Содержание
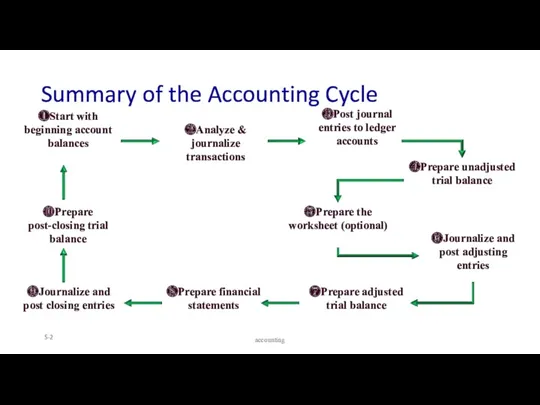
- 2. Summary of the Accounting Cycle 5- ❷Analyze & journalize transactions ❸Post journal entries to ledger accounts
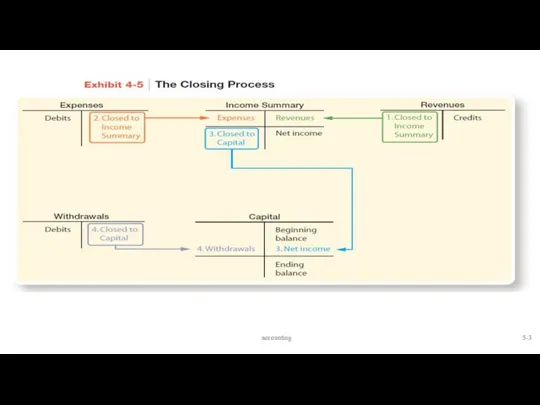
- 3. 5- accounting
- 4. Learning Objectives – Chapter 5 Describe merchandising operations and the two types of merchandise inventory systems
- 5. Learning Objectives – Chapter 5 Adjust and close the accounts of a merchandising business Prepare a
- 6. Learning Objectives 1 Describe merchandising operations and the two types of merchandise inventory systems Accounting
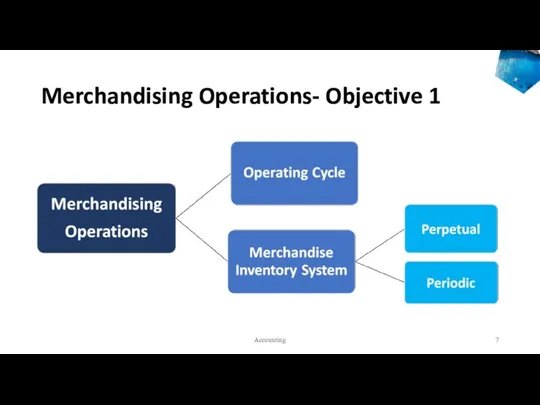
- 7. Merchandising Operations- Objective 1 Accounting
- 8. What Are Merchandising Operations? Merchandiser: Seller of goods, not producer (not manufacturer) Can be wholesaler or
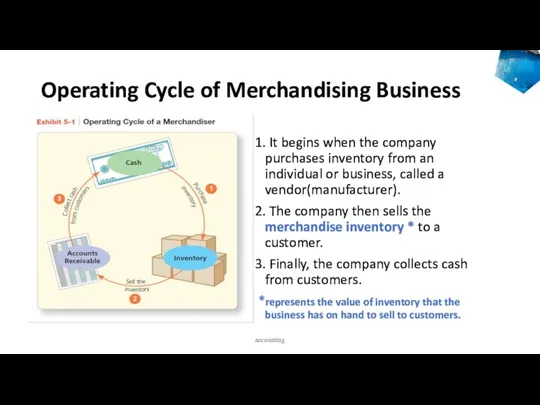
- 9. Operating Cycle of Merchandising Business 1. It begins when the company purchases inventory from an individual
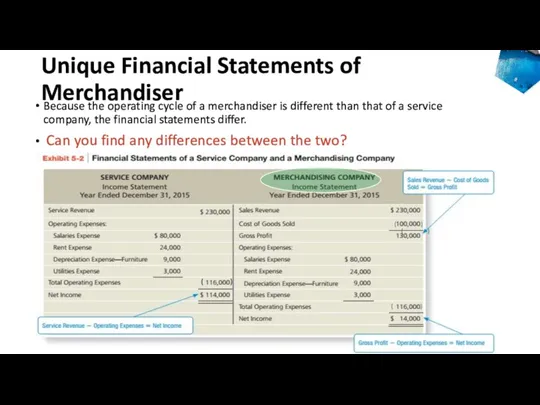
- 10. Unique Financial Statements of Merchandiser accounting Because the operating cycle of a merchandiser is different than
