Chemical reaction rate. Influence of conditions on the rate of chemical reactions. Topic 3.2 презентация
Содержание
- 2. OUTLINE: 1. Chemical reaction rate 2. Collision theory 3. Influencing factors 4. Catalysis 5. Inhibitors
- 3. Definition The Reaction Rate for a given chemical reaction is the measure of the change in
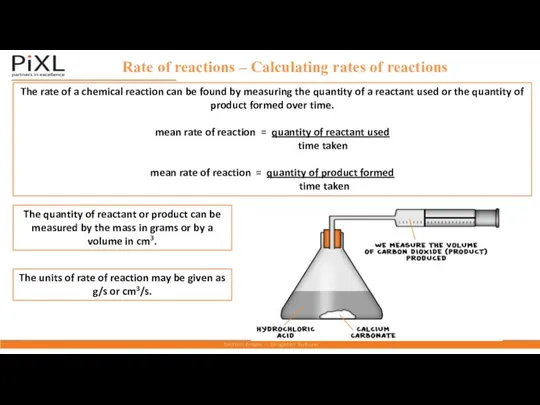
- 4. Rate of reactions – Calculating rates of reactions The rate of a chemical reaction can be
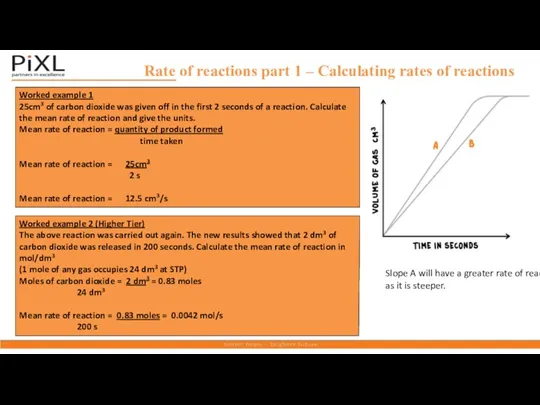
- 5. Rate of reactions part 1 – Calculating rates of reactions Worked example 1 25cm3 of carbon
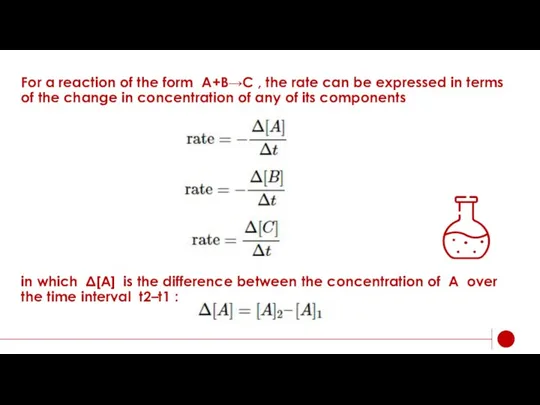
- 6. For a reaction of the form A+B→C , the rate can be expressed in terms of
- 7. State two ways of finding the rate of reaction. State two units of rate of reaction.
