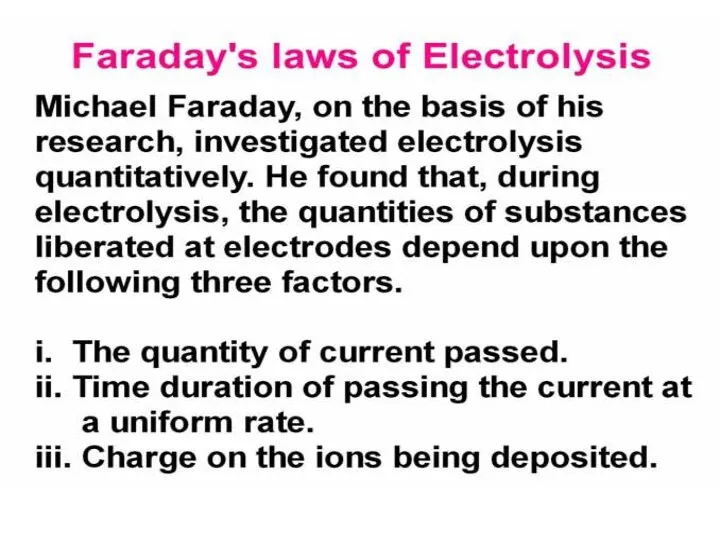
Содержание
- 2. Learning Objectives: Definition an electrolysis Learn to predict products of electrolysis: molten compounds and aqueous solutions
- 3. GLOSSARY An electrolyte is an ionic compound which, when molten or in aqueous solution, conducts an
- 4. Sir Humphry Davy (1778 – 1829)
- 6. Electrolytes are substances able to conduct electricity in molten state or liquid state and undergo chemical
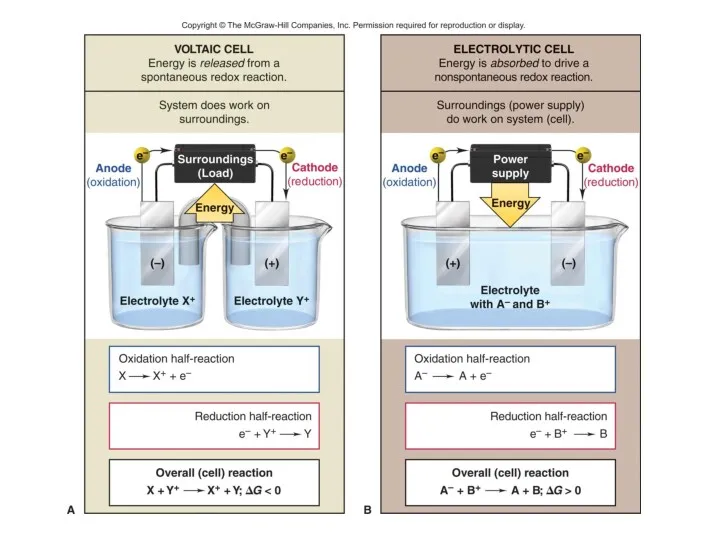
- 7. Introducing Electrolysis Electrolysis is the redox decomposition of an ionic compounds by passing electricity through molten
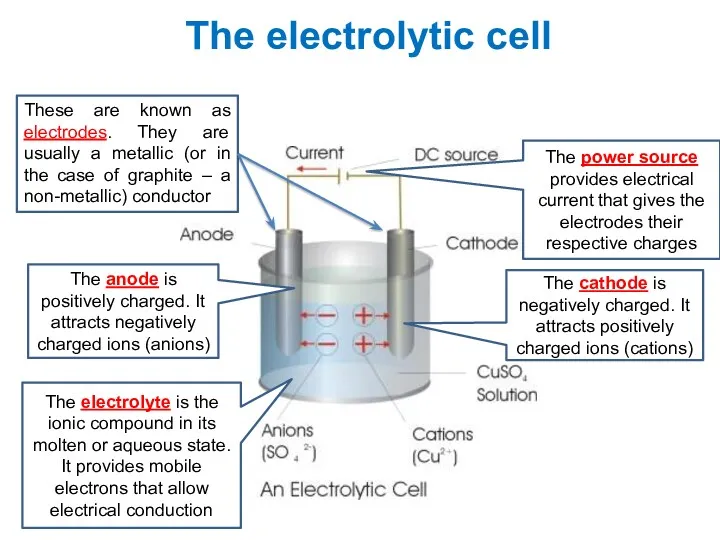
- 8. The electrolytic cell The cathode is negatively charged. It attracts positively charged ions (cations) The anode
