Содержание
- 2. Topics Covered Company and Project Costs of Capital Measuring the Cost of Equity Capital Structure and
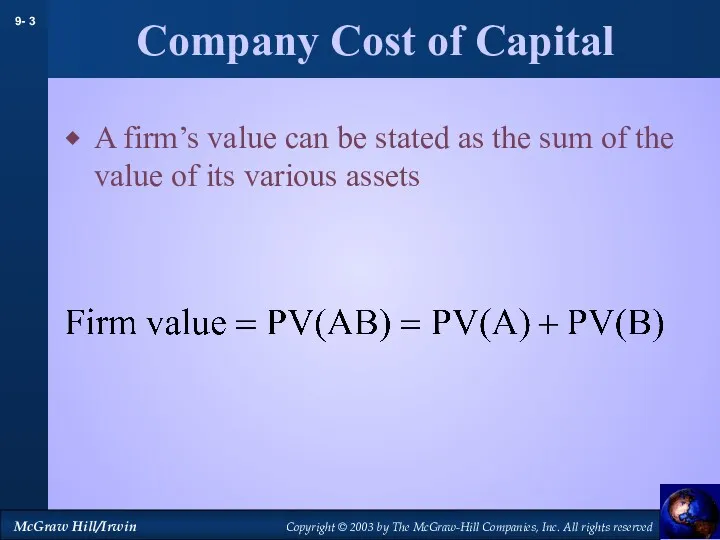
- 3. Company Cost of Capital A firm’s value can be stated as the sum of the value
- 4. Company Cost of Capital
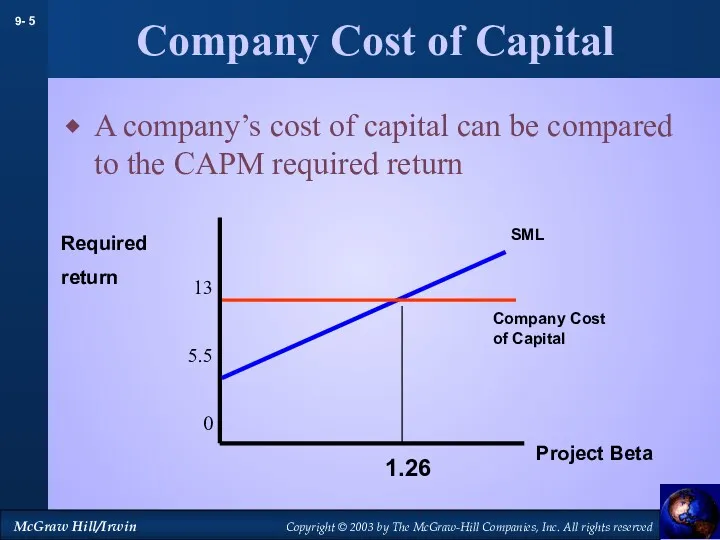
- 5. Company Cost of Capital A company’s cost of capital can be compared to the CAPM required
- 6. Measuring Betas The SML shows the relationship between return and risk CAPM uses Beta as a
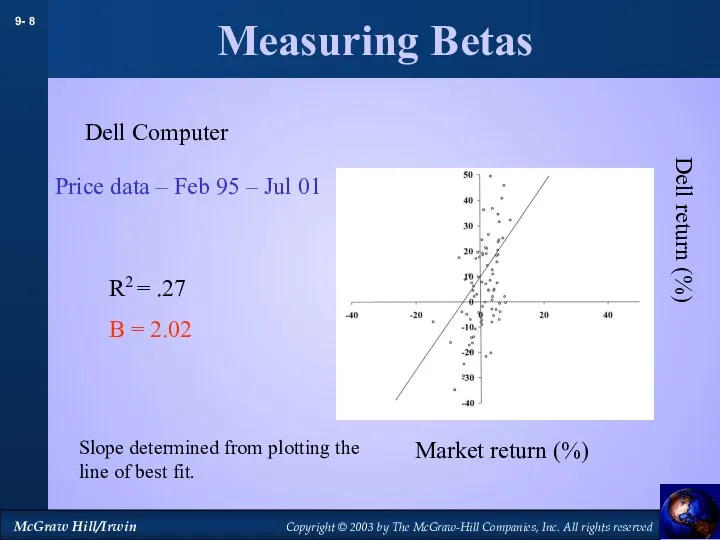
- 7. Measuring Betas Dell Computer Slope determined from plotting the line of best fit. Price data –
- 8. Measuring Betas Dell Computer Slope determined from plotting the line of best fit. Price data –
