Содержание
- 2. Organic chemistry — chemistry of carbon containing compounds Elements Н, О, N, S, P – organigenic
- 3. Charles Frédéric Gerhardt (21 August 1816 – 19 August 1856). French chemist, known for his work
- 4. In1853 C. Gerhardt elaborated «theory of the types» and use it for classification of organic compounds.
- 5. Alexander Mikhaylovich Butlerov (September 15, 1828 – August 17, 1886) - a Russian chemist, one of
- 6. Basic statements of structure theory of organic compounds(1861) 1) In organic molecules atoms connected to each
- 7. 4) In organic molecules exists mutual effects between as bonded, so non-bonded atoms; 5) Chemical structure
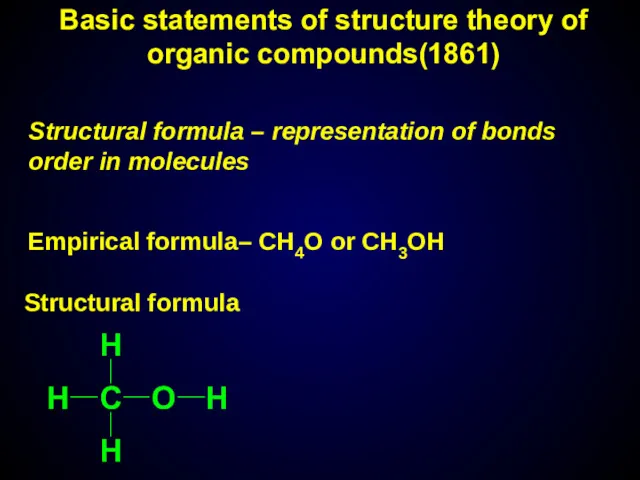
- 8. Structural formula – representation of bonds order in molecules Empirical formula– СН4О or CH3OH Structural formula
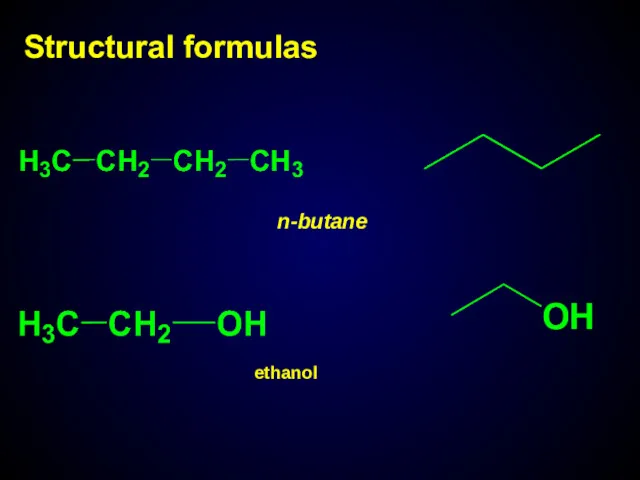
- 9. Structural formulas n-butane ethanol
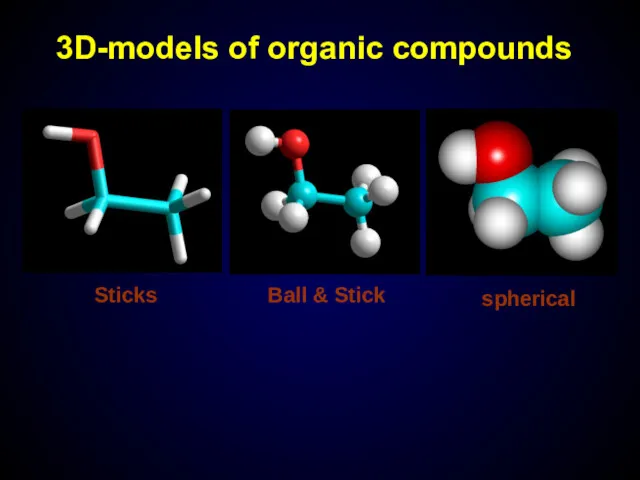
- 10. 3D-models of organic compounds Sticks Ball & Stick spherical
