Содержание
- 2. Minority the portion of a subsidiary corporation's stock that is not owned by the parent corporation.
- 3. Balance Sheet. Fixed assets Investment Property Intangible assets Financial assets Investment using the equity method Inventories
- 4. Fixed assets a long-term tangible piece of property that a firm owns and uses in the
- 5. Investment property (IAS 40) Investment property is property (land or a building or part of a
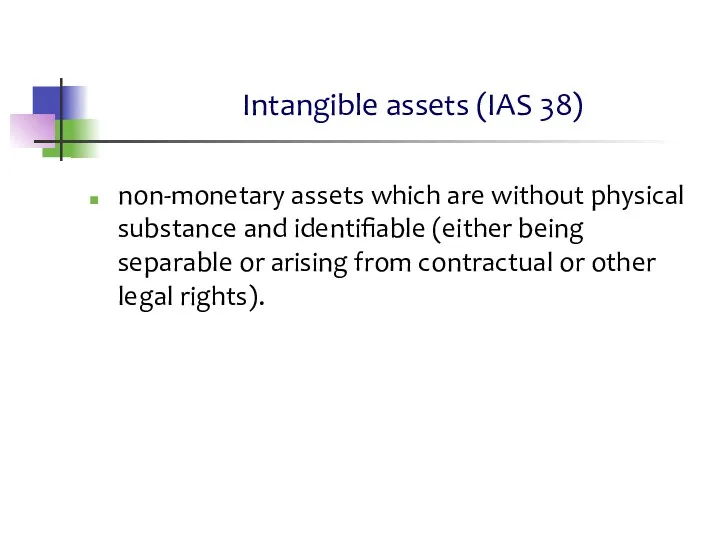
- 6. Intangible assets (IAS 38) non-monetary assets which are without physical substance and identifiable (either being separable
- 7. Financial assets (IAS 39, IFRS 9) A financial asset is a tangible liquid asset that derives
- 8. Investment using the equity method http://www.investopedia.com/terms/e/equitymethod.asp?ad=dirN&qo=investopediaSiteSearch&qsrc=0&o=40186
- 9. Inventories (IAS 2) Inventories include: assets held for sale in the ordinary course of business (finished
- 10. Accounts receivable Accounts receivable refers to the outstanding invoices a company has or the money the
- 11. Cash and cash equivalents (IAS 7) Cash and cash equivalents refer to the line item on
- 12. Deferred and current tax assets Deferred tax asset is an accounting term that refers to a
- 13. Deferred and current tax liabilities A deferred tax liability is an account on a company's balance
- 14. Provision for contingent liabilities A contingent liability is a potential liability that may occur, depending on
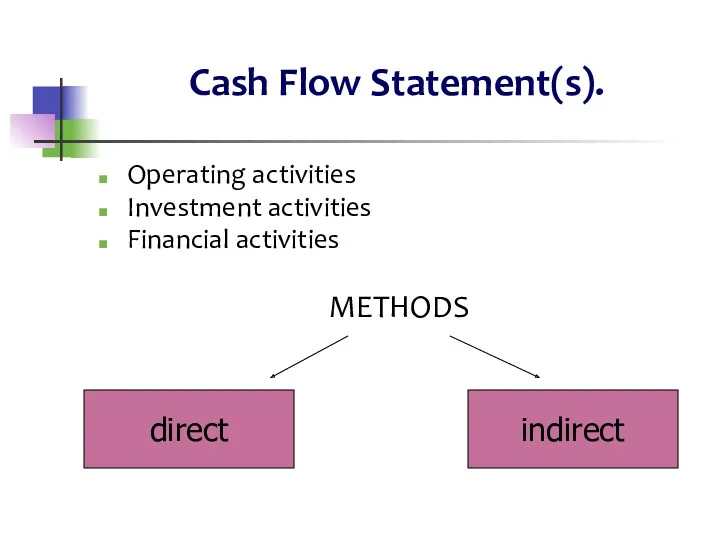
- 15. Cash Flow Statement(s). Operating activities Investment activities Financial activities METHODS direct indirect
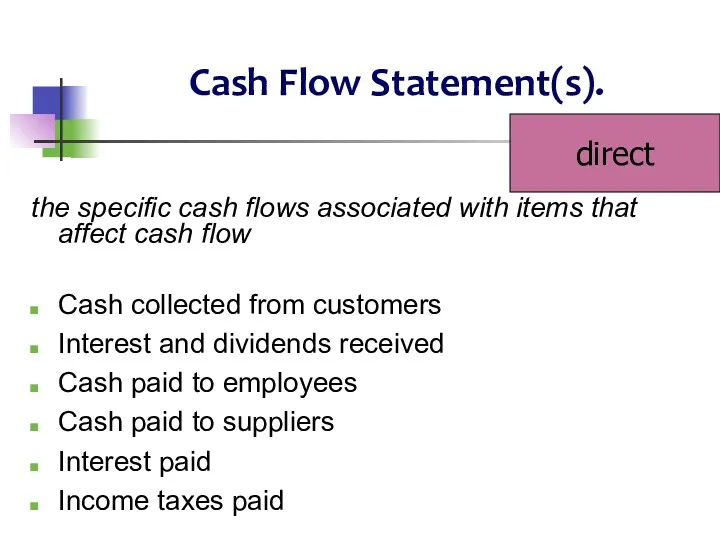
- 16. Cash Flow Statement(s). the specific cash flows associated with items that affect cash flow Cash collected
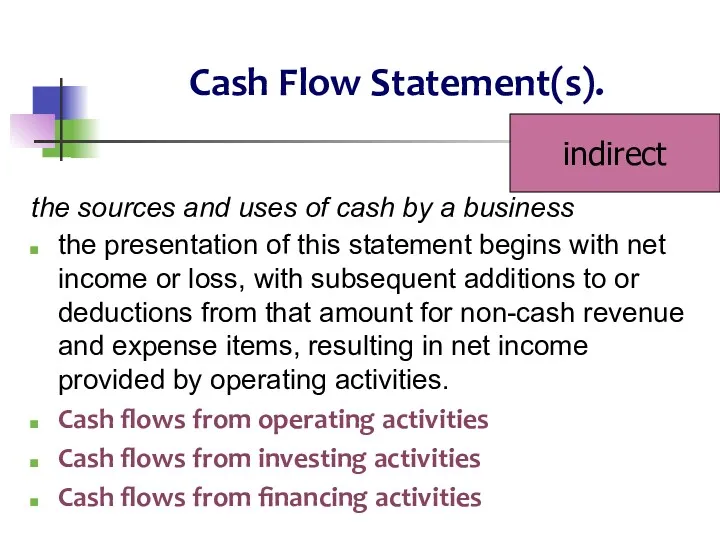
- 18. Cash Flow Statement(s). the sources and uses of cash by a business the presentation of this
- 20. Statement of Changes in Own Equity. Basic approach Profit / loss for the period Profit /
- 22. Скачать презентацию















 Налог на доходы физических лиц
Налог на доходы физических лиц Античне страхування
Античне страхування Кроссворд по финансовой грамотности дошкольников 5-7 лет
Кроссворд по финансовой грамотности дошкольников 5-7 лет Судебные споры, банкротство и субсидиарная ответственность в финансовом секторе