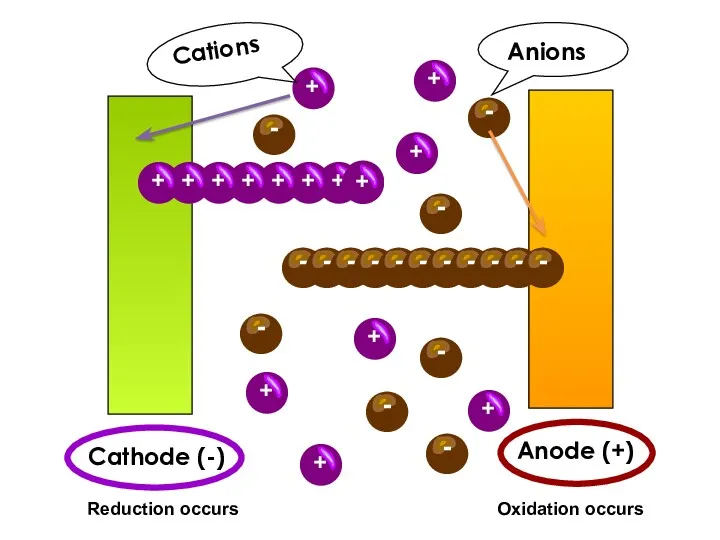
- 9. Cathode (-) Anode (+) Reduction occurs Oxidation occurs
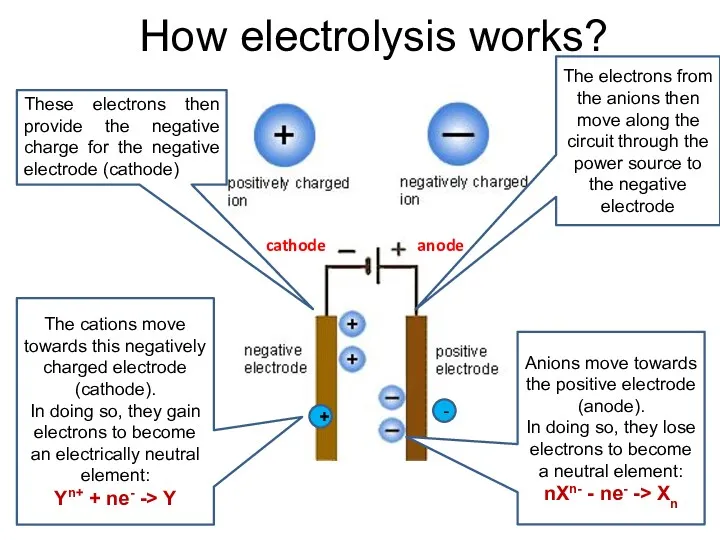
- 10. How electrolysis works? Anions move towards the positive electrode (anode). In doing so, they lose electrons
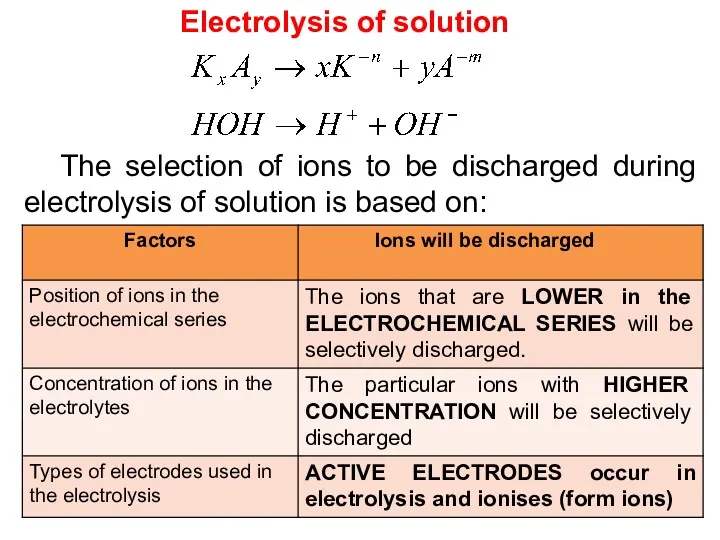
- 11. How do you know which ions will be discharged? The selection of ions to be discharged
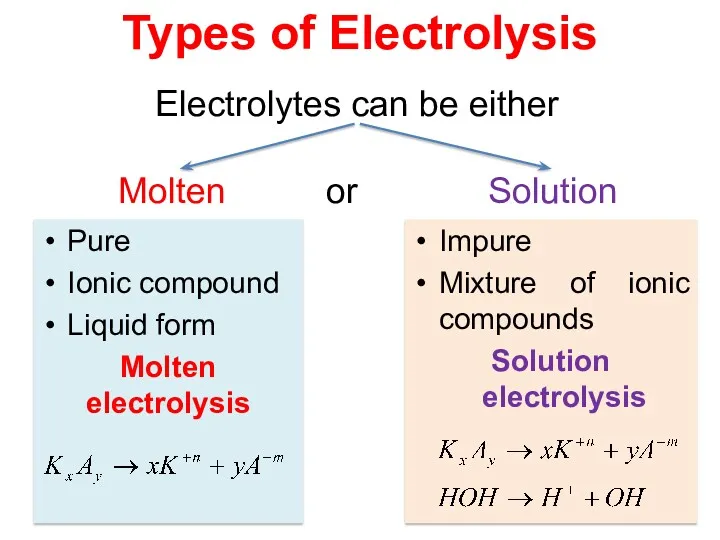
- 12. Pure Ionic compound Liquid form Molten electrolysis Impure Mixture of ionic compounds Solution electrolysis Types of
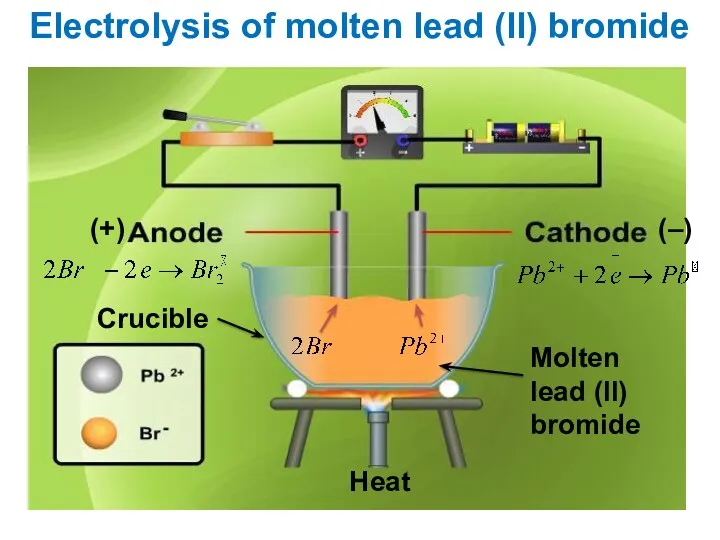
- 13. Electrolysis of molten lead (ll) bromide Molten lead (ll) bromide Crucible (+) (–) Heat
