Содержание
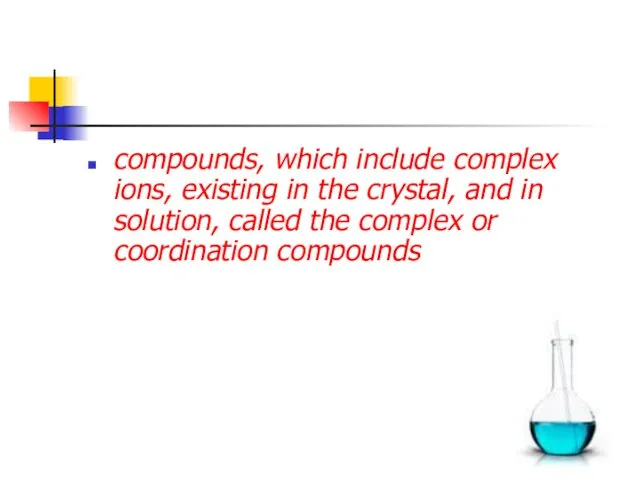
- 4. compounds, which include complex ions, existing in the crystal, and in solution, called the complex or
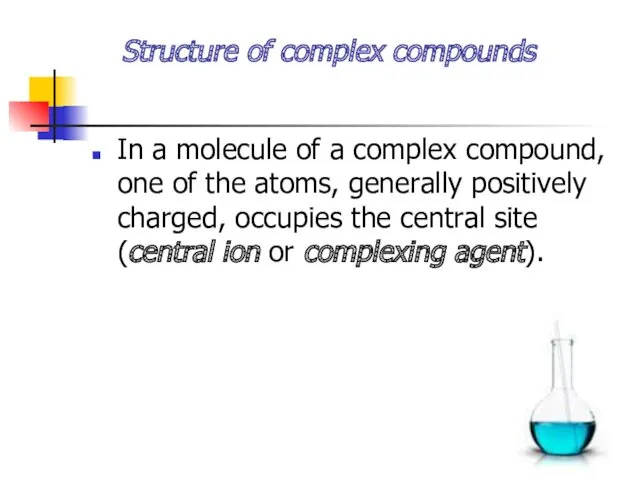
- 5. Structure of complex compounds In a molecule of a complex compound, one of the atoms, generally
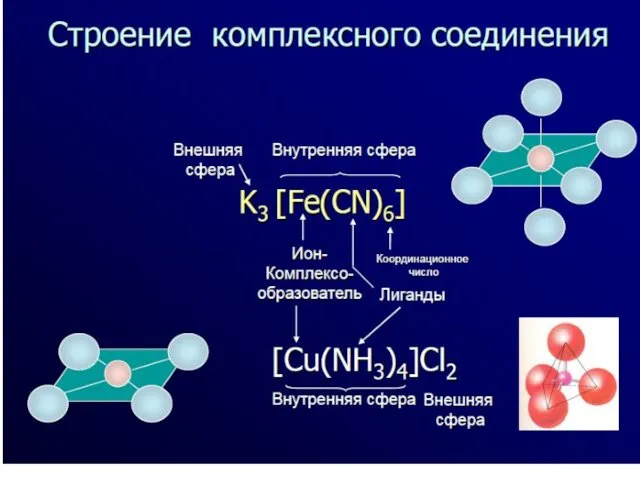
- 6. Oppositely charged ions or neutral molecules called ligands are coordinated around the central ion.