- 8. State two ways of finding the rate of reaction. Measuring the quantity of reactant used or
- 9. The student collects 50 cm3 of carbon dioxide gas in 10 seconds. What is the rate
- 10. (HT only) What mass of carbon dioxide are they collecting per second if the rate of
- 11. Rates of reactions – Factors which affect rates of reactions Factors which affect the rates of
- 12. Collision theory Collision theory explains why some reactions like the formation of water or carbon dioxide
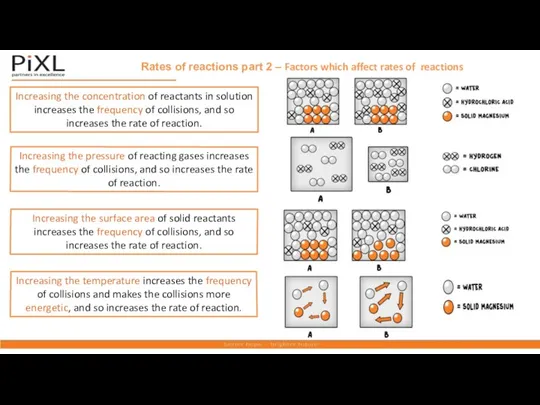
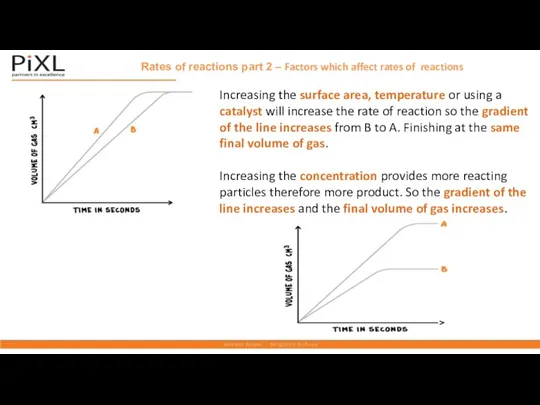
- 13. Rates of reactions part 2 – Factors which affect rates of reactions Increasing the concentration of
- 14. temperature usually speeds up chemical reactions Temperature at high temperature, reactant particles are more chaotic and
- 15. Rates of reactions part 2 – Factors which affect rates of reactions Increasing the surface area,
- 16. Question! What is meant by the term ‘collision theory’? What happens to the gradient of a
- 17. What is meant by the term ‘collision theory’? Explains how reactions occur when particles collide, and
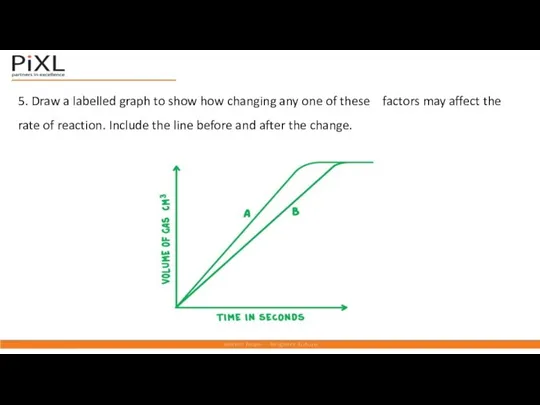
- 18. 5. Draw a labelled graph to show how changing any one of these factors may affect
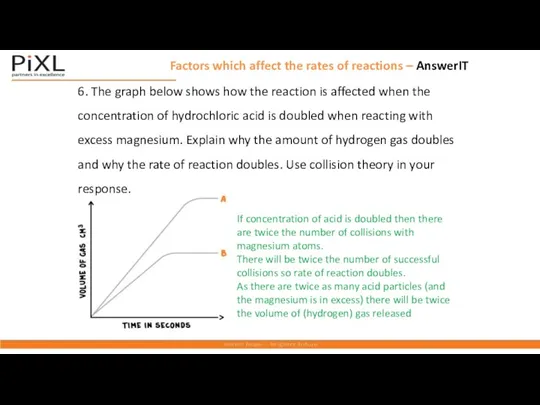
- 19. Factors which affect the rates of reactions – AnswerIT If concentration of acid is doubled then
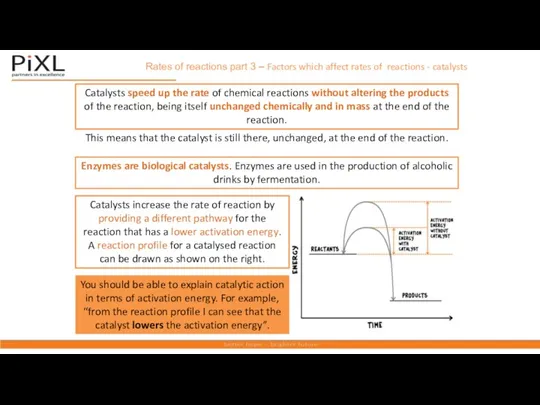
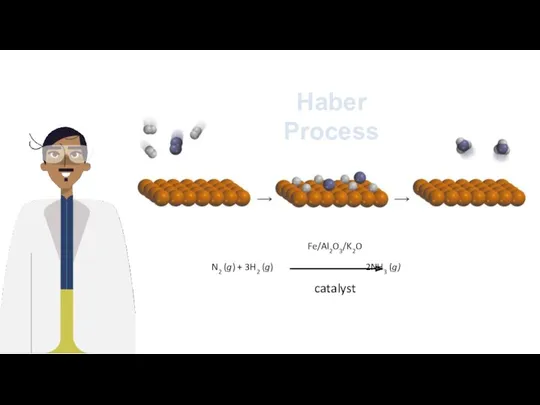
- 20. Rates of reactions part 3 – Factors which affect rates of reactions - catalysts Catalysts speed
- 21. Haber Process
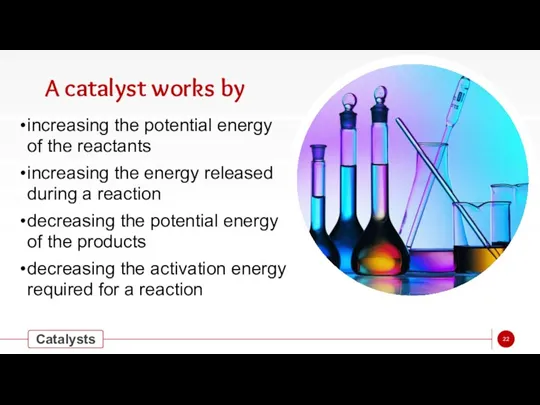
- 22. A catalyst works by increasing the potential energy of the reactants increasing the energy released during
- 23. Inhibitors are an agent that slows or interferes with a chemical action, a substance that reduces
- 24. 1. What is the formula for rate of reaction A) Quantity of product X Time B)
- 25. 5. Increasing the pressure of a reacting vessel only affects: A) Gaseous reactants B) Solid reactants
- 27. Скачать презентацию