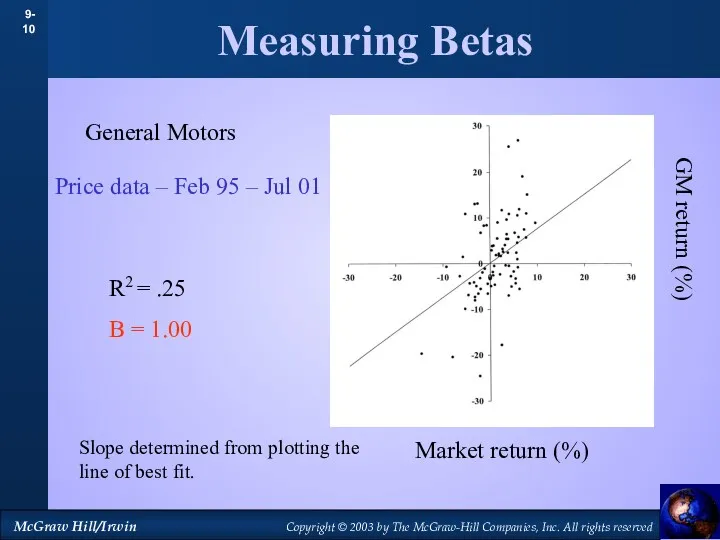
- 9. Measuring Betas General Motors Slope determined from plotting the line of best fit. Price data –
- 10. Measuring Betas General Motors Slope determined from plotting the line of best fit. Price data –
- 11. Measuring Betas Exxon Mobil Slope determined from plotting the line of best fit. Price data –
- 12. Measuring Betas Exxon Mobil Slope determined from plotting the line of best fit. Price data –
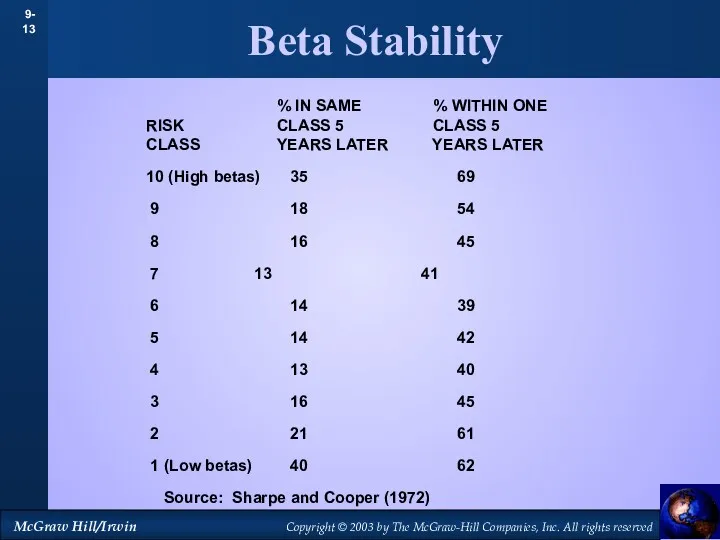
- 13. Beta Stability % IN SAME % WITHIN ONE RISK CLASS 5 CLASS 5 CLASS YEARS LATER
- 14. Company Cost of Capital simple approach Company Cost of Capital (COC) is based on the average
