Содержание
- 3. Essential amino acids valine, leucine, isoleucine, lysine, methionine, threonine, tryptophan, phenylalanine Semi-essential amino acids arginine and
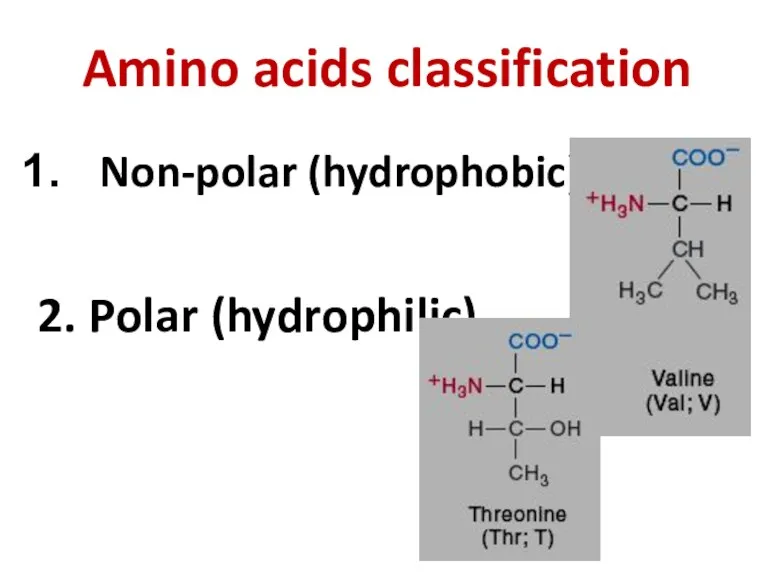
- 4. Amino acids classification Non-polar (hydrophobic) 2. Polar (hydrophilic)