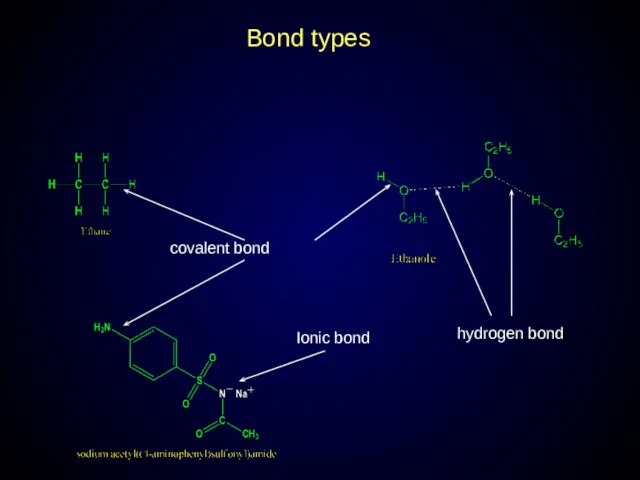
- 11. Bond types covalent bond hydrogen bond Ionic bond
- 12. Covalent bond in organic molecules: Polar Non-polar Single (σ-bond) Double or triple (σ-bond and π-bond) Hydrogen
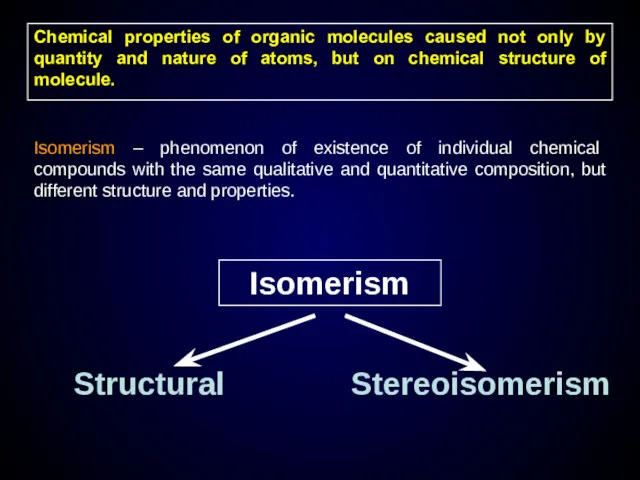
- 13. Chemical properties of organic molecules caused not only by quantity and nature of atoms, but on
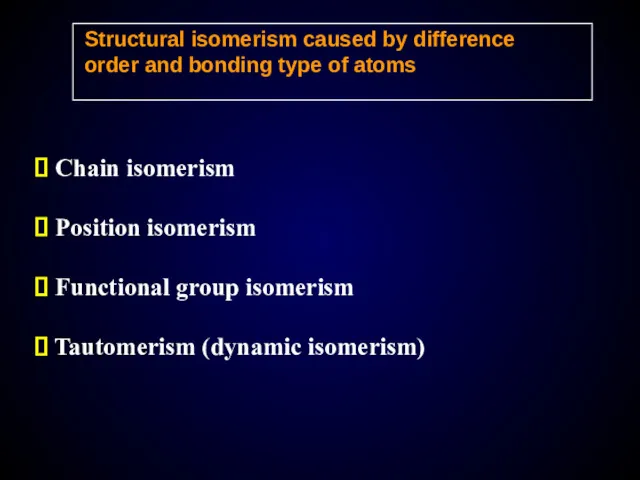
- 14. Structural isomerism caused by difference order and bonding type of atoms Chain isomerism Position isomerism Functional
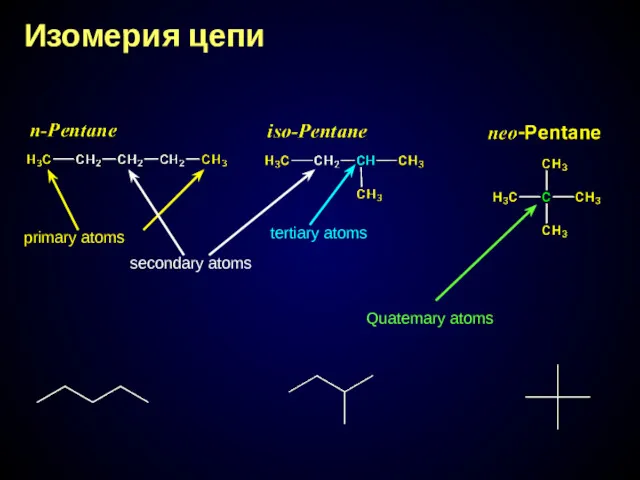
- 15. Изомерия цепи primary atoms secondary atoms tertiary atoms Quatemary atoms
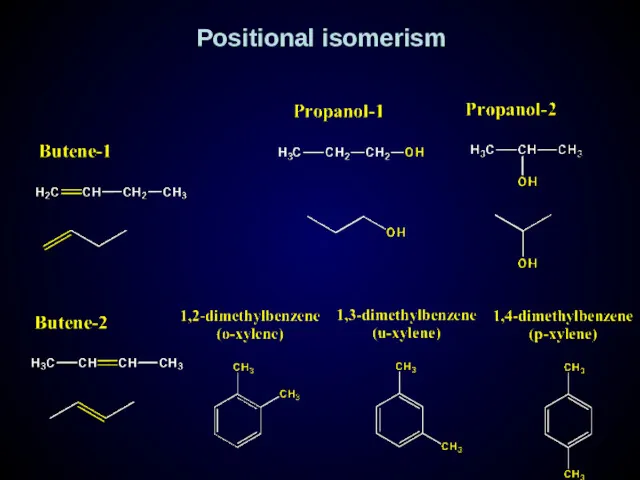
- 16. Positional isomerism
- 17. Functional group - atom or group of atom which contain elements differ from carbon and hydrogen
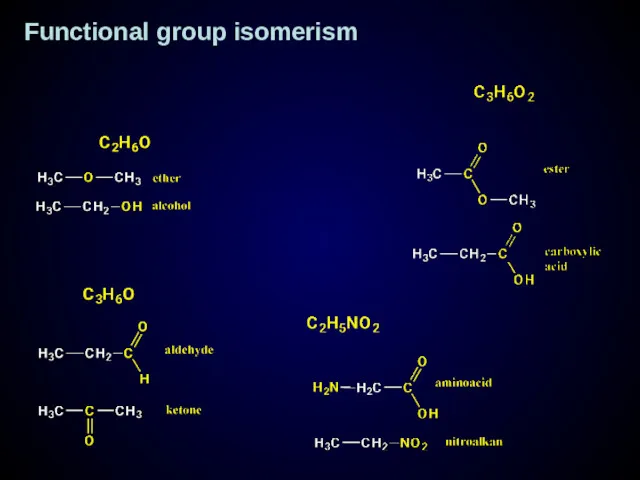
- 18. Functional group isomerism
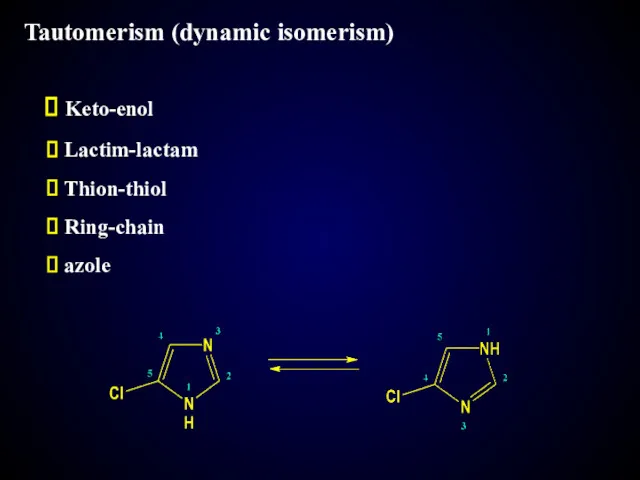