- 7. The complexing agent and ligands form inner sphere of a complex compound. It is characterized by
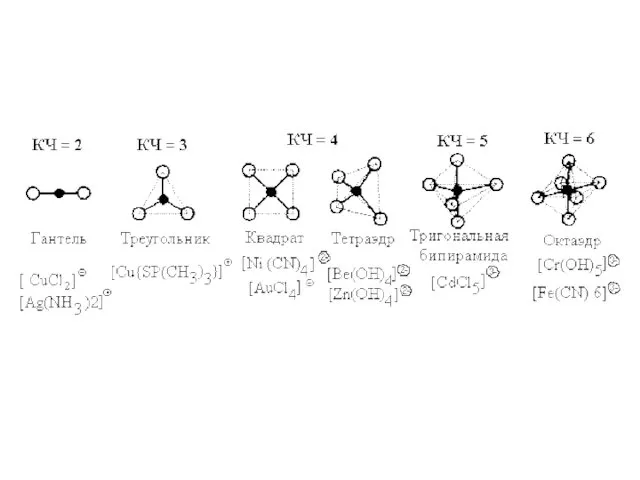
- 8. The total number of coordinate bonds formed by the complexing agent is known as coordination number
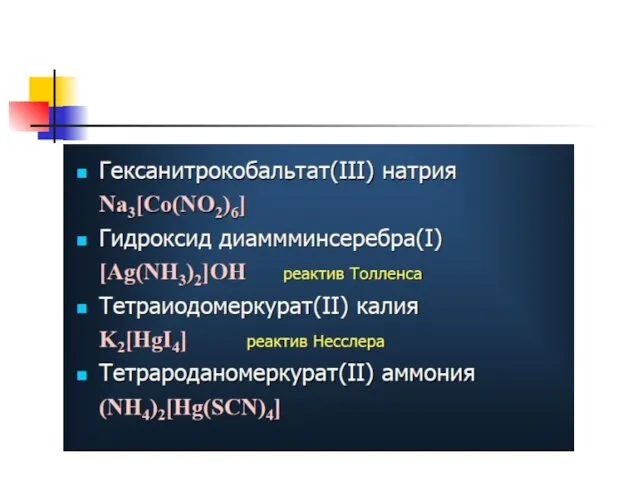
- 10. Nomenclature of complex compounds Names of complex compounds are similar to the names of simple salts.
- 12. [Cu(NH3)4]Cl2 – tetraammine copper(II) chloride; K2 [Cu(OH)4] – potassium tetrahydroxocupprate(II); [Cr(NH3)3Cl3] – trichloro triammine chromium(III).
- 14. Classification of complex compounds There are several types of classification of complex compounds.