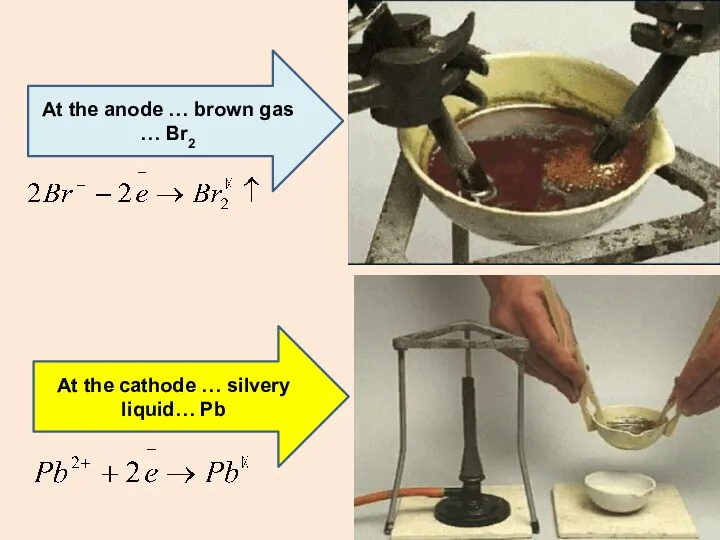
- 14. At the anode … brown gas … Br2 At the cathode … silvery liquid… Pb
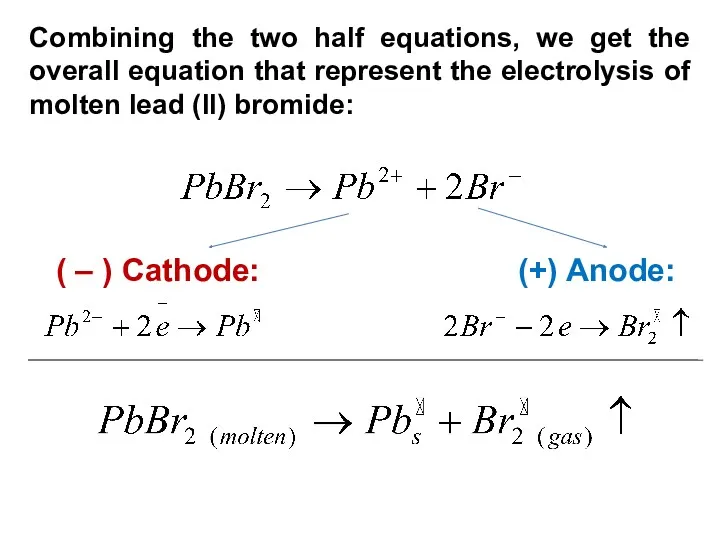
- 15. Combining the two half equations, we get the overall equation that represent the electrolysis of molten
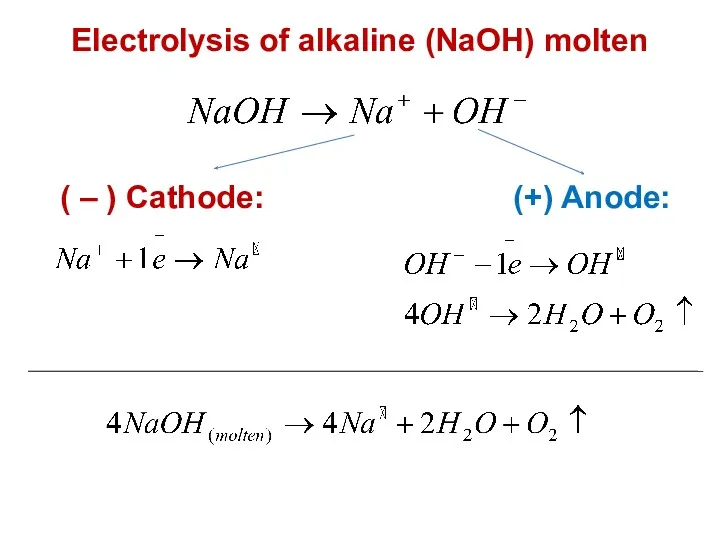
- 16. Electrolysis of alkaline (NaOH) molten ( – ) Cathode: (+) Anode:
- 17. Electrolysis of solution The selection of ions to be discharged during electrolysis of solution is based
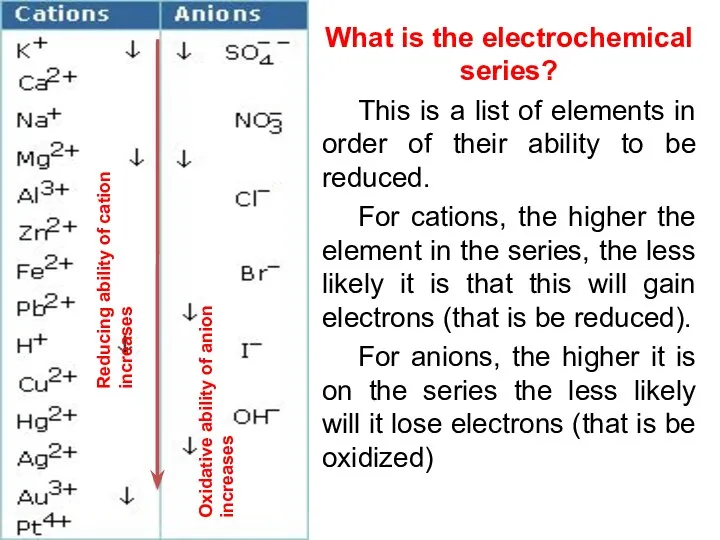
- 18. What is the electrochemical series? This is a list of elements in order of their ability
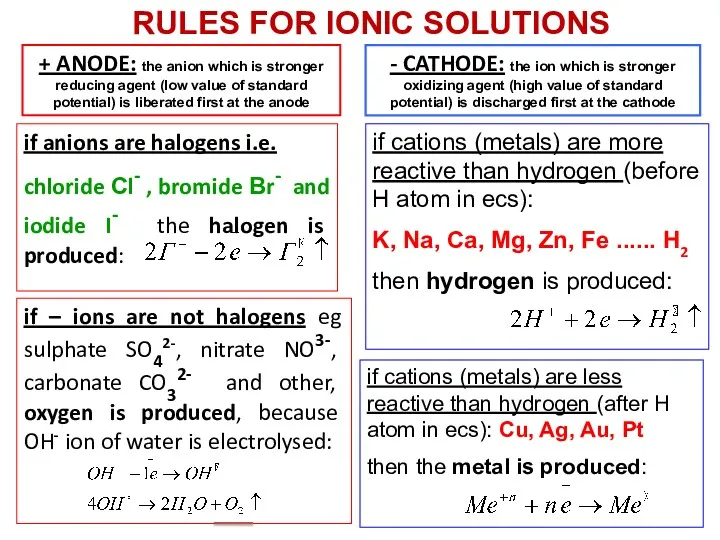
