Содержание
- 2. Pricing What is price?; Pricing approaches and considerations; Pricing strategies;
- 3. What is price? Everything given in exchange for something else. The amount of money charged for
- 4. Most common mistakes in pricing pricing that is too cost-oriented; prices that are not revised often
- 5. Pricing approaches and considerations Factors influencing pricing Internal factors – marketing objectives, marketing mix strategy, costs,
- 6. Internal Factors Affecting Pricing Decisions Marketing Objectives: examples of common objectives are survival, current profit maximization,
- 7. Internal Factors Affecting Pricing Decisions Costs: fixed costs - costs that do not vary with production
- 8. External Factors Affecting Pricing Decisions: The Market and Demand Pricing in different types of market Pure
- 9. External Factors Affecting Pricing Decisions: The Market and Demand oligopolistic competition: the market consists of a
- 10. External Factors Affecting Pricing Decisions: The Market and Demand Consumer perceptions of price and value: If
- 11. External Factors Affecting Pricing Decisions: Relationship Between Level of Prices and Demand Each price the company
- 13. Price elasticity Price elasticity: A measure of the sensitivity of demand to changes in price. If
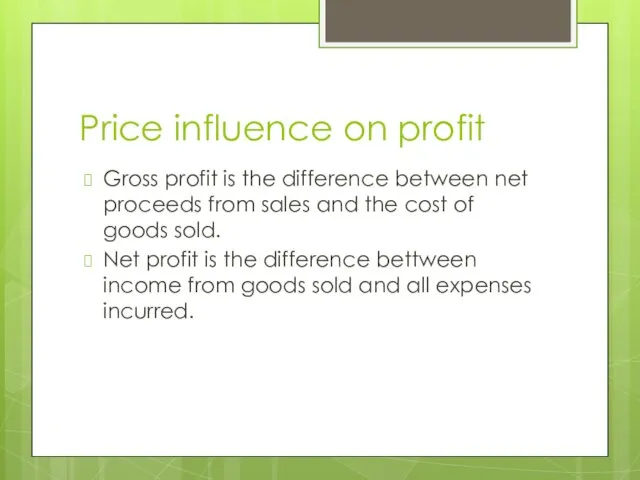
- 14. Price influence on profit Gross profit is the difference between net proceeds from sales and the
- 15. External Factors Affecting Pricing Decisions: Competitors' Costs, Prices and Offers By knowing what the competition charges
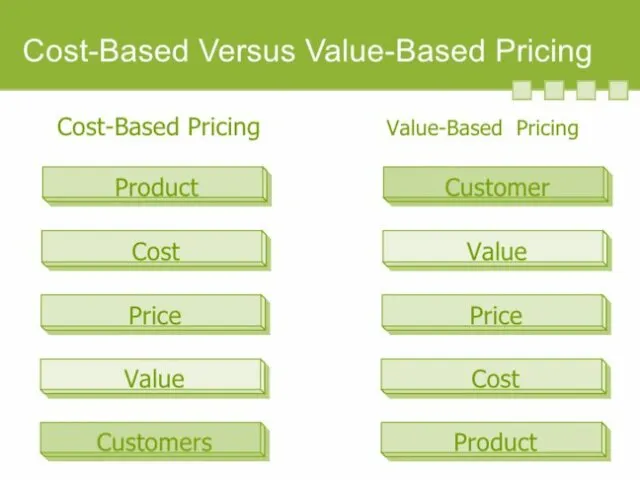
- 16. Pricing approaches and considerations Pricing approaches Cost based pricing Break-even analysis Value based pricing Competition based
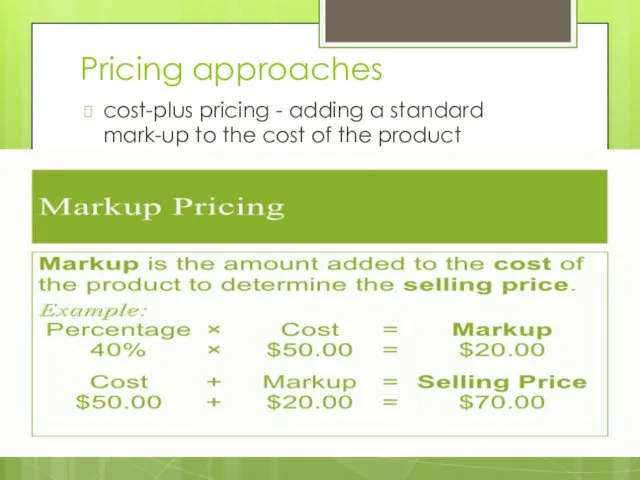
- 17. Pricing approaches cost-plus pricing - adding a standard mark-up to the cost of the product
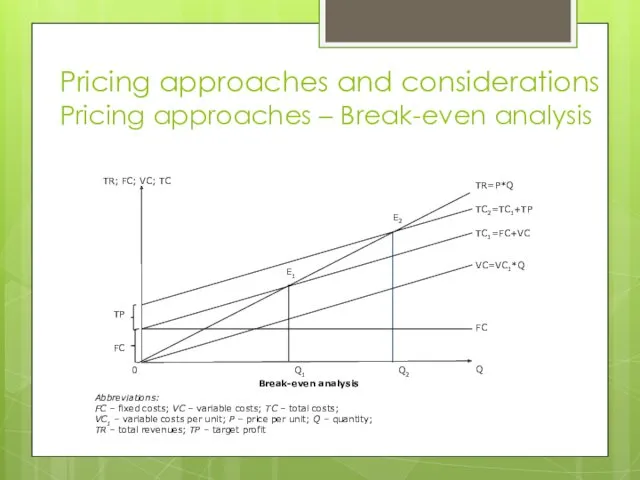
- 18. Pricing approaches and considerations Pricing approaches – Break-even analysis
- 19. Value-Based Pricing Value based pricing is the practice of setting the price of a product or
- 21. Advantages of Value Based Pricing Increases profits. This method results in the highest possible price that
- 22. Disadvantages of Value Based Pricing The very high prices to be expected under this method will
- 23. Competitor based pricing Advantages: It’s fairly simple; It’s low risk; It can be accurate; Disadvantages It
- 24. Pricing strategies New product pricing strategies – market-skimming pricing and market penetration pricing Product-mix pricing strategies
- 25. New product pricing strategies Penetration pricing: setting a relatively low initial entry price to attract new
- 26. New product pricing strategies Skimming: Selling a product at a high price and sacrificing high sales
- 27. Product mix strategies Product line pricing refers to the practice of reviewing and setting prices for
- 28. Price adjustment strategies Discounts and Allowances: reductions to the selling price of goods or services. Cash