 Металлы, их свойства и область применения
Металлы, их свойства и область применения Галогены - химические элементы 17-й группы периодической таблицы химических элементов Д.И. Менделеева
Галогены - химические элементы 17-й группы периодической таблицы химических элементов Д.И. Менделеева Тяжелые металлы
Тяжелые металлы Гидрокси(окси) кислоты
Гидрокси(окси) кислоты Значение пищи и ее состав
Значение пищи и ее состав Коррозия металлов
Коррозия металлов Изучение процесса коррозии железа (домашний эксперимент)
Изучение процесса коррозии железа (домашний эксперимент) Борьба с биологической коррозией
Борьба с биологической коррозией Реакции ионного обмена
Реакции ионного обмена Спирты
Спирты Газовые смеси
Газовые смеси Химический элемент, минерал, горная порода. (Лекция 6)
Химический элемент, минерал, горная порода. (Лекция 6) Титриметрический анализ. Кривые титрования
Титриметрический анализ. Кривые титрования Адсорбция
Адсорбция Ендотермічні реакції на службі людини
Ендотермічні реакції на службі людини Поверхностные явления. Адсорбция
Поверхностные явления. Адсорбция Химические реакции или химические явления
Химические реакции или химические явления Спирты. Понятия о предельных одноатомных спиртах. Химические свойства этанола и его применение
Спирты. Понятия о предельных одноатомных спиртах. Химические свойства этанола и его применение Хром, марганец
Хром, марганец Химическая кинетика и катализ
Химическая кинетика и катализ Свойства фосфора
Свойства фосфора Общие сведения о полезных ископаемых. (Лекция 2)
Общие сведения о полезных ископаемых. (Лекция 2) Тұндыру әдістері
Тұндыру әдістері Термодинамика химических процессов
Термодинамика химических процессов Чистые вещества и смеси. Химия. 8 кл
Чистые вещества и смеси. Химия. 8 кл Обед под микроскопом. Минеральные вещества
Обед под микроскопом. Минеральные вещества Типы химических реакций на примере свойств воды
Типы химических реакций на примере свойств воды Реакции солей в растворе. Гидролиз солей. Водородный показатель рН
Реакции солей в растворе. Гидролиз солей. Водородный показатель рН