Судебные споры, банкротство и субсидиарная ответственность в финансовом секторе Денежные фонды и резервы организации
Денежные фонды и резервы организации Структура и содержание внешнеторгового контракта
Структура и содержание внешнеторгового контракта Страхование в банковском секторе. Проблемы и меры по усовершенствованию
Страхование в банковском секторе. Проблемы и меры по усовершенствованию Оплата труда
Оплата труда Таможенные платежи в ЕАЭС: общая характеристика и назначение
Таможенные платежи в ЕАЭС: общая характеристика и назначение Fortebank
Fortebank Зарплатный проект Росбанка
Зарплатный проект Росбанка Налоговый контроль
Налоговый контроль Аудит достоверности строк финансовой отчетности организации
Аудит достоверности строк финансовой отчетности организации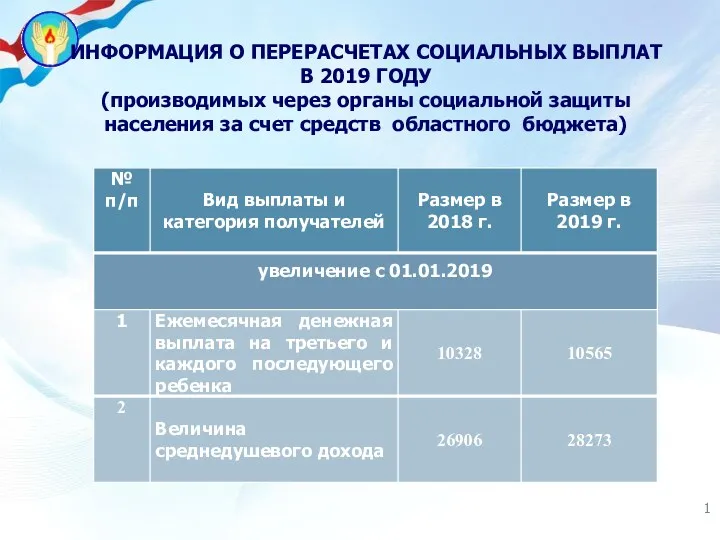 Информация о перерасчетах социальных выплат (через органы социальной защиты населения за счет средств областного бюджета)
Информация о перерасчетах социальных выплат (через органы социальной защиты населения за счет средств областного бюджета) Кредит - жизнь в долг или способ удовлетворения потребностей
Кредит - жизнь в долг или способ удовлетворения потребностей Основные принципы кадровой и социальной работы ПАО НК Роснефть
Основные принципы кадровой и социальной работы ПАО НК Роснефть Организация документооборота и внутреннего контроля в бухгалтерском учете коммерческого банка
Организация документооборота и внутреннего контроля в бухгалтерском учете коммерческого банка The world of money
The world of money Понятие налоговой системы и ее элементы
Понятие налоговой системы и ее элементы Аудит учета матариально-производственных запасов и готовой продукции
Аудит учета матариально-производственных запасов и готовой продукции Экономическая сущность и природа налогов
Экономическая сущность и природа налогов НДФЛ-2016. Внесение изменения в статью 218 части второй Налогового кодекса РФ
НДФЛ-2016. Внесение изменения в статью 218 части второй Налогового кодекса РФ Фінанси домогосподарств
Фінанси домогосподарств Қаржы нарығы және делдалдары
Қаржы нарығы және делдалдары Заработная плата и факторы, влияющие на ее размер
Заработная плата и факторы, влияющие на ее размер Организация финансов коммерческих организаций в современных условиях
Организация финансов коммерческих организаций в современных условиях Учёт денежных средств
Учёт денежных средств Price Equilibrium 11.2a
Price Equilibrium 11.2a