- 15. Company Cost of Capital simple approach Company Cost of Capital (COC) is based on the average
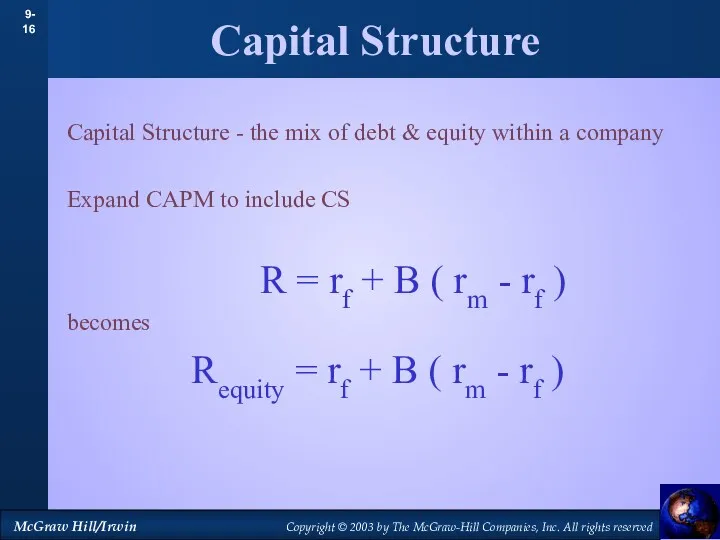
- 16. Capital Structure - the mix of debt & equity within a company Expand CAPM to include
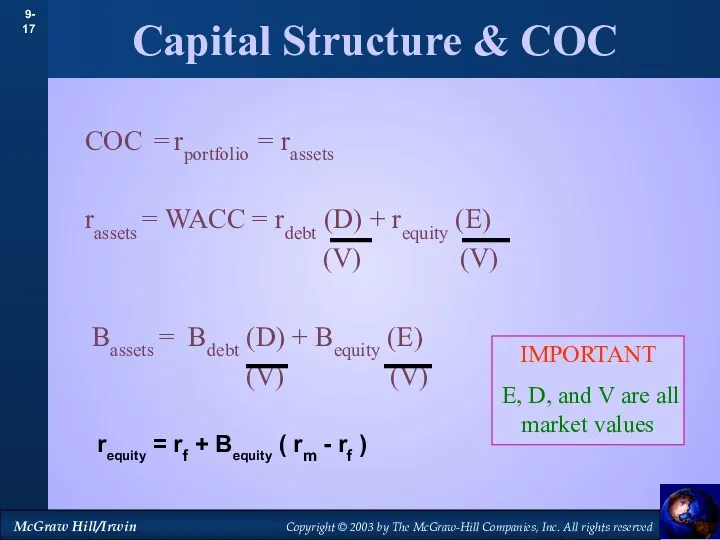
- 17. Capital Structure & COC COC = rportfolio = rassets rassets = WACC = rdebt (D) +
- 18. Capital Structure & COC Expected return (%) Bdebt Bassets Bequity Rrdebt=8 Rassets=12.2 Requity=15 Expected Returns and
- 19. Union Pacific Corp. Requity = Return on Stock = 15% Rdebt = YTM on bonds =
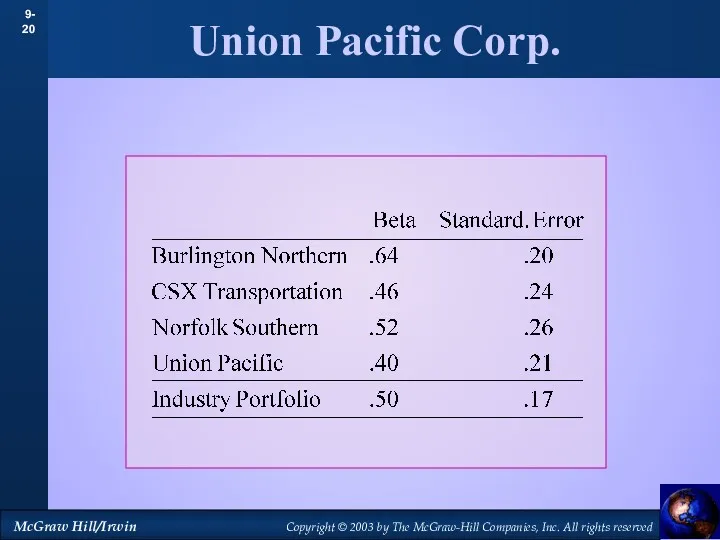
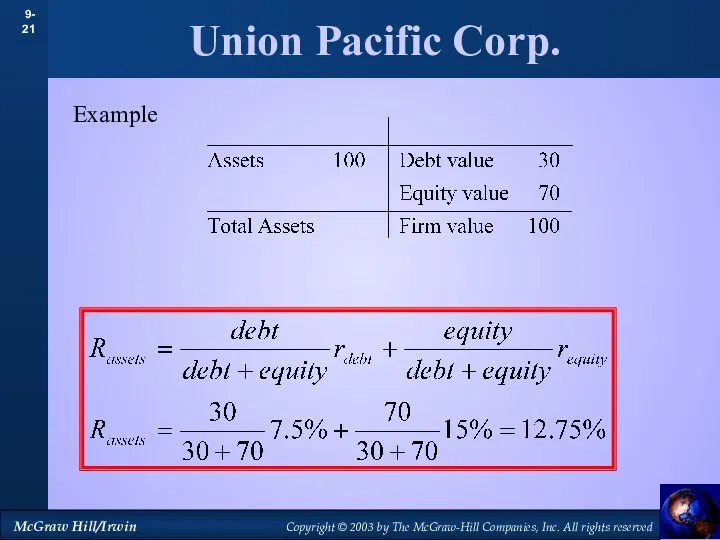
- 20. Union Pacific Corp.
