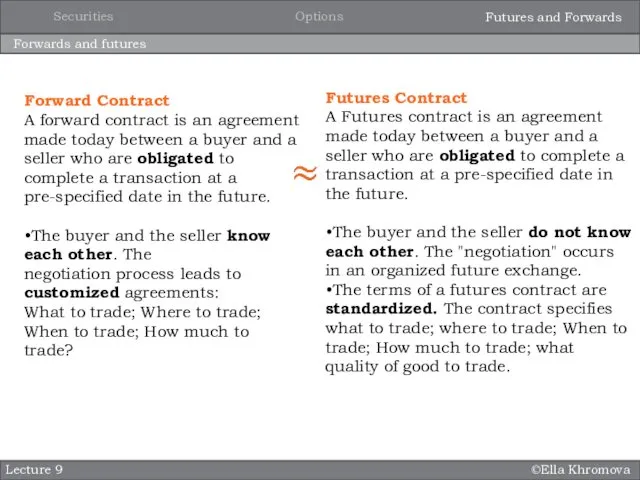
- 16. ©Ella Khromova Forwards and futures Lecture 9 Forward Contract A forward contract is an agreement made
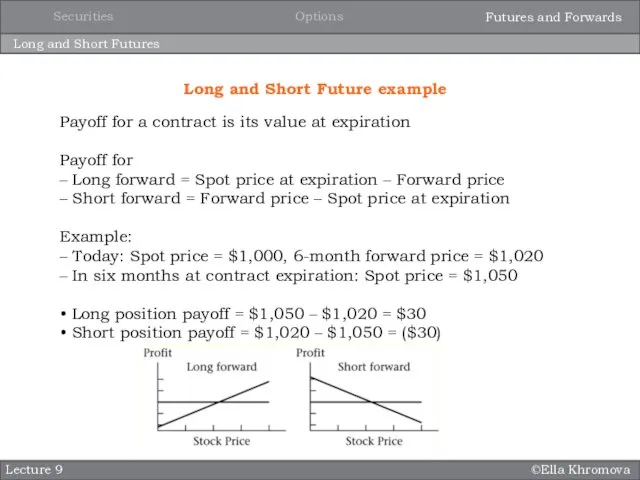
- 17. ©Ella Khromova Long and Short Futures Lecture 9 Long and Short Future example Payoff for a
- 18. ©Ella Khromova Long Futures Lecture 9 Options Securities Futures and Forwards
- 19. ©Ella Khromova Short futures Lecture 9 Options Securities Futures and Forwards
- 21. Скачать презентацию




 Характеристика бухгалтерского учета. Основы калькуляции и учета
Характеристика бухгалтерского учета. Основы калькуляции и учета Налоговый учет доходов и расходов, признаваемых в целях налогообложения
Налоговый учет доходов и расходов, признаваемых в целях налогообложения Предложения по улучшению жилищных условий. Город Лабытнанги
Предложения по улучшению жилищных условий. Город Лабытнанги Корпоративные финансы
Корпоративные финансы Финансовый анализ предприятия, его виды, содержание и информационное обеспечение
Финансовый анализ предприятия, его виды, содержание и информационное обеспечение Профессия бухгалтер
Профессия бухгалтер Анализ финансового состояния коммерческого банка (на примере ОАО КБ Пойдем)
Анализ финансового состояния коммерческого банка (на примере ОАО КБ Пойдем) История денег
История денег Судебно-правовая бухгалтерия. Счета бухгалтерского учёта и бухгалтерская проводка. Тема 3
Судебно-правовая бухгалтерия. Счета бухгалтерского учёта и бухгалтерская проводка. Тема 3 Zarządzanie ryzykiem finansowym przedsiębiorstwa na temat: ”Metody (sposoby) ograniczenia ryzyka”
Zarządzanie ryzykiem finansowym przedsiębiorstwa na temat: ”Metody (sposoby) ograniczenia ryzyka” Тема: Податки і податкове право в Україні
Тема: Податки і податкове право в Україні Финансовая деятельность юридических лиц
Финансовая деятельность юридических лиц Business angels
Business angels Еңбекақы статистикасы
Еңбекақы статистикасы Денежная единица Зимбабве
Денежная единица Зимбабве Систематизация источников права социального обеспечения
Систематизация источников права социального обеспечения Метод бухгалтерського обліку. Баланс як елемент методу. Лекція 2
Метод бухгалтерського обліку. Баланс як елемент методу. Лекція 2 Страховой рынок Казахстана: современное состояние и перспективы развития
Страховой рынок Казахстана: современное состояние и перспективы развития Стоимость и структура капитала корпорации. (Тема 9)
Стоимость и структура капитала корпорации. (Тема 9) Косвенные налоги. Налог на добавленную стоимость (НДС) (глава 21 НК РФ)
Косвенные налоги. Налог на добавленную стоимость (НДС) (глава 21 НК РФ) ГКУСЗ Центр социальной работы Олонецкого района
ГКУСЗ Центр социальной работы Олонецкого района Предоставление субсидий СФР
Предоставление субсидий СФР Правовое регулирование налоговых отношений. Налоговое право и его основные понятия
Правовое регулирование налоговых отношений. Налоговое право и его основные понятия Прием подраздела 1.2. Сведения о страховом стаже формы ЕФС-1
Прием подраздела 1.2. Сведения о страховом стаже формы ЕФС-1 Продолжительность экономической жизни инвестиций и фактор времени
Продолжительность экономической жизни инвестиций и фактор времени Проект Народный бюджет в Республике Коми
Проект Народный бюджет в Республике Коми Электронные платежные системы в таможенном деле
Электронные платежные системы в таможенном деле Денежно-кредитная политика ЕС
Денежно-кредитная политика ЕС