- 11. Merchandiser Financial Statements Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) The cost of the Merchandise inventory that the
- 12. Unique Financial Statements of Merchandiser accounting Can you find any differences? Merchandise Inventory (CA) is usually
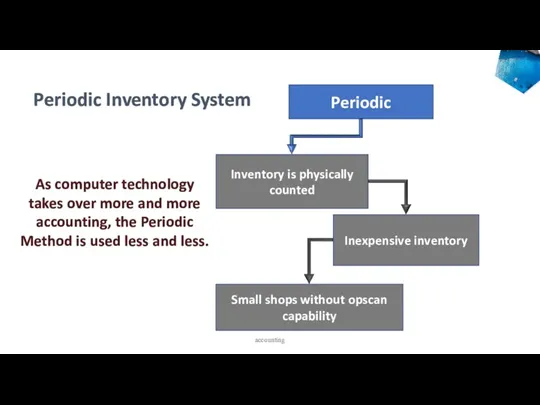
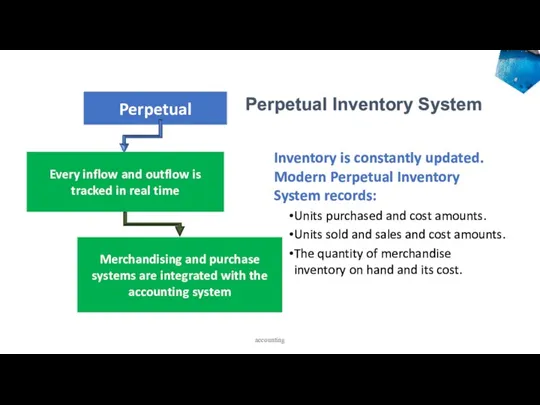
- 13. Main types of Merchandise Inventory systems Perpetual Inventory System An inventory system that keeps a running
- 14. Periodic Inventory is physically counted Inexpensive inventory Small shops without opscan capability As computer technology takes
- 15. Perpetual Inventory is constantly updated. Modern Perpetual Inventory System records: Units purchased and cost amounts. Units
- 16. Accounting Merchandise Inventory systems
- 17. Practice Questions p341 accounting
- 18. Practice Questions p341 accounting
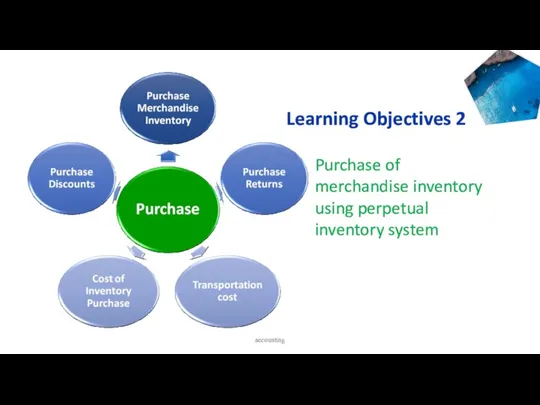
- 19. accounting Learning Objectives 2 Purchase of merchandise inventory using perpetual inventory system
- 20. Smart Touch Learning Example Smart Touch Learning has now decided to discontinue its service business and
- 21. accounting
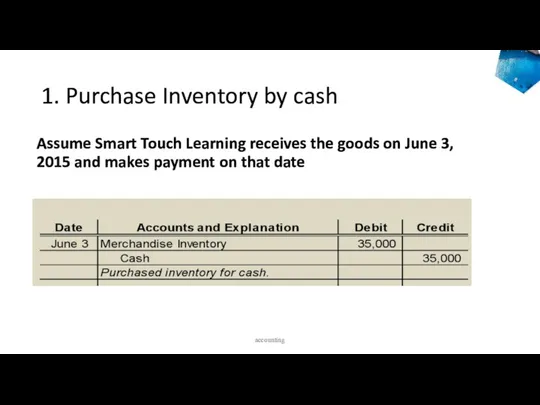
- 22. 1. Purchase Inventory by cash Assume Smart Touch Learning receives the goods on June 3, 2015