- 21. Union Pacific Corp. Example
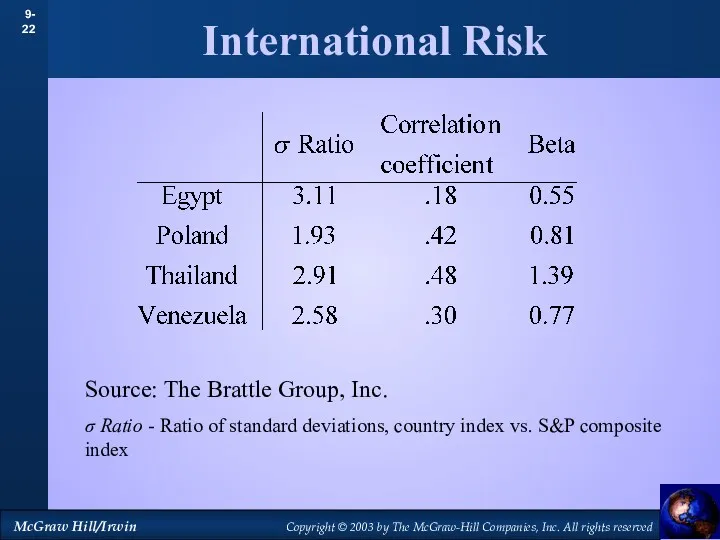
- 22. International Risk Source: The Brattle Group, Inc. σ Ratio - Ratio of standard deviations, country index
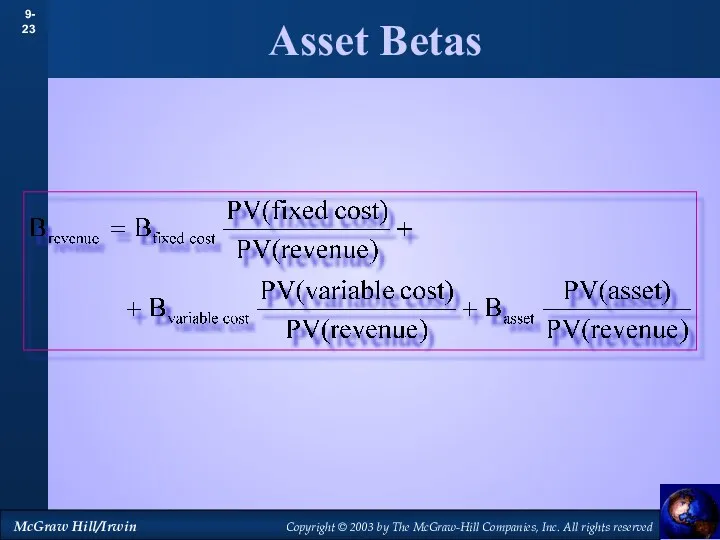
- 23. Asset Betas
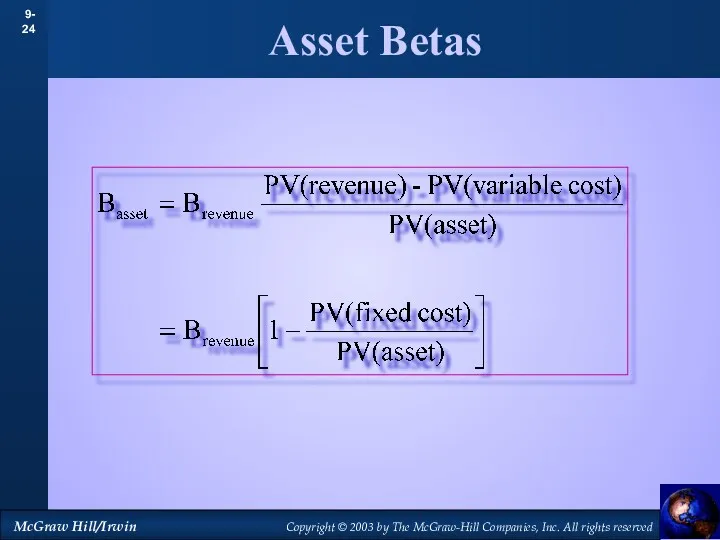
- 24. Asset Betas
- 25. Risk,DCF and CEQ
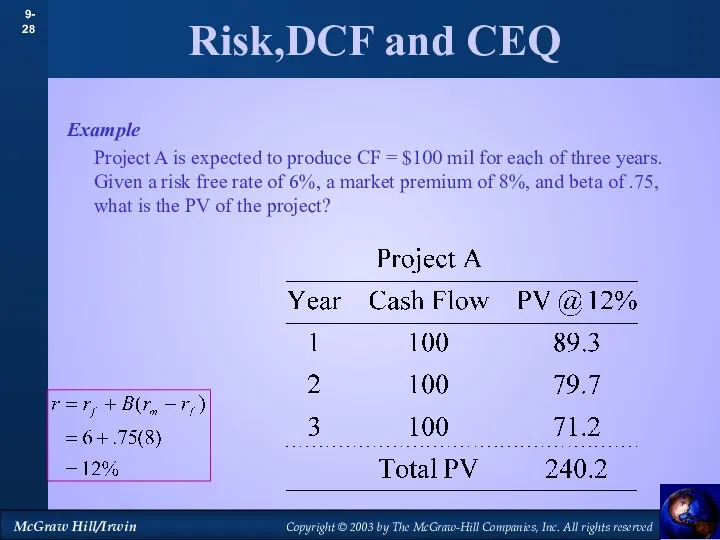
- 26. Risk,DCF and CEQ Example Project A is expected to produce CF = $100 mil for each
- 27. Risk,DCF and CEQ Example Project A is expected to produce CF = $100 mil for each
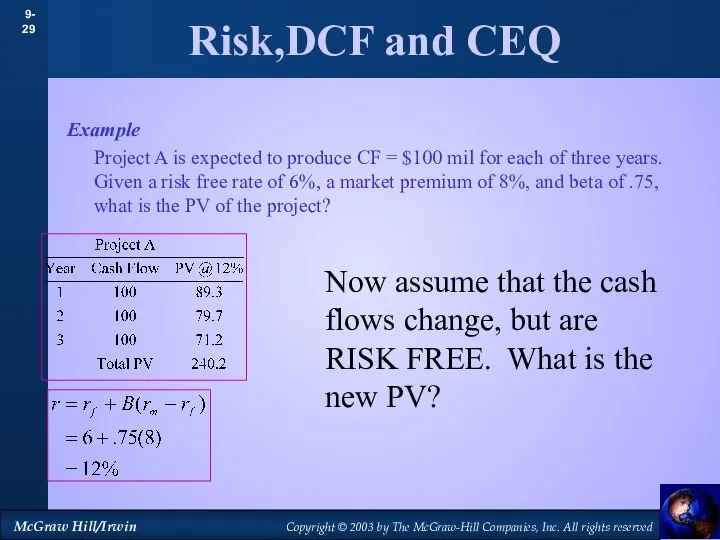
- 28. Risk,DCF and CEQ Example Project A is expected to produce CF = $100 mil for each
- 29. Risk,DCF and CEQ Example Project A is expected to produce CF = $100 mil for each
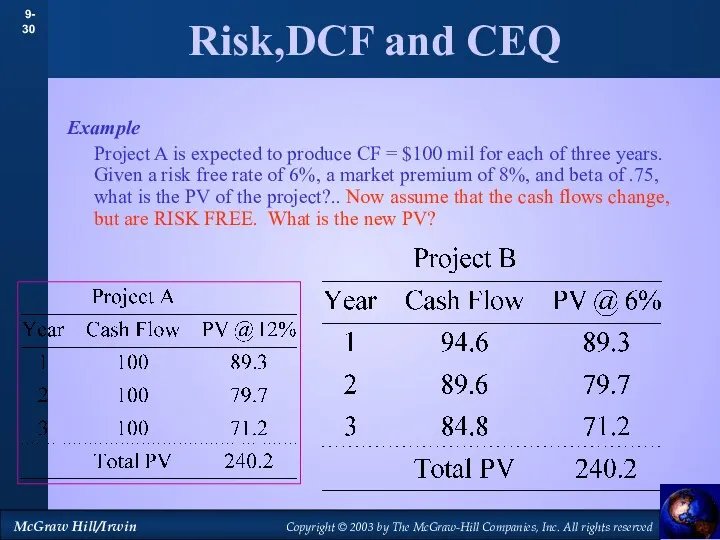
- 30. Risk,DCF and CEQ Example Project A is expected to produce CF = $100 mil for each
- 31. Risk,DCF and CEQ Example Project A is expected to produce CF = $100 mil for each
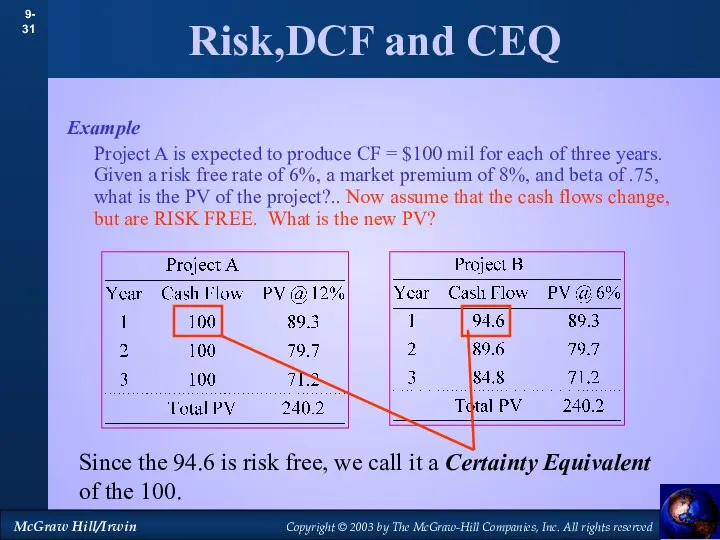
- 32. Risk,DCF and CEQ Example Project A is expected to produce CF = $100 mil for each
- 33. Risk,DCF and CEQ Example Project A is expected to produce CF = $100 mil for each
- 35. Скачать презентацию
















 Тау самал'' тұрғын үй кешенінің электрэнергетикасы шығынын төмендетуді есептеу мен саралау