- 19. Tautomerism (dynamic isomerism) Keto-enol Lactim-lactam Thion-thiol Ring-chain azole
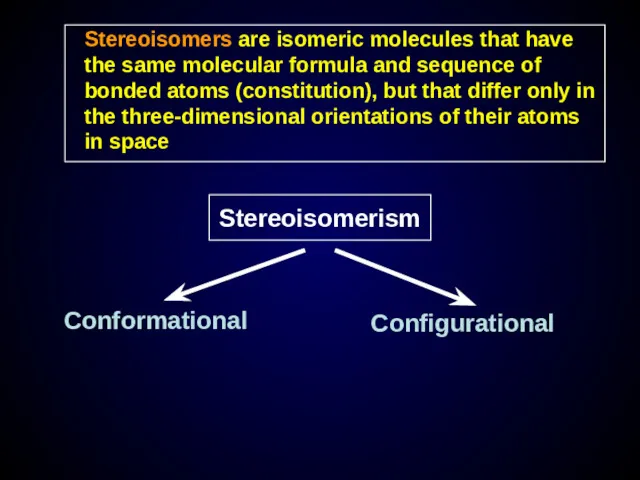
- 20. Stereoisomers are isomeric molecules that have the same molecular formula and sequence of bonded atoms (constitution),
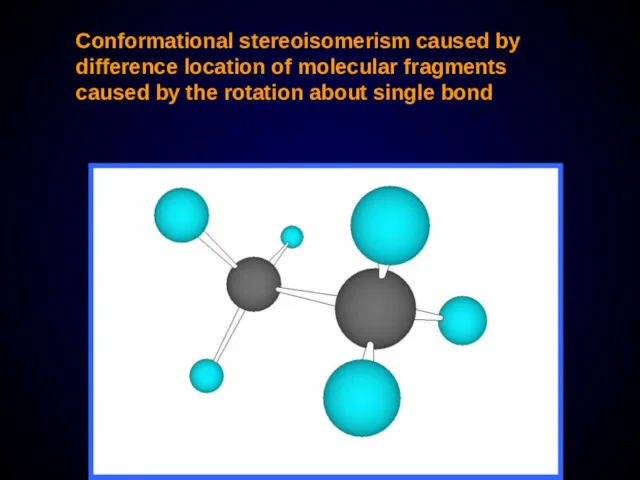
- 21. Conformational stereoisomerism caused by difference location of molecular fragments caused by the rotation about single bond
- 22. Conformations types
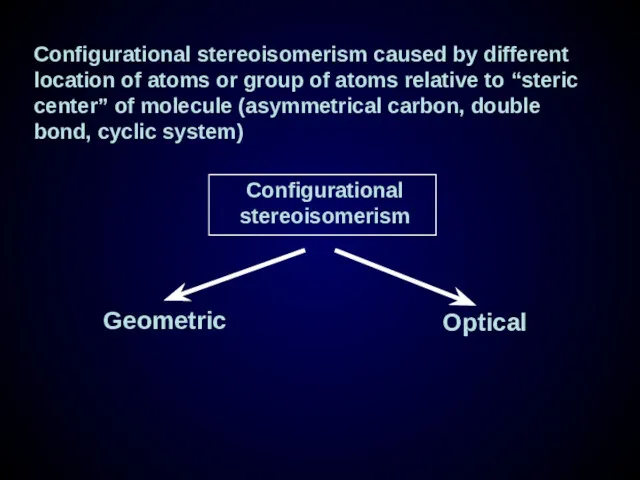
- 23. Configurational stereoisomerism caused by different location of atoms or group of atoms relative to “steric center”
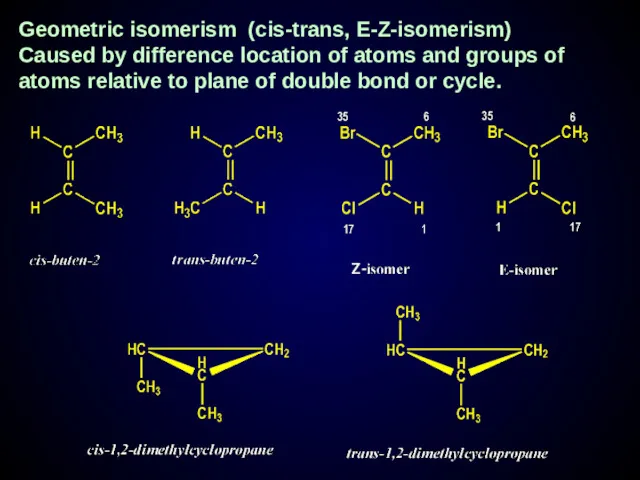
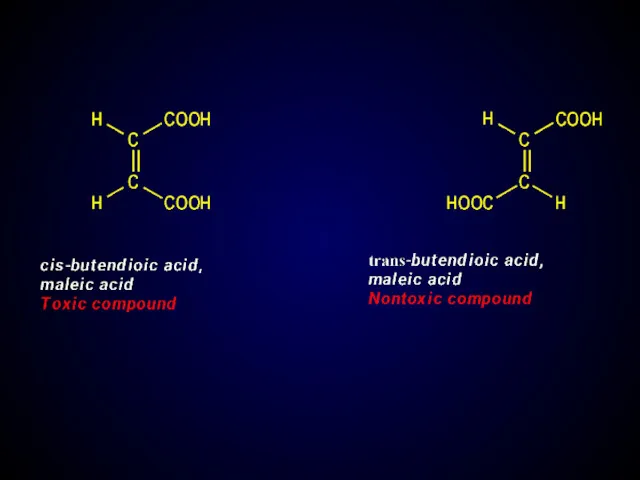
- 24. Geometric isomerism (cis-trans, E-Z-isomerism) Caused by difference location of atoms and groups of atoms relative to
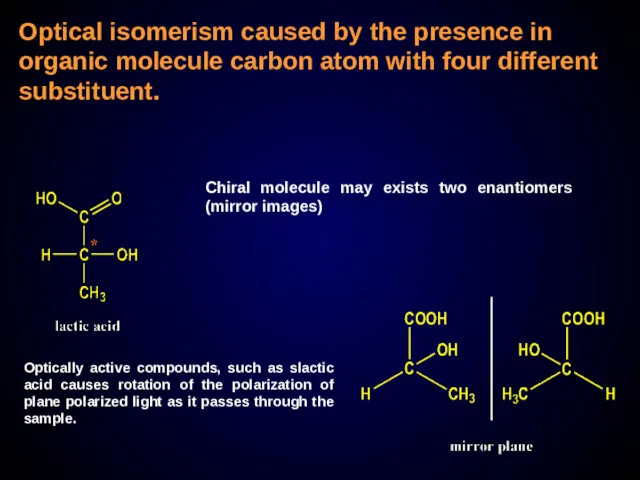
- 26. Optical isomerism caused by the presence in organic molecule carbon atom with four different substituent. Chiral
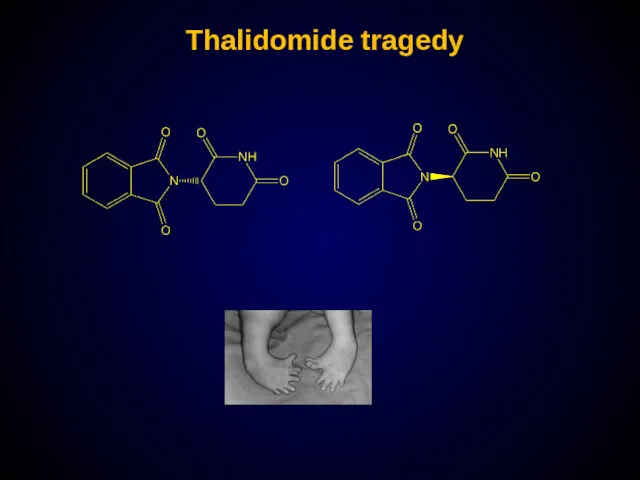
