Содержание
- 2. Outline Introduction Main part 1. Phosphorus 2. Phosphorus (V) oxide. Phosphine 3. Phosphoric acid and its
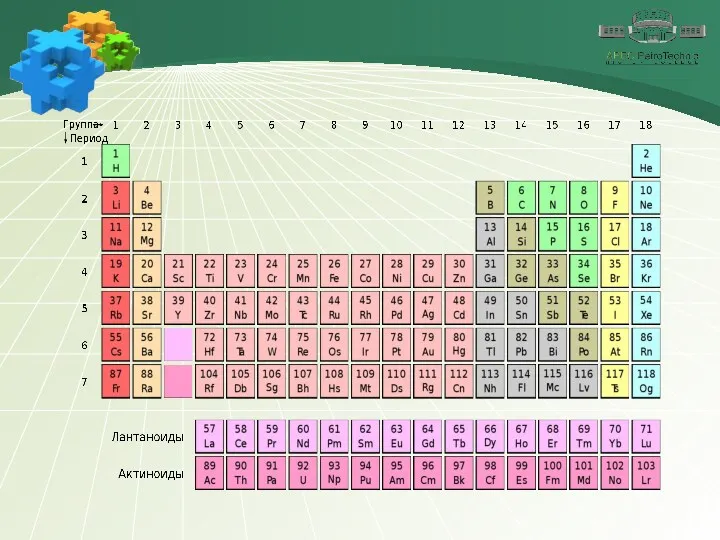
- 4. 1. Phosphorus Chemical element Phosphorus is a chemical element number 15. It is located in the
- 5. 1. Phosphorus Chemical element The phosphorus atom has more electronic layers than the nitrogen atom, therefore
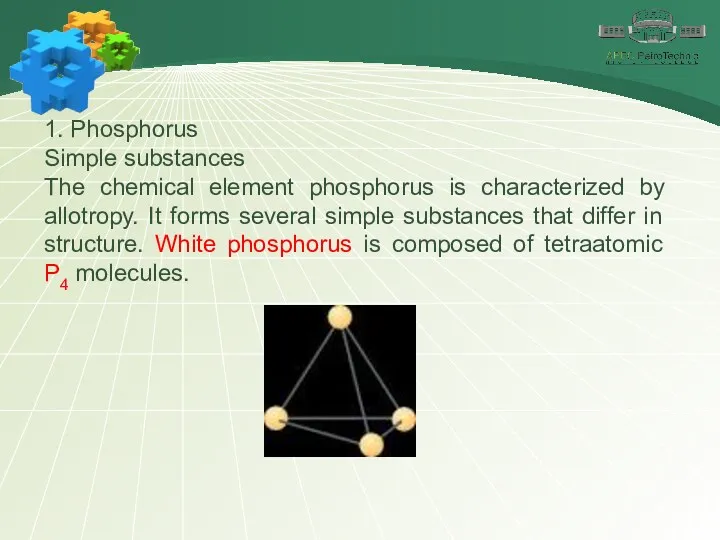
- 6. 1. Phosphorus Simple substances The chemical element phosphorus is characterized by allotropy. It forms several simple
- 7. 1. Phosphorus Simple substances It is a white (with a yellow tinge), wax-like substance that glows
- 8. 1. Phosphorus Simple substances Red phosphorus has an atomic crystal lattice Red phosphorus is a powder
- 9. 1. Phosphorus Simple substances Allotropic modifications of phosphorus are interconvertible. White phosphorus turns to red in
- 10. Chemical properties The chemical properties of different allotropic phosphorus modifications are similar. White phosphorus is more
- 11. Chemical properties Phosphorus exhibits reducing properties in reaction with oxygen. White phosphorus ignites spontaneously in air,
- 12. Phosphorus (V) oxide Phosphorus (V) oxide P2O5 is formed during the combustion of phosphorus: t 4P0
- 13. Phosphorus (V) oxide Phosphorus (V) oxide is very hygroscopic. It actively joins water, therefore it is
- 14. Phosphine The hydrogen phosphorus compound phosphine PH3 can be obtained from phosphides: Ca3P2 + 6HCl =
- 15. Phosphoric acid Phosphoric (orthophosphoric) acid H3PO4 is a solid transparent crystalline substance. Solid phosphoric acid It
- 16. Phosphoric acid In aqueous solutions, phosphoric acid dissociates in steps: H3PO4⇄H++ H2PO− 4, H2PO− 4⇄H++ HPO2−4,
- 17. Phosphoric acid Phosphoric acid reacts: with metals located in the line of activity before hydrogen: 2H3PO4
- 18. Phosphoric acid The reactions can form not only normal phosphate salts with an acidic residue PO3-4,
- 19. Phosphoric acid salts Medium salts of phosphoric acid phosphates (eg Ca3(PO4)2) are insoluble in water, except
- 20. Application Phosphoric acid is used: -for the production of mineral fertilizers, -as a food additive in
- 21. Question for selfcontrol: 1. Select the characteristic of red phosphorus: A)a molecule consists of four atoms
- 22. 4.A compound of the composition Ba (H2PO4)2 is called: А)barium phosphate В)barium phosphide С)barium hydrogen phosphate
- 23. 8.Phosphoric acid reacts with substances: А)KOH В)Na2O С)H2SO3 D)NaCl 9. Phosphoric acid does not react with