Тау самал'' тұрғын үй кешенінің электрэнергетикасы шығынын төмендетуді есептеу мен саралау Акцизы. Плательщики акциза
Акцизы. Плательщики акциза Фондовый рынок
Фондовый рынок Налоги и налогообложение
Налоги и налогообложение Кредиты и рассрочки
Кредиты и рассрочки Бюджетирование проекта. Основы фандрайзинга
Бюджетирование проекта. Основы фандрайзинга Анализ имущественного потенциала
Анализ имущественного потенциала Инвестиционная деятельность организации
Инвестиционная деятельность организации Учет выпуска и продажи готовой продукции
Учет выпуска и продажи готовой продукции The theory of exchange rate determination
The theory of exchange rate determination Cодержание электронной коммерции и электронного бизнеса
Cодержание электронной коммерции и электронного бизнеса Учёт материально-производственных запасов
Учёт материально-производственных запасов Поняття та економічна сутність інвестування
Поняття та економічна сутність інвестування Финансы государственного сектора экономики: понятие и структура
Финансы государственного сектора экономики: понятие и структура Администрация сельского поседения Сосновка. Об исполнении бюджета за 1 квартал 2023 г
Администрация сельского поседения Сосновка. Об исполнении бюджета за 1 квартал 2023 г Международный стандарт аудита 220. Контроль качества при проведении аудита финансовой отчетности
