Содержание
- 2. Learning Objectives Make good buying decisions. Choose a vehicle that suits your needs and budget. Choose
- 3. Smart Buying Step 1: Differentiate Want From Need Smart buying requires separating wants from needs. “Want”
- 4. Smart Buying Step 2: Do Your Homework After deciding to make a purchase, comparison shop. Start
- 5. Smart Buying Step 3: Make Your Purchase Getting the best price might involve negotiations. Conduct research
- 6. Smart Buying Step 4: Maintain Your Purchase Maintain your purchase after the deal is complete. Resolve
- 7. Smart Buying Checklist 8.1 Before You Buy Decide in advance what you need and can afford.
- 8. Smart Buying Checklist 8.2 Making a Complaint Keep a record of your efforts to resolve the
- 9. Smart Buying in Action: Buying a Vehicle Vehicles are your largest purchase, next to buying a
- 10. Smart Buying in Action: Buying a Vehicle Step 1: Differentiate Want From Need Determine which features
- 11. Smart Buying in Action: Buying a Vehicle Step 2: Do Your Homework How much can you
- 12. Smart Buying in Action: Buying a Vehicle Step 3: Make Your Purchase Be sure to get
- 13. Smart Buying in Action: Buying a Vehicle Step 3: Make Your Purchase Financing Alternatives: Cheapest way
- 14. Smart Buying in Action: Buying a Vehicle Step 3: Make Your Purchase Leasing: Appeals to those
- 15. Smart Buying in Action: Buying a Vehicle Step 4: Maintain Your Purchase Keep vehicle in best
- 16. Smart Buying in Action: Housing Many people equate home ownership with financial success. Housing costs can
- 17. Your Housing Options A House: Popular choice for most individuals. Offers space and privacy. Offers greater
- 18. Your Housing Options A Cooperative (Co-op) is a building owned by a corporation in which residents
- 19. Your Housing Options A Condominium (Condo) is an apartment complex that allows individual ownership of the
- 20. Your Housing Options Apartments and other rental housing offer: Affordability Low maintenance situations Little financial commitment
- 21. Smart Buying in Action: Housing Step 1: Differentiate Want From Need Determine what you need versus
- 22. Smart Buying in Action: Housing Step 2: Do Your Homework Investigate the potential home and all
- 23. Smart Buying in Action: Housing One-time Costs Down payment Closing/settlement costs Points Loan origination fee Application
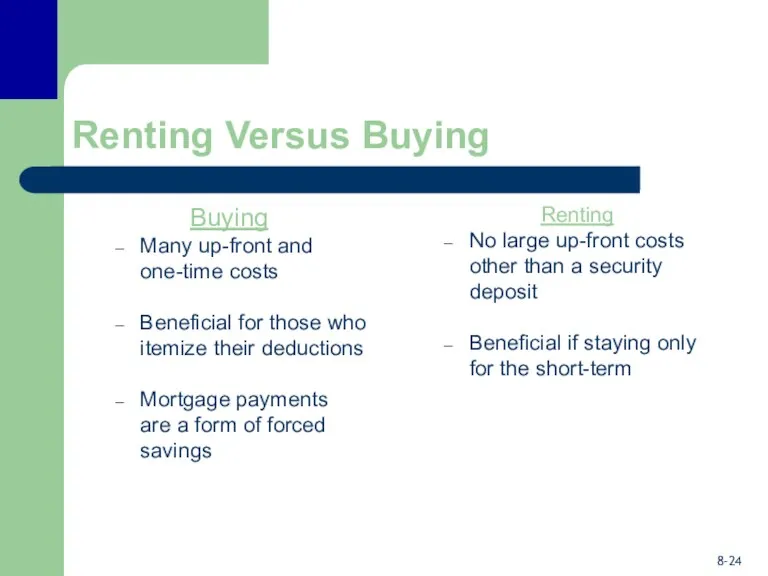
- 24. Renting Versus Buying Buying Many up-front and one-time costs Beneficial for those who itemize their deductions
- 25. Determining What You Can Afford Before house hunting, ask yourself: What is the maximum amount the
- 26. What is the Maximum Amount the Bank Will Lend Me? Lenders look at: Your financial history
- 27. How Much Should You Borrow? A mortgage is a large financial commitment of future earnings. Look
- 28. Financing the Purchase: The Mortgage Sources of mortgages: S&Ls and commercial banks are the primary sources
- 29. Conventional and Government-Backed Mortgages Conventional loans - from a bank or S&L and secured by the
- 30. Conventional and Government-Backed Mortgages Government-backed loans – lender makes loan and government insures it. VA and
- 31. Fixed-Rate Mortgages Monthly payment doesn’t change regardless of changes in market interest rates. If rates are
- 32. Adjustable-Rate Mortgages With an ARM, the interest rate fluctuates based on current market interest rates within