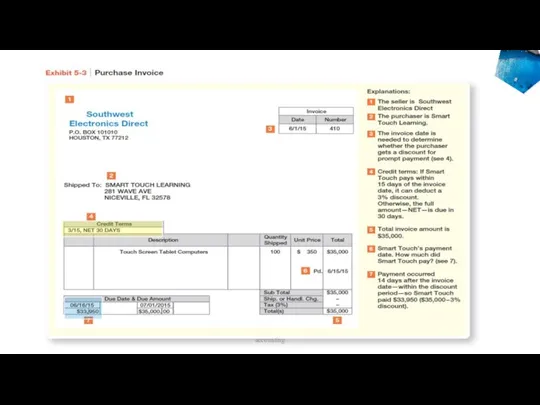
- 23. 1. Purchase inventory on Account If we had received the inventory on June 3, but chosen
- 24. 2. Purchase Discounts Many businesses offer purchases a discount for early payment. Invoices that accompany credit
- 25. 2. Purchase Discounts The discount amount is determined by the “credit terms” indicated on the invoice.
- 26. 2. Purchase Discounts If Smart Touch Learning pays within the 15 day period, they get a
- 27. 3. Purchase Returns and Allowances Purchase Return:A situation in which sellers allow purchasers to return merchandise
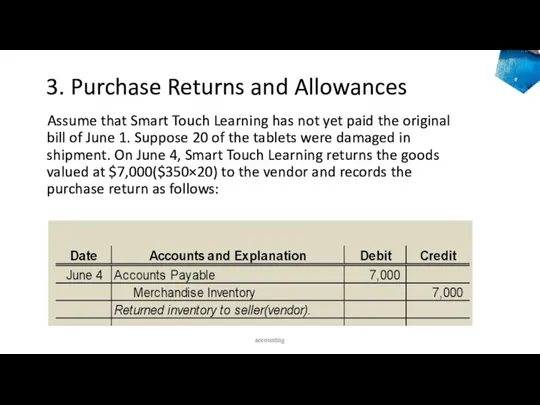
- 28. 3. Purchase Returns and Allowances Assume that Smart Touch Learning has not yet paid the original
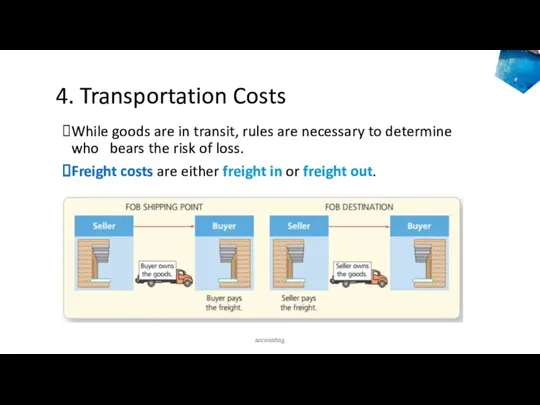
- 29. 4. Transportation Costs When goods are in transit from the seller to the buyer, an issue
- 30. 4. Transportation Costs The purchase agreement specifies that either the seller or the buyer must pay
- 31. 4. Transportation Costs While goods are in transit, rules are necessary to determine who bears the
- 32. Freight In Freight in is the transportation cost to ship goods into the purchaser’s warehouse; thus,