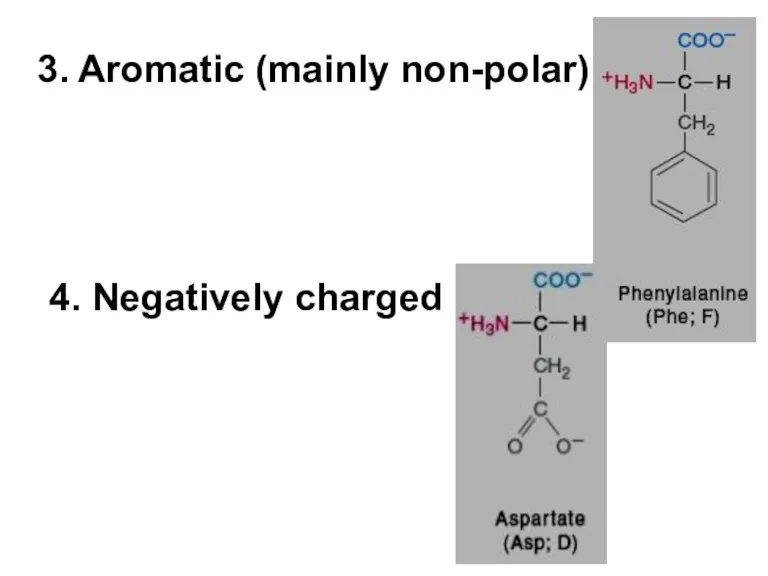
- 5. 3. Aromatic (mainly non-polar) 4. Negatively charged
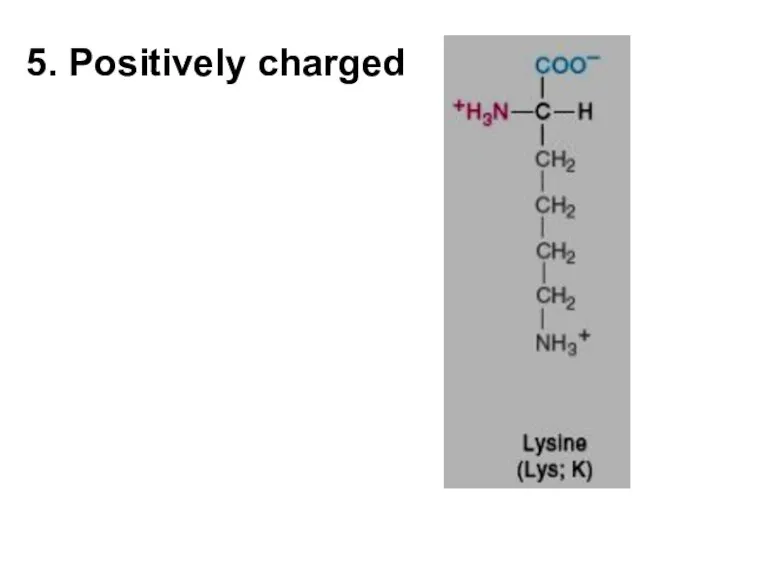
- 6. 5. Positively charged
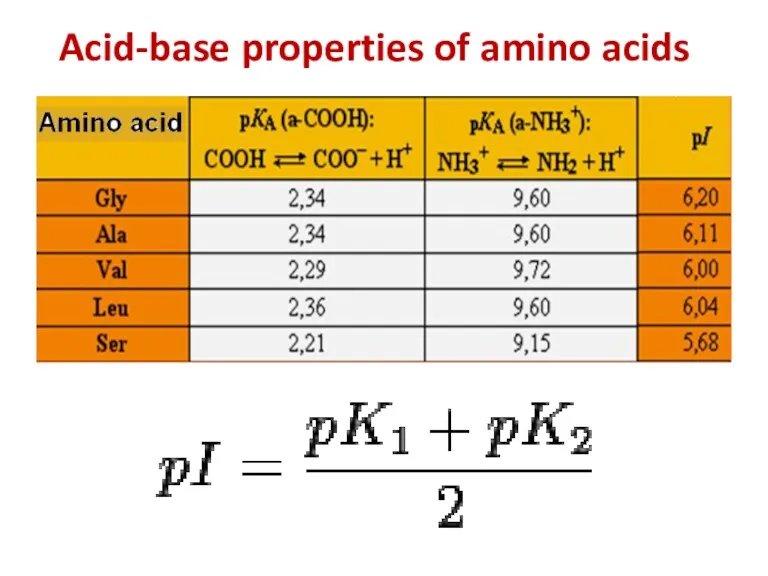
- 7. Acid-base properties of amino acids
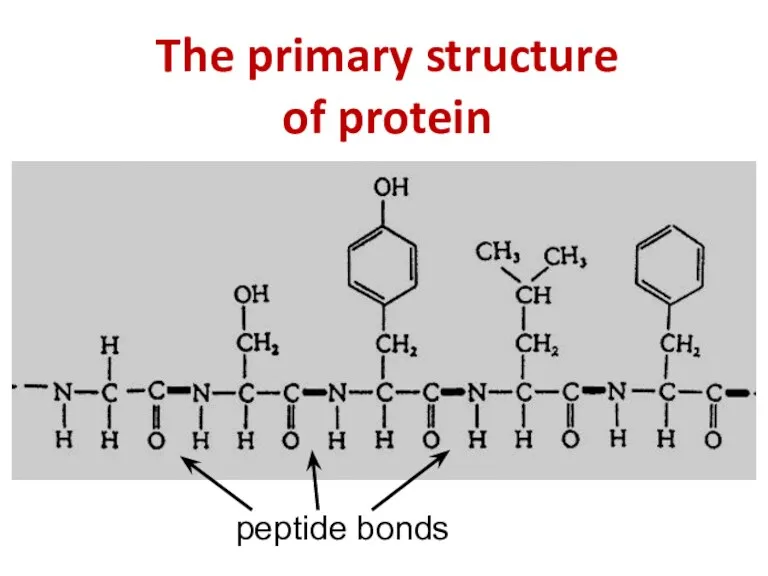