- 19. + ANODE: the anion which is stronger reducing agent (low value of standard potential) is liberated
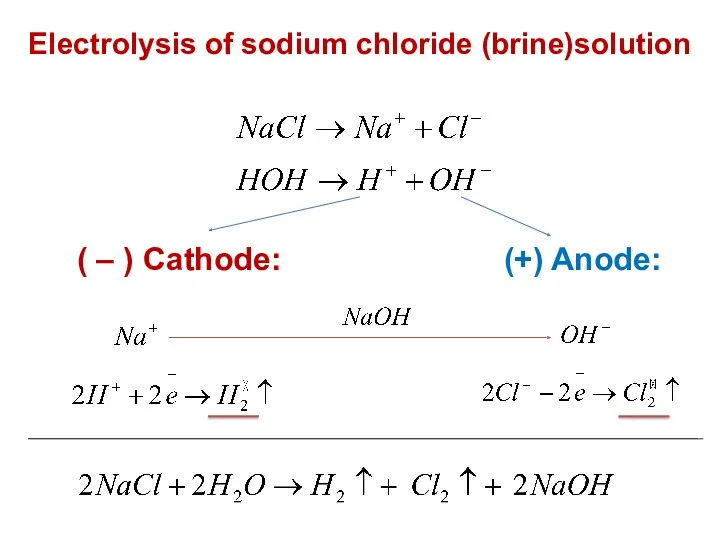
- 20. Electrolysis of sodium chloride (brine)solution ( – ) Cathode: (+) Anode:
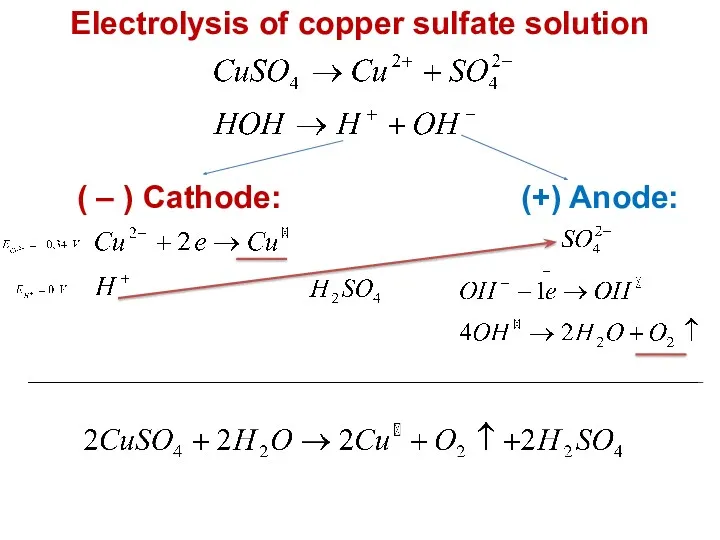
- 21. Electrolysis of copper sulfate solution ( – ) Cathode: (+) Anode:
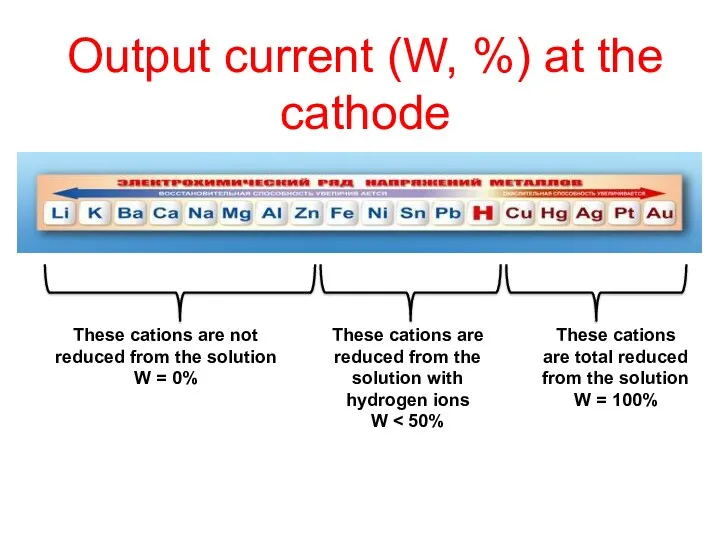
- 22. Output current (W, %) at the cathode These cations are not reduced from the solution W
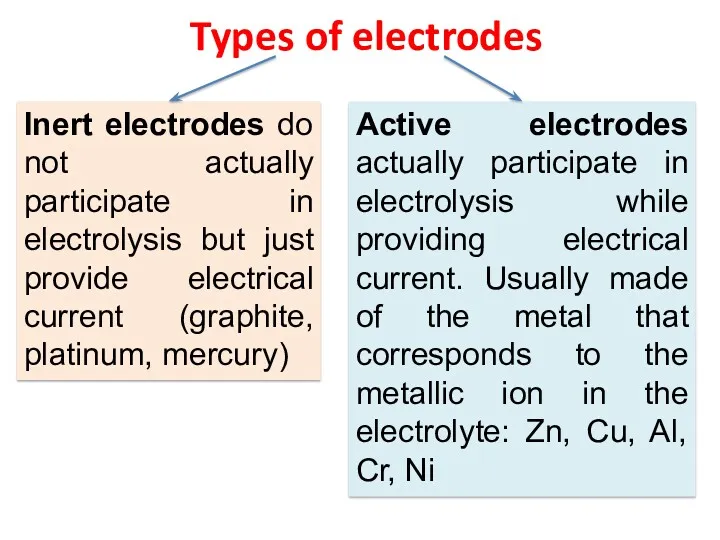
- 23. Types of electrodes Inert electrodes do not actually participate in electrolysis but just provide electrical current
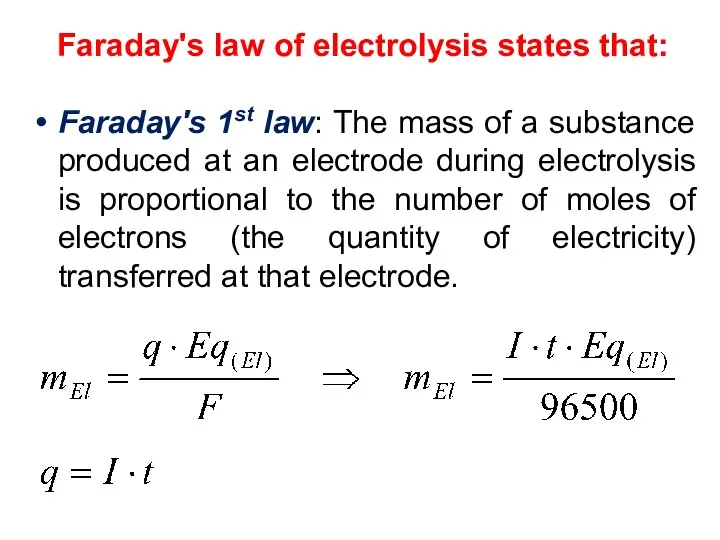
- 25. Faraday's law of electrolysis states that: Faraday's 1st law: The mass of a substance produced at