- 33. Merchandise Inventory Account The merchandise inventory account will reflect the net results of all the transactions
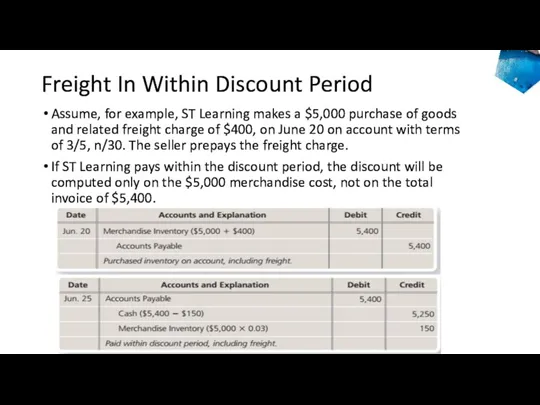
- 34. Freight In Within Discount Period Under FOB shipping point, the seller sometimes prepays the transportation cost
- 35. Freight In Within Discount Period Assume, for example, ST Learning makes a $5,000 purchase of goods
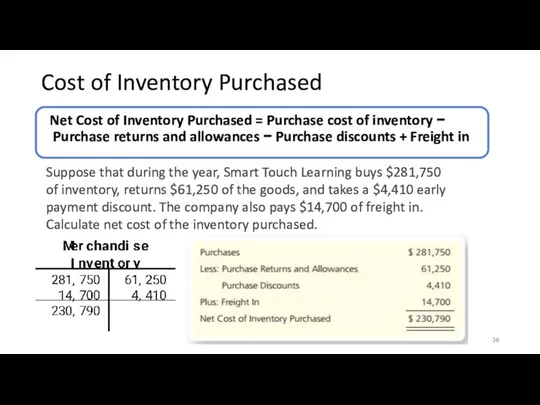
- 36. Cost of Inventory Purchased Net Cost of Inventory Purchased = Purchase cost of inventory − Purchase
- 37. Practice Questions p341 accounting
- 38. Practice Questions - Solution accounting The inventory cost for Dady is $14,882 = ($20,250 + $90
- 39. accounting Learning Objectives 3 Account for the sale of merchandise inventory using a perpetual inventory system
- 40. 1. Sale of Merchandise Inventory In a perpetual system, two entries must be made for every
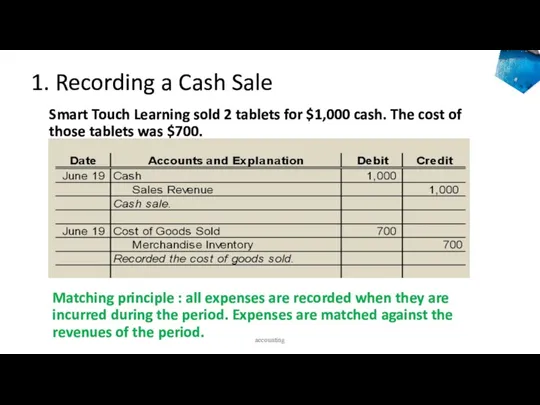
- 41. 1. Recording a Cash Sale Smart Touch Learning sold 2 tablets for $1,000 cash. The cost
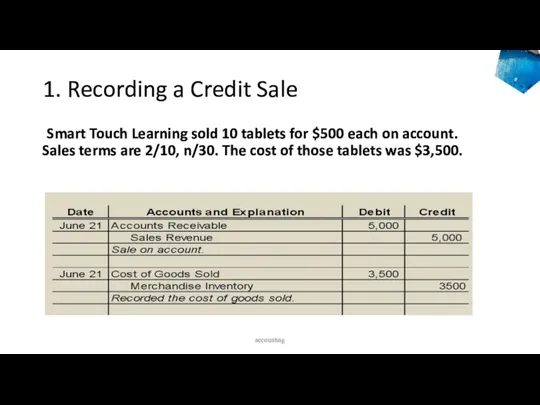
- 42. 1. Recording a Credit Sale Smart Touch Learning sold 10 tablets for $500 each on account.