- 29. Price adjustment strategies Segmented Pricing: a company fixes or sets more than one price for a
- 30. Price adjustment strategies Promotional Pricing: Temporarily reducing prices to increase short-run sales Value-Based Pricing: Adjusting prices
- 31. Price adjustment strategies Geographical Pricing: Adjusting prices to account for the geographic location of customers International
- 33. Скачать презентацию


























 Бухгалтерский учет и контроль оплаты труда в бюджетном учреждение
Бухгалтерский учет и контроль оплаты труда в бюджетном учреждение Сравнительный подход в оценке бизнеса
Сравнительный подход в оценке бизнеса Валютное регулирование и валютный контроль. Лекция 8-13 - Международные расчеты, их условия и формы
Валютное регулирование и валютный контроль. Лекция 8-13 - Международные расчеты, их условия и формы Графические ценовые модели
Графические ценовые модели Финансовый анализ компании
Финансовый анализ компании Обязательства компании: структура и методы управления
Обязательства компании: структура и методы управления Налоги, их виды и функции
Налоги, их виды и функции Бюджетный процесс
Бюджетный процесс Новые аспекты юридической и финансовой деятельности СО НКО
Новые аспекты юридической и финансовой деятельности СО НКО Студия Уроки настоящего МКОУ Нижнекарачанская СОШ
Студия Уроки настоящего МКОУ Нижнекарачанская СОШ Деньги в системе. Распределение денег
Деньги в системе. Распределение денег Семинар об изменении порядка налогообложения доходов от продажи недвижимости
Семинар об изменении порядка налогообложения доходов от продажи недвижимости Основные правила финансовой безопасности в информационной сфере
Основные правила финансовой безопасности в информационной сфере Операції банків із векселями
Операції банків із векселями Налоговый и бухгалтерский учет средств бюджетного гранта в сельскохозяйственных кооперативах
Налоговый и бухгалтерский учет средств бюджетного гранта в сельскохозяйственных кооперативах Условия предоставления и порядок расчета отпускных
Условия предоставления и порядок расчета отпускных Бюджет для граждан к проекту бюджета на 2020-2022гг
Бюджет для граждан к проекту бюджета на 2020-2022гг Рынок ценных бумаг
Рынок ценных бумаг Центральный Банк (Банк России)
Центральный Банк (Банк России) Балансовый отчет за 2019 год
Балансовый отчет за 2019 год Выбор аудиторской компании клиентами
Выбор аудиторской компании клиентами Платежеспособность и ликвидность предприятия. Основные определения, порядок проведения анализа. (Тема 11)
Платежеспособность и ликвидность предприятия. Основные определения, порядок проведения анализа. (Тема 11) Эмиссия безналичных денег
Эмиссия безналичных денег Бюджет для граждан простыми словами, пгт. Оричи
Бюджет для граждан простыми словами, пгт. Оричи Перевозка пассажиров на территории Волгограда. Виды транспортных карт
Перевозка пассажиров на территории Волгограда. Виды транспортных карт Базель I и Базель II
Базель I и Базель II МСФО 7. Отчеты о движении денежных средств
МСФО 7. Отчеты о движении денежных средств Страхование. Участники страхового рынка
Страхование. Участники страхового рынка