- 8. The primary structure of protein peptide bonds
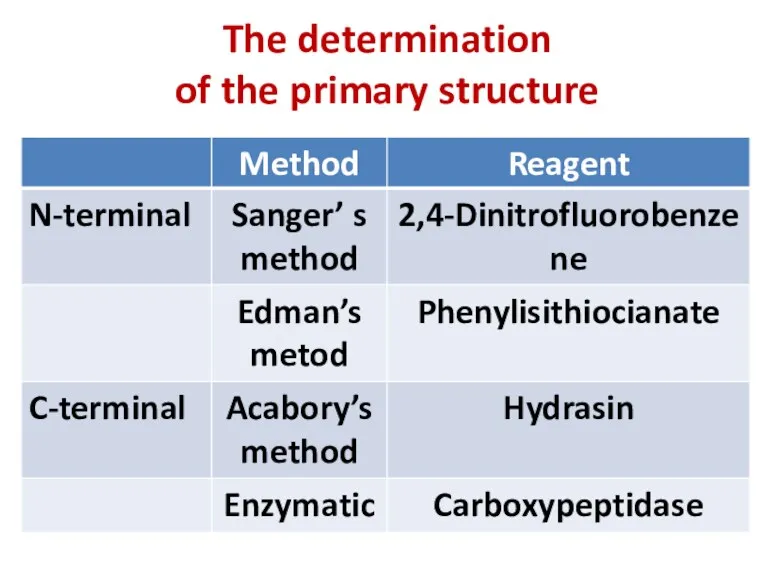
- 9. The determination of the primary structure
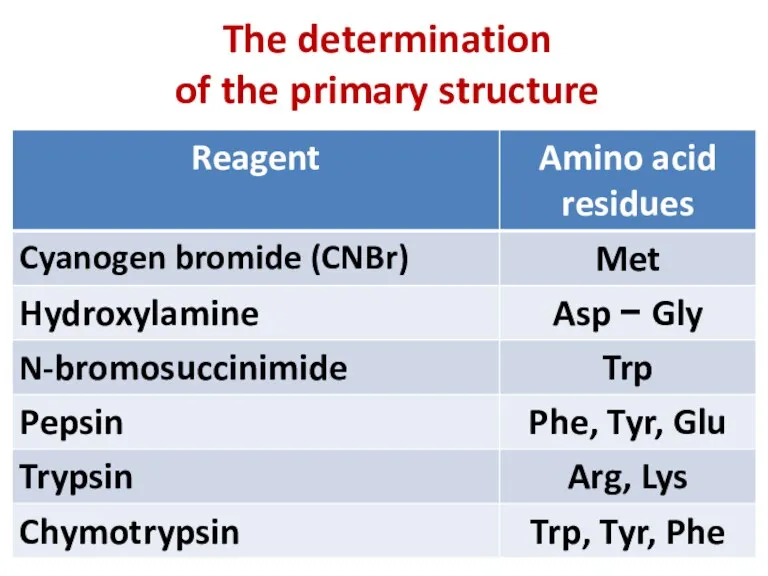
- 10. The determination of the primary structure
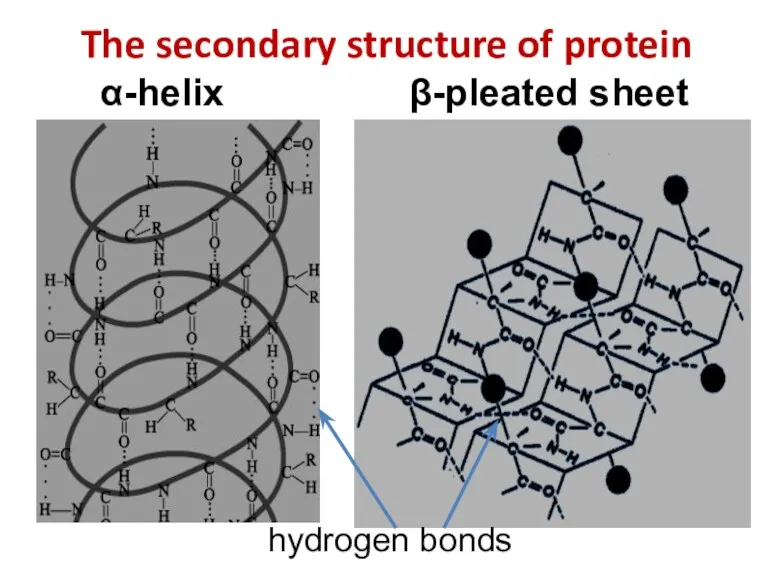