- 43. 2. Sales Returns and Allowances Sometimes, companies may have customers that return goods, asking for a
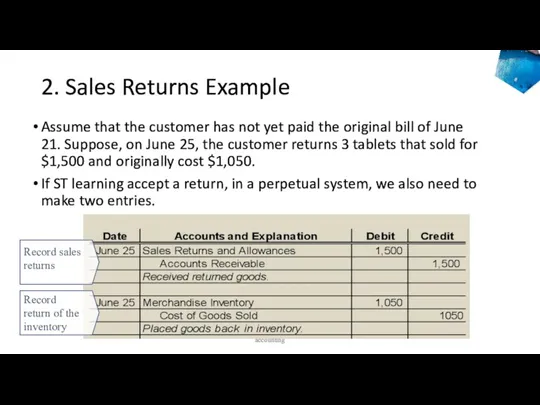
- 44. 2. Sales Returns Example Assume that the customer has not yet paid the original bill of
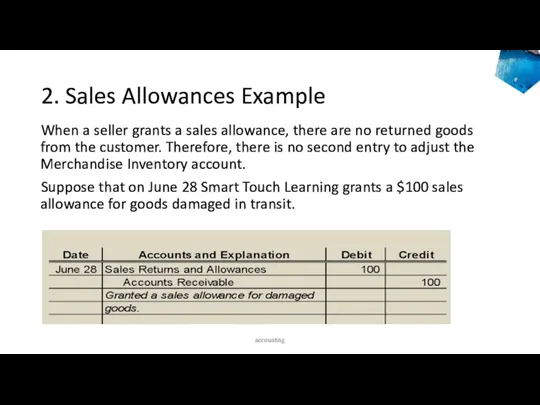
- 45. 2. Sales Allowances Example When a seller grants a sales allowance, there are no returned goods
- 46. 3. Sales Discounts after Sales Return Many sellers offer customers a discount for early payment. Sales
- 47. 4. Transportation Cost - Freight Out The freight in is part of the inventory cost for
- 48. Homework p306 accounting
- 49. Homework p342 accounting
- 51. Скачать презентацию




























 Бюджетное управление на предприятии. Тема 7
Бюджетное управление на предприятии. Тема 7 Характеристика финансовых институтов, как объекта оценки. (Лекция 1)
Характеристика финансовых институтов, как объекта оценки. (Лекция 1) Инструкция TopMission для тайных покупателей. Аудит офиса продаж
Инструкция TopMission для тайных покупателей. Аудит офиса продаж Сущность, содержание и организация бухгалтерского учета. Тема 1
Сущность, содержание и организация бухгалтерского учета. Тема 1 Рабочая тетрадь. Автокредитование. Этапы продаж
Рабочая тетрадь. Автокредитование. Этапы продаж Электронный документооборот в учреждениях госсектора
Электронный документооборот в учреждениях госсектора Кредитная политика банка. Кредитные продукты
Кредитная политика банка. Кредитные продукты Вьетнамский донг
Вьетнамский донг Фінансовий ринок
Фінансовий ринок Проблемы наличного обращения
Проблемы наличного обращения МСФО 16. Основные средства
МСФО 16. Основные средства Учет материалов на счете 10
Учет материалов на счете 10 Консультация по системе оплаты труда педагогических работников
Консультация по системе оплаты труда педагогических работников Отчёт о финансовых результатах. Форма № 2
Отчёт о финансовых результатах. Форма № 2 Світовий фінансовий ринок та його структура
Світовий фінансовий ринок та його структура Судебно-правовая бухгалтерия. Предмет, объекты и метод бухгалтерского учёта. Тема 2
Судебно-правовая бухгалтерия. Предмет, объекты и метод бухгалтерского учёта. Тема 2 Система сбалансированных показателей Balanced Scorecard
Система сбалансированных показателей Balanced Scorecard Управление финансовыми рисками
Управление финансовыми рисками НДФЛ и страховые взносы 2023
НДФЛ и страховые взносы 2023 Роль и назначение международных стандартов финансовой отчётности. Лекция 1
Роль и назначение международных стандартов финансовой отчётности. Лекция 1 Flood Risk Solutions, Inc Insurance Technology
Flood Risk Solutions, Inc Insurance Technology Бюджетирование как элемент внутрикорпоративного управления
Бюджетирование как элемент внутрикорпоративного управления Кредитная Х5 карта. Перекресток и Пятерочка
Кредитная Х5 карта. Перекресток и Пятерочка Учет денежных средств и расчетов
Учет денежных средств и расчетов Оцінка рухомого майна. Визначення вартості рухомого майна витратним підходом
Оцінка рухомого майна. Визначення вартості рухомого майна витратним підходом Республикалық бюджет жобасын құрастыру кезеңдері
Республикалық бюджет жобасын құрастыру кезеңдері Страхование и его виды
Страхование и его виды Деньги: причины возникновения, формы и функции
Деньги: причины возникновения, формы и функции