- 24. 10. Establish an accordance between a substance and its characteristics. 1 - white phosphorus; 2 -
- 25. Literature 1.Basic literature : 1. Jenkins, Chemistry, ISBN 978-0-17-628930-0 2. Alberta Learning, Chemistry data booklet 2010,
- 26. 2.Additional literature : 1.Б.А.Мансуров «Химия» 10-11 кл., Атамура 2015 г 2.Б.Мансуров., Н.Торшина «Методика преподавания органической химии»
- 28. Скачать презентацию






















 Алкены. Непредельные углеводороды
Алкены. Непредельные углеводороды Массовая доля вещества в растворе
Массовая доля вещества в растворе Металлы подгруппы железа Fe, Co, Ni
Металлы подгруппы железа Fe, Co, Ni АЛКАНЫ 9 класс
АЛКАНЫ 9 класс Поддержание заданного качества свинцового теплоносителя для энергетических ядерных реакторов
Поддержание заданного качества свинцового теплоносителя для энергетических ядерных реакторов Гониометрическое исследование кристаллов
Гониометрическое исследование кристаллов Закон сохранения массы веществ. Химические уравнения
Закон сохранения массы веществ. Химические уравнения Растворы. Смеси веществ
Растворы. Смеси веществ Полистирол өндірісі
Полистирол өндірісі Степень загрязнения почвы по химическому составу снежного покрова на разном удалении от источника загрязнения
Степень загрязнения почвы по химическому составу снежного покрова на разном удалении от источника загрязнения Электролиз. Коррозия и защита металлов
Электролиз. Коррозия и защита металлов Коррозия металлов. Методы защиты металлов от коррозии
Коррозия металлов. Методы защиты металлов от коррозии Химия в повседневной жизни
Химия в повседневной жизни Химические формулы
Химические формулы Драгоценные камни
Драгоценные камни Рекомендации по оформлению развёрнутых ответов на задания ЕГЭ
Рекомендации по оформлению развёрнутых ответов на задания ЕГЭ Нано-порошки. Способы получения нано-порошков
Нано-порошки. Способы получения нано-порошков Полимеры и пластические массы
Полимеры и пластические массы Anionic Polymerization
Anionic Polymerization Физико-химические свойства аммиака. Производство аммиака
Физико-химические свойства аммиака. Производство аммиака Обмен липидов
Обмен липидов Кислотно-основные свойства органических соединений. (Лекция 3)
Кислотно-основные свойства органических соединений. (Лекция 3) Массовая доля элемента в сложном веществе
Массовая доля элемента в сложном веществе Типы химических реакций
Типы химических реакций Кислоты. Растворы всех кислот
Кислоты. Растворы всех кислот Периодический закон Д.И. Менделеева. Строение атома. Химическая связь
Периодический закон Д.И. Менделеева. Строение атома. Химическая связь Алюминий
Алюминий Применение спиртов
Применение спиртов