- 33. Adjustable-Rate Mortgages Interest Rate Index – rates on ARMs are tied to an index not controlled
- 34. Adjustable-Rate Mortgages Payment Cap – sets dollar limit on how much the monthly payment can increase
- 35. Adjustable-Rate Mortgages ARM Innovations: Convertible ARM – convert traditional ARM to a fixed rate loan during
- 36. Other Mortgage Loan Options Balloon Payment Loan – small monthly payments for 5-7 years, then entire
- 37. Other Mortgage Loan Options Shared Appreciation Mortgage – borrower receives below-market interest rate and lender receives
- 39. Скачать презентацию



































 Переоценка товаров и их потери
Переоценка товаров и их потери Деньги, кредит, банки
Деньги, кредит, банки МСФО (IAS) 41: Сельское хозяйство
МСФО (IAS) 41: Сельское хозяйство Общая характеристика бухгалтерского учета
Общая характеристика бухгалтерского учета Калькулирование затрат и себестоимость продукции
Калькулирование затрат и себестоимость продукции Система управления прибылью предприятия OAO Молодечноторг
Система управления прибылью предприятия OAO Молодечноторг Фискальная политика и бюджетный дефицит
Фискальная политика и бюджетный дефицит Алгоритм получения родителями компенсации стоимости путевок загородные лагеря круглогодичного действия и детские санатории
Алгоритм получения родителями компенсации стоимости путевок загородные лагеря круглогодичного действия и детские санатории Валютный рынок FOREX. Технический анализ на рынке FOREX
Валютный рынок FOREX. Технический анализ на рынке FOREX Несостоятельность (банкротство) Тема 3
Несостоятельность (банкротство) Тема 3 Финансовый менеджмент. Управление затратами
Финансовый менеджмент. Управление затратами Текущие счета и банковские карты
Текущие счета и банковские карты Страхові фонди як матеріальна основа страхового захисту та його форми
Страхові фонди як матеріальна основа страхового захисту та його форми Отчет о выполнении отраслевого соглашения в области оплаты труда. Росатом
Отчет о выполнении отраслевого соглашения в области оплаты труда. Росатом Анализ бюджета г. Брянска за 2015-2017 годы
Анализ бюджета г. Брянска за 2015-2017 годы Исполнение бюджета Юрьевецкого городского поселения
Исполнение бюджета Юрьевецкого городского поселения Управление личными финансами
Управление личными финансами Модели прогнозирования вероятности банкротства коммерческой организации (часть 3)
Модели прогнозирования вероятности банкротства коммерческой организации (часть 3) Операции коммерческого банка с пластиковыми картами и их роль в обеспечении комплексного обслуживания клиентов
Операции коммерческого банка с пластиковыми картами и их роль в обеспечении комплексного обслуживания клиентов Основы финансовой системы Канады
Основы финансовой системы Канады Налог на добавленную стоимость (НДС)
Налог на добавленную стоимость (НДС) Бизнес-планирование
Бизнес-планирование Фiнансовi iнструменти. Фінансовий інжиніринг
Фiнансовi iнструменти. Фінансовий інжиніринг Методы внутреннего аудита. Аудиторская выборка
Методы внутреннего аудита. Аудиторская выборка Отчет о финансовых результатах. Нормативное регулирование
Отчет о финансовых результатах. Нормативное регулирование Пенсия по старости
Пенсия по старости Как раздробить бизнес и не привлечь внимание налоговиков. 17 признаков дробления и 3 главных правила
Как раздробить бизнес и не привлечь внимание налоговиков. 17 признаков дробления и 3 главных правила Инвестиционный анализ
Инвестиционный анализ