- 15. Classification of complex compounds 1. Depending upon a charge of the inner sphere: (i) Cationic complexes
- 16. 22) Depending upon the type of the ligand: (i) Aqua-complexes (ligands are water molecules – [Cu(H2O)5]SO4).
- 17. б)Гидроксокомплексы – это комплексные анионы, в которых лигандами являются гидроксид-ионы OH–. Комплексообразователями являются металлы, склонные к
- 18. Depending upon the nature of a central ion: complexes of copper, silver, iron, chrome etc.
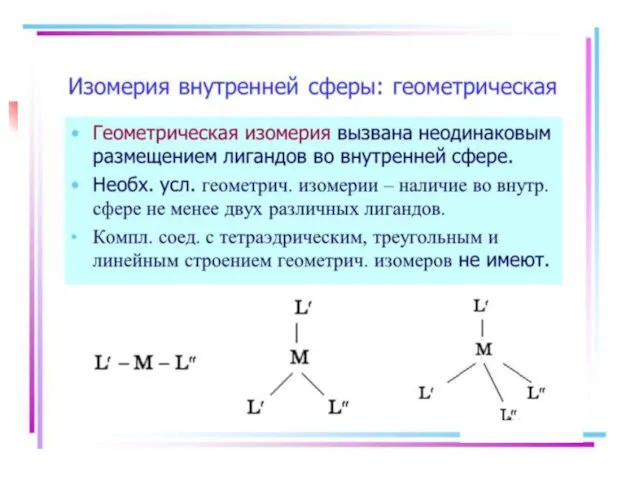
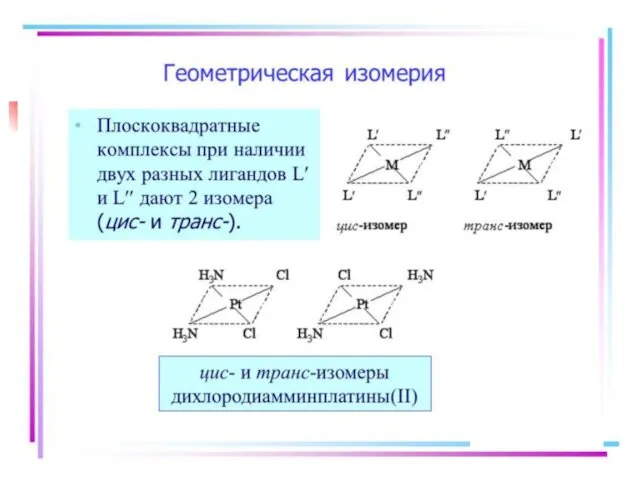
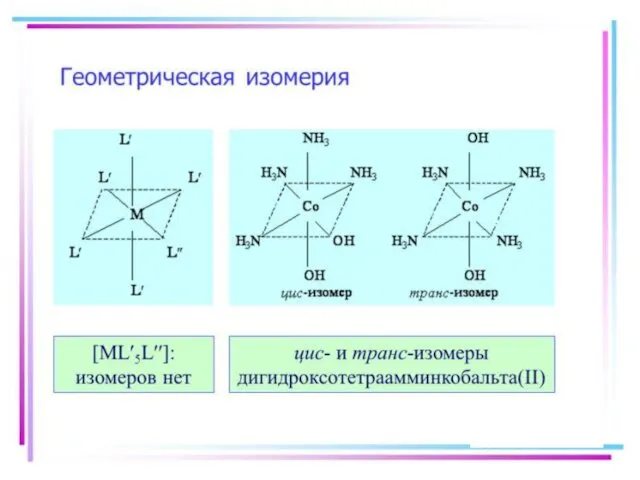
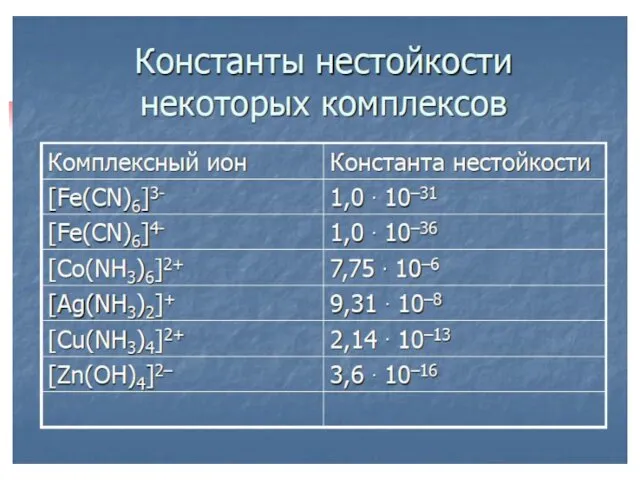
- 21. Isomerism
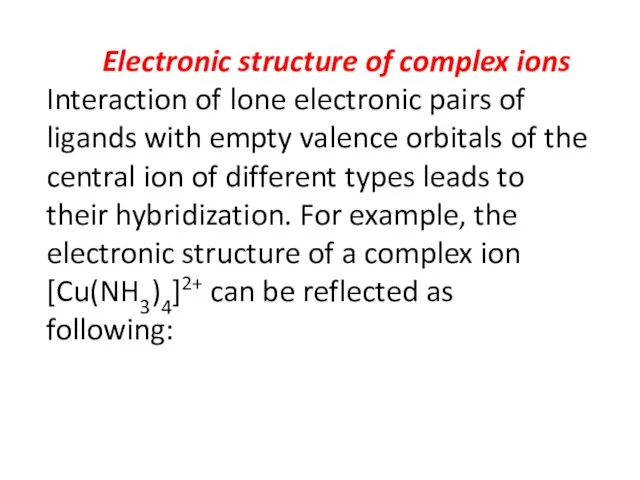