- 27. Thalidomide tragedy
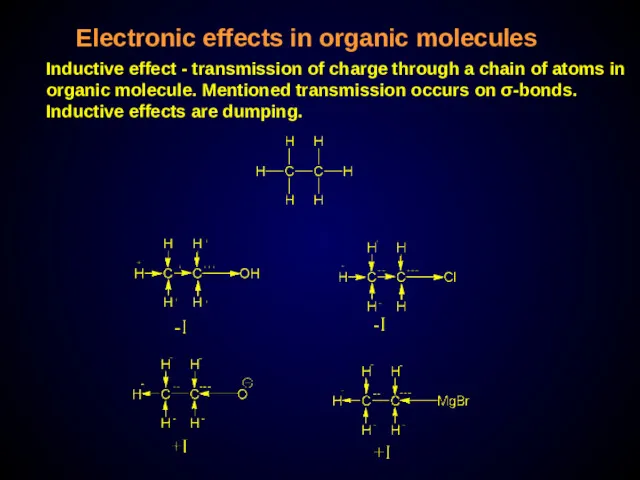
- 28. Electronic effects in organic molecules Inductive effect - transmission of charge through a chain of atoms
- 29. Electronic effects in organic molecules Mesomeric effect - transmission of charge through a conjugated system in
- 31. Скачать презентацию










 Теория химического строения органических соединений
Теория химического строения органических соединений Plastic is one of the challenges of the 21st century
Plastic is one of the challenges of the 21st century Непредельные углеводороды ряда этилена. Олефины
Непредельные углеводороды ряда этилена. Олефины Почвенный раствор. Химический состав почвенных растворов. Водный режим почв. Кислотность и щелочность почвенных растворов
Почвенный раствор. Химический состав почвенных растворов. Водный режим почв. Кислотность и щелочность почвенных растворов Фазовые равновесия в растворах
Фазовые равновесия в растворах Сера. Аллотропные модификации