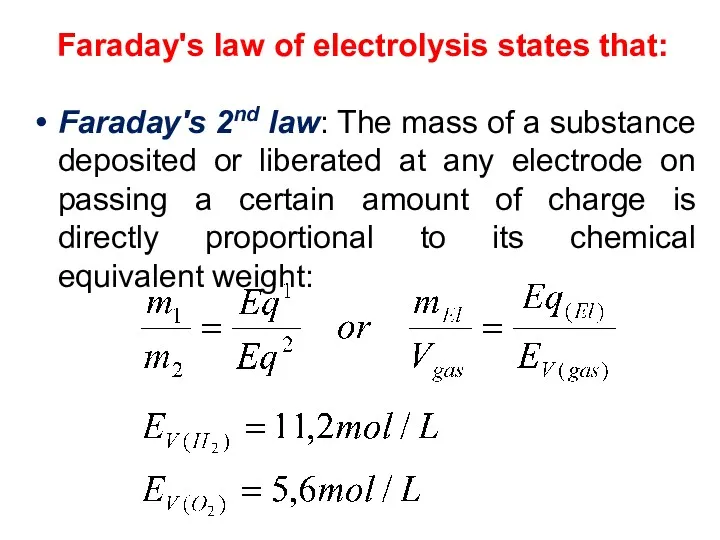
- 26. Faraday's law of electrolysis states that: Faraday's 2nd law: The mass of a substance deposited or
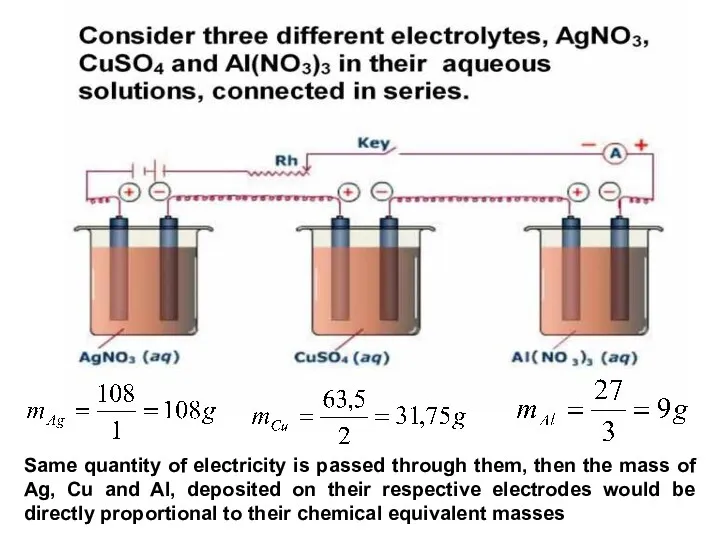
- 27. Same quantity of electricity is passed through them, then the mass of Ag, Cu and Al,
- 28. Some important uses of electrolysis:
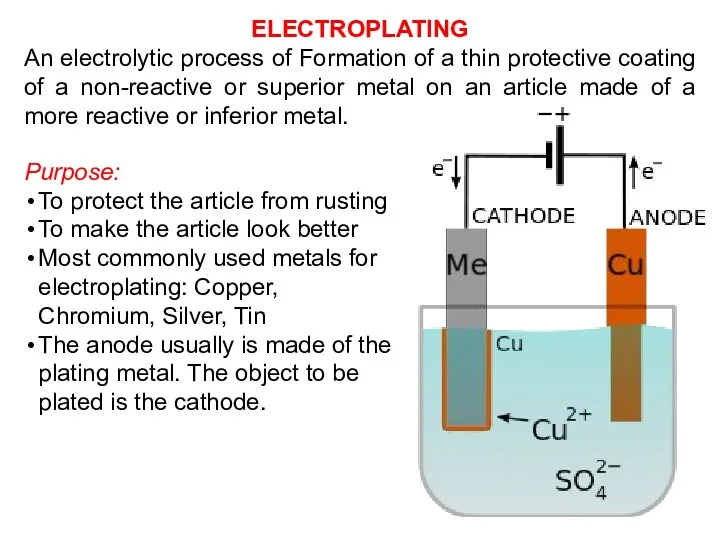
- 29. Purpose: To protect the article from rusting To make the article look better Most commonly used
- 30. Electrometallurgy: Electrometallurgy is the process of extraction of metal from ore by electrolysis. Manufacture of metals:
- 32. Скачать презентацию








 Химическая промышленность
Химическая промышленность Приёмы обращения с лабораторным оборудованием