- 30. Electronic structure of complex ions Interaction of lone electronic pairs of ligands with empty valence orbitals
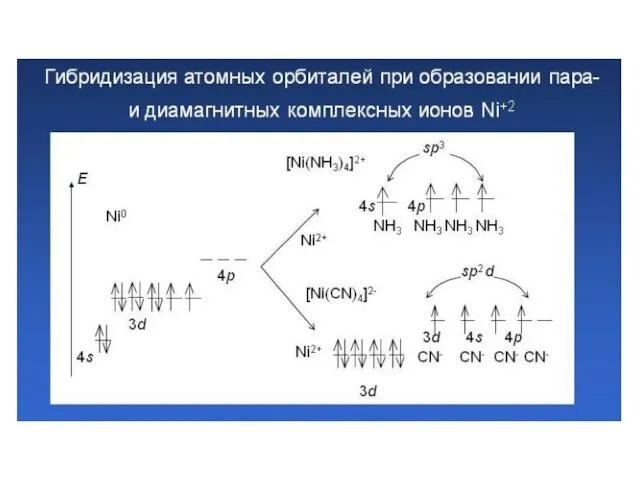
- 34. Возможны октаэдрические комплексы: внутриорбитальные (d2sp3); внешнеорбитальные (sp3d2);
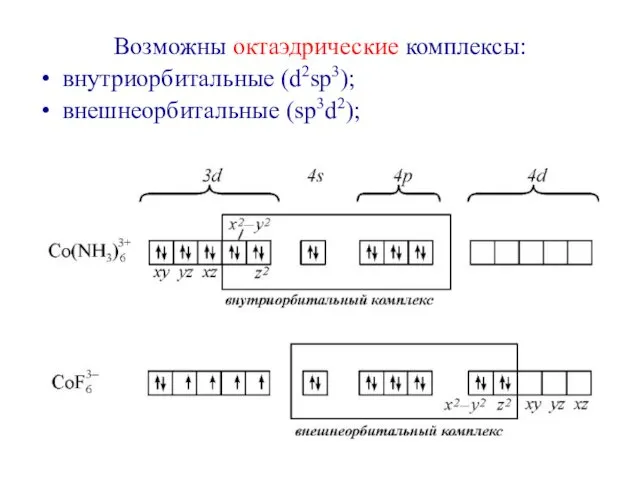
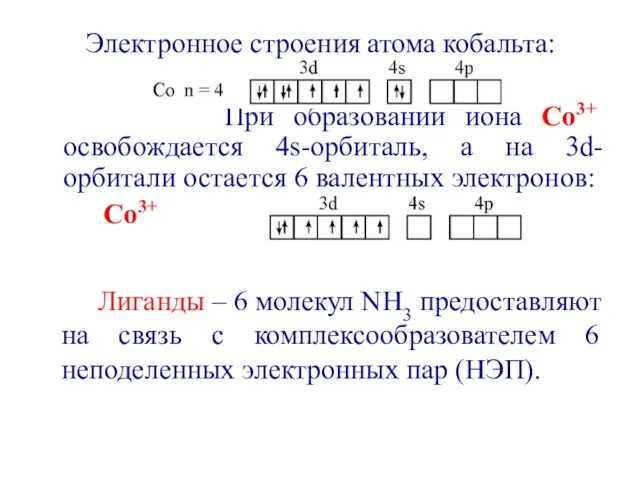
- 35. Электронное строения атома кобальта: При образовании иона Со3+ освобождается 4s-орбиталь, а на 3d-орбитали остается 6 валентных
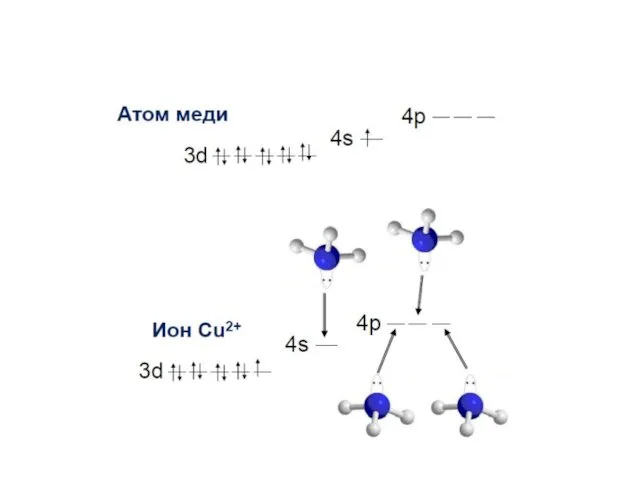
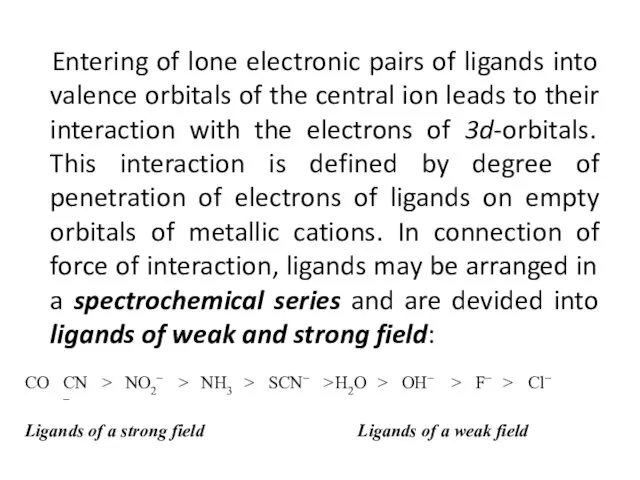
- 36. Entering of lone electronic pairs of ligands into valence orbitals of the central ion leads to
- 37. Все валентные электроны спарены. Комплекс [Co(NH3)6]3+ - диамагнитный, что согласуется с экспериментом.