Международный стандарт аудита 220. Контроль качества при проведении аудита финансовой отчетности Понятие финансов и финансовой деятельности государства
Понятие финансов и финансовой деятельности государства Единый налог на вменённый доход для отдельных видов деятельности (ЕНВД)
Единый налог на вменённый доход для отдельных видов деятельности (ЕНВД) расходы
расходы Налоги и налогообложение
Налоги и налогообложение Почта Банк для СНТ
Почта Банк для СНТ Система права социального обеспечения. Общее понятие отрасли
Система права социального обеспечения. Общее понятие отрасли Затраты предприятия
Затраты предприятия Государственный кредит (государственные и муниципальные заимствования)
Государственный кредит (государственные и муниципальные заимствования) Валютный рынок FOREX. Технический анализ на рынке FOREX
Валютный рынок FOREX. Технический анализ на рынке FOREX Операции коммерческого банка с пластиковыми картами и их роль в обеспечении комплексного обслуживания клиентов
Операции коммерческого банка с пластиковыми картами и их роль в обеспечении комплексного обслуживания клиентов Доходы, расходы и прибыль организации
Доходы, расходы и прибыль организации Комплексная оценка эффективности финансовохозяйственной деятельности предприятия
Комплексная оценка эффективности финансовохозяйственной деятельности предприятия