Приёмы обращения с лабораторным оборудованием Химические свойства металлов
Химические свойства металлов Анализ жидких средств для мытья посуды
Анализ жидких средств для мытья посуды Химический элемент уран
Химический элемент уран Контрольная работа по дисциплине Физическая химия. Раздел: Электрохимия
Контрольная работа по дисциплине Физическая химия. Раздел: Электрохимия Мыловарение. Мыло своими руками
Мыловарение. Мыло своими руками Характеристика химического элемента Металла на основании его положения в периодической системе Д.И. Менделеева
Характеристика химического элемента Металла на основании его положения в периодической системе Д.И. Менделеева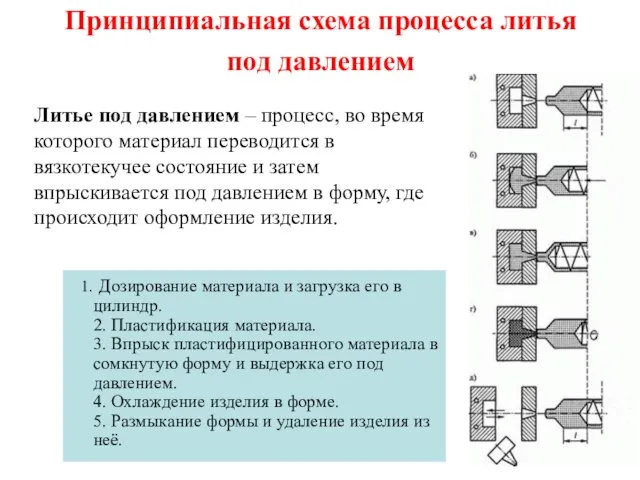 Принципиальная схема процесса литья под давлением