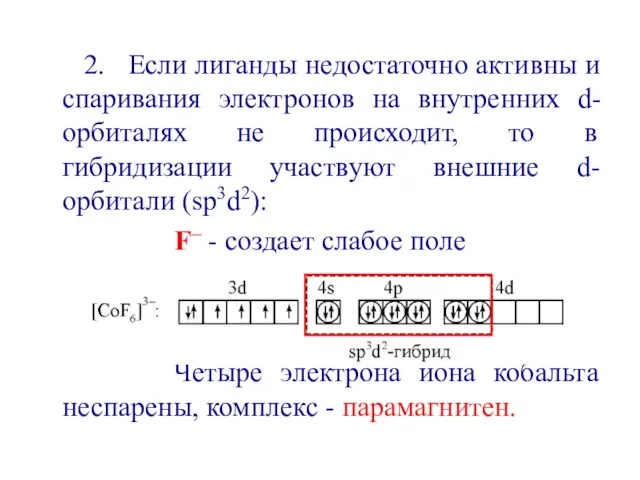
- 38. 2. Если лиганды недостаточно активны и спаривания электронов на внутренних d-орбиталях не происходит, то в гибридизации
- 41. Скачать презентацию







![[Cu(NH3)4]Cl2 – tetraammine copper(II) chloride; K2 [Cu(OH)4] – potassium tetrahydroxocupprate(II); [Cr(NH3)3Cl3] – trichloro triammine chromium(III).](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/103155/slide-11.jpg)









![Все валентные электроны спарены. Комплекс [Co(NH3)6]3+ - диамагнитный, что согласуется с экспериментом.](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/103155/slide-36.jpg)
 Правила роботи на уроці
Правила роботи на уроці Взрывоопасные грузы
Взрывоопасные грузы Инструментальные методы исследования органических веществ
Инструментальные методы исследования органических веществ Обмен нуклеотидов
Обмен нуклеотидов Ауылшаруашылық дақылдарының тұқымдарын фунгецидтермен улау және химиялық қорғау тәсілдерінің биологиялық
Ауылшаруашылық дақылдарының тұқымдарын фунгецидтермен улау және химиялық қорғау тәсілдерінің биологиялық Классификация химических реакций по тепловому эффекту
Классификация химических реакций по тепловому эффекту Кислоты, их классификация и свойства. 8 класс
Кислоты, их классификация и свойства. 8 класс Химиялық жарыс кеші
Химиялық жарыс кеші Основные виды и понятия курса органической химии в старшей школе
Основные виды и понятия курса органической химии в старшей школе Обзор свойств неметаллов.. Окислительно-восстановительные свойства типичных неметаллов
Обзор свойств неметаллов.. Окислительно-восстановительные свойства типичных неметаллов Оборотні і необоротні реакції. Хімічна рівновага
Оборотні і необоротні реакції. Хімічна рівновага Биохимия. Критерии оценки косметических средств. Лекция 4. Индустрия красоты
Биохимия. Критерии оценки косметических средств. Лекция 4. Индустрия красоты Органічні речовини в живій природі. Рівні структурної органшзації
Органічні речовини в живій природі. Рівні структурної органшзації Классификация химических реакций
Классификация химических реакций Характеристика строения и свойств химических элементов
Характеристика строения и свойств химических элементов Оттекті органикалық қосылыстар тақырыбын пәнаралық байланыс арқылы оқыту әдістемесі
Оттекті органикалық қосылыстар тақырыбын пәнаралық байланыс арқылы оқыту әдістемесі Производство полимеров
Производство полимеров Химические свойства альдегидов
Химические свойства альдегидов Алкины. Характеристика тройной связи
Алкины. Характеристика тройной связи Биохимия
Биохимия Галогены. 9 класс
Галогены. 9 класс Производство синтетической нефти
Производство синтетической нефти Пниктогены элеметны VA группы
Пниктогены элеметны VA группы Сложные эфиры. Жиры
Сложные эфиры. Жиры Побочная подгруппа 1 и 2. Медь
Побочная подгруппа 1 и 2. Медь Способы выражения состава растворов
Способы выражения состава растворов Кислородсодержащие соединения. Тема 1: спирты
Кислородсодержащие соединения. Тема 1: спирты Амины. Номенклатура аминов
Амины. Номенклатура аминов