- 11. The secondary structure of protein α-helix β-pleated sheet hydrogen bonds
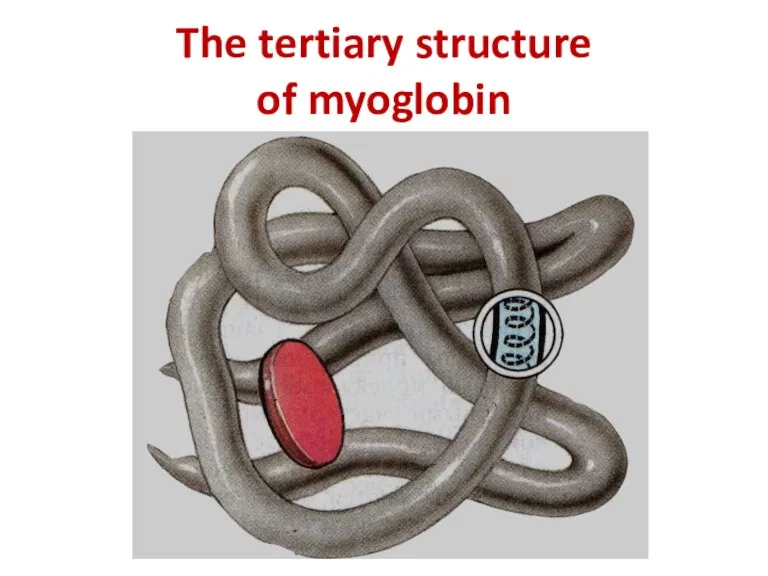
- 12. The tertiary structure of myoglobin
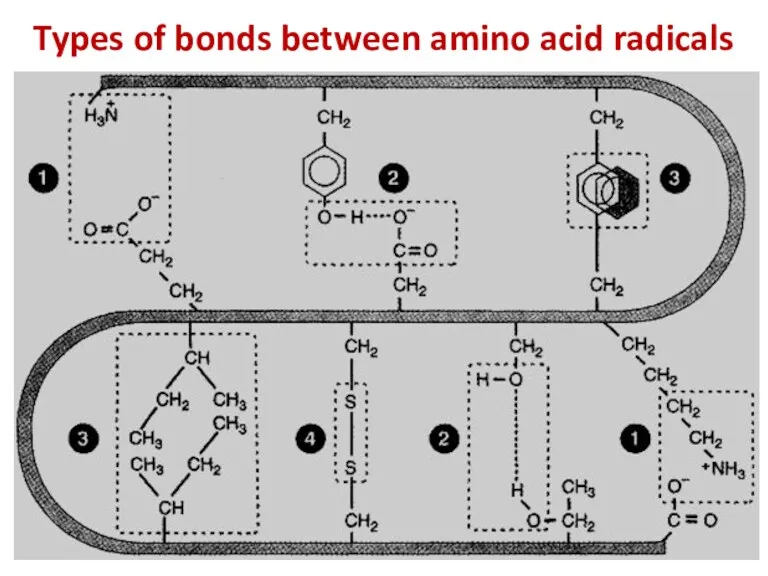
- 13. Types of bonds between amino acid radicals
- 14. Chaperone