Принципиальная схема процесса литья под давлением Алкены. Гомологический ряд и изомерия
Алкены. Гомологический ряд и изомерия Железо и его свойства
Железо и его свойства Строение атома
Строение атома Такой разный песок
Такой разный песок Адсорбция на твердых телах
Адсорбция на твердых телах Самое удивительное на свете вещество - вода
Самое удивительное на свете вещество - вода Кам’яне вугілля, продукти його переробки
Кам’яне вугілля, продукти його переробки Чисті речовини та суміші. Способи розділення
Чисті речовини та суміші. Способи розділення Механизмы органических реакций. (Лекция 2)
Механизмы органических реакций. (Лекция 2)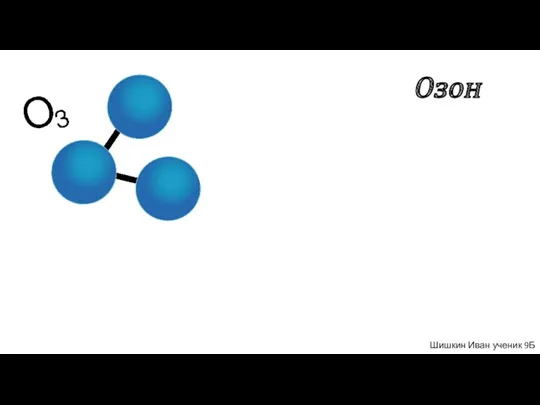 Озон. Значение Озона
Озон. Значение Озона Понятия и определения химической термодинамики. (Лекция 11)
Понятия и определения химической термодинамики. (Лекция 11) Периодические изменения свойств химических элементов
Периодические изменения свойств химических элементов Простые эфиры
Простые эфиры Электролитическая диссоциация химических элементов
Электролитическая диссоциация химических элементов Экспериментально исследовательский проект Соль волшебница
Экспериментально исследовательский проект Соль волшебница Аминокислоты. Пептиды. Белки
Аминокислоты. Пептиды. Белки Кислоты. Состав кислот
Кислоты. Состав кислот Массовая доля вещества в растворе
Массовая доля вещества в растворе Получение и применение алканов
Получение и применение алканов