Сера. Аллотропные модификации Carbohydrates and their metabolism. Digestion of carbohydrates
Carbohydrates and their metabolism. Digestion of carbohydrates Правила работы в лаборатории и приёмы обращения с лабораторным оборудованием (8 класс)
Правила работы в лаборатории и приёмы обращения с лабораторным оборудованием (8 класс) Химическая связь
Химическая связь Термическая и химико-термическая обработка
Термическая и химико-термическая обработка Обчислення за хімічними рівняннями відносного виходу продукту реакції. Урок №19. 11 клас
Обчислення за хімічними рівняннями відносного виходу продукту реакції. Урок №19. 11 клас Методические подходы к решению химических задач. Задание 34
Методические подходы к решению химических задач. Задание 34 Методика обучения решению задач на соотношение атомов в школьном курсе химии
Методика обучения решению задач на соотношение атомов в школьном курсе химии Химические уравнения
Химические уравнения Аммиак
Аммиак Техника безопасности в кабинете химии
Техника безопасности в кабинете химии Виды камней
Виды камней Альдегиды, свойства, получение, применение
Альдегиды, свойства, получение, применение Соли. 11 класс
Соли. 11 класс CaSO4 кристаллының ас жазықтығына проекциясының құрылымдық моделі
CaSO4 кристаллының ас жазықтығына проекциясының құрылымдық моделі Обмен жиров в организме
Обмен жиров в организме Введение в органическую химию
Введение в органическую химию Фосфор и его соединения. Урок по химии для 9 класса
Фосфор и его соединения. Урок по химии для 9 класса Электролиттік диссоциациялану теориясы тұрғысынан қышқыл, негіз, тұздардың химиялық қасиеттері
Электролиттік диссоциациялану теориясы тұрғысынан қышқыл, негіз, тұздардың химиялық қасиеттері Элементы группы галогенов
Элементы группы галогенов Кислород, его характеристика, получение и свойства
Кислород, его характеристика, получение и свойства Спирти. 3агальна характеристика спиртів
Спирти. 3агальна характеристика спиртів Щелочи
Щелочи