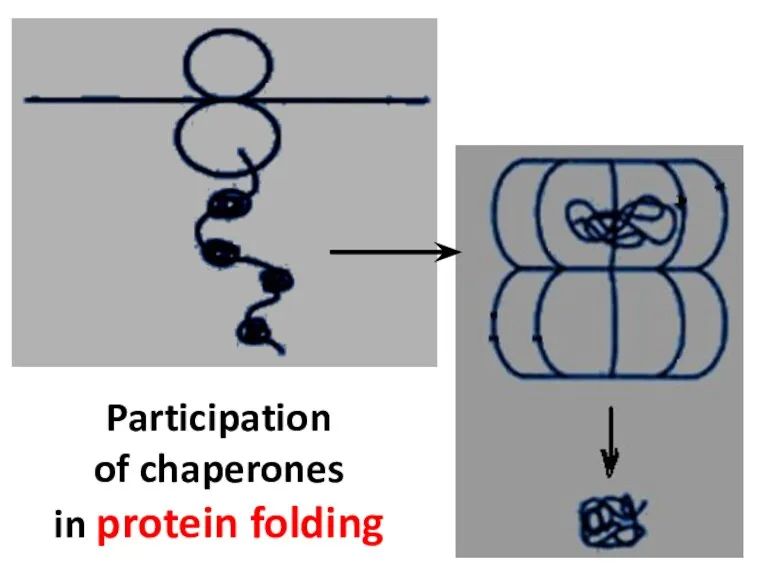
- 15. Participation of chaperones in protein folding
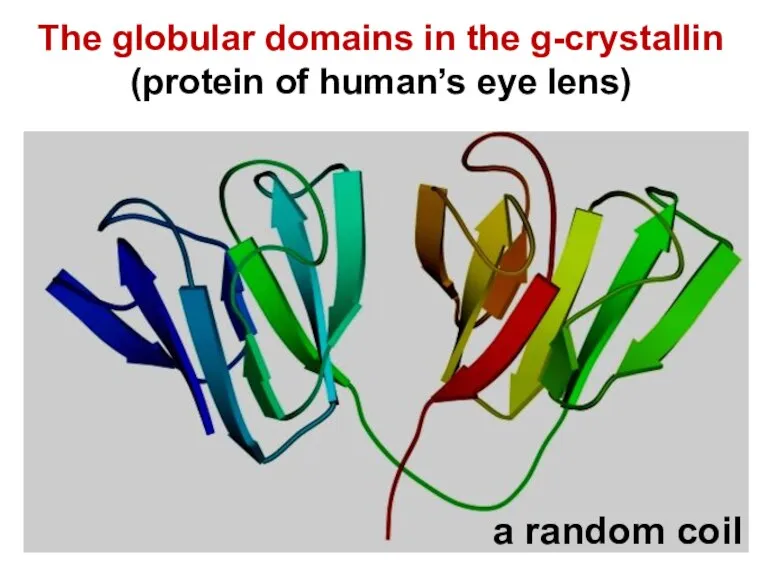
- 16. The globular domains in the g-crystallin (protein of human’s eye lens) a random coil
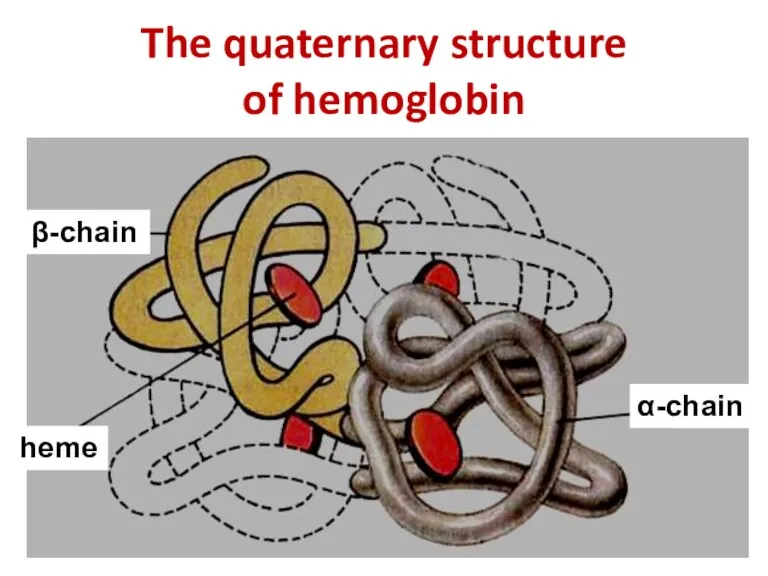
- 17. The quaternary structure of hemoglobin α-chain β-chain heme
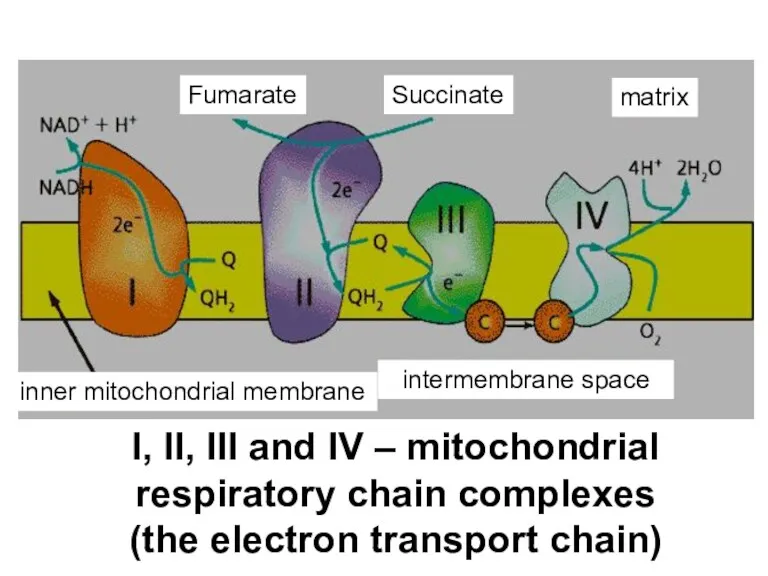
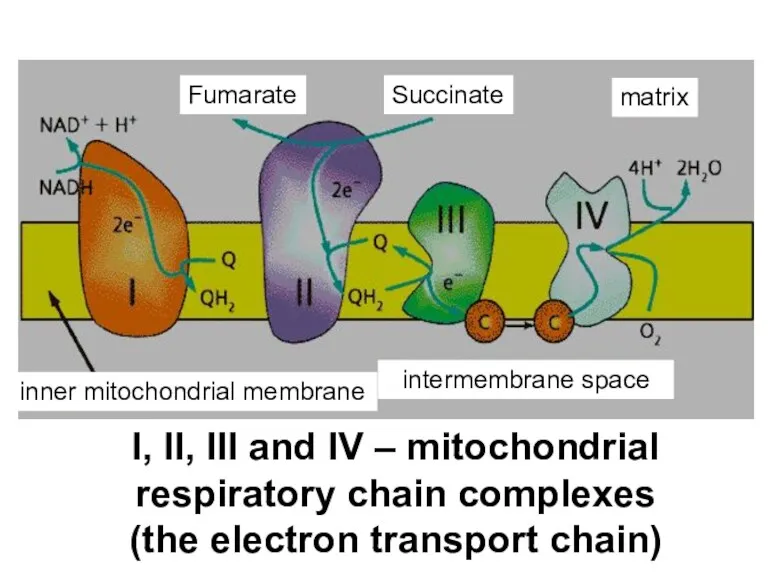
- 18. I, II, III and IV – mitochondrial respiratory chain complexes (the electron transport chain) Fumarate Succinate
- 19. Classification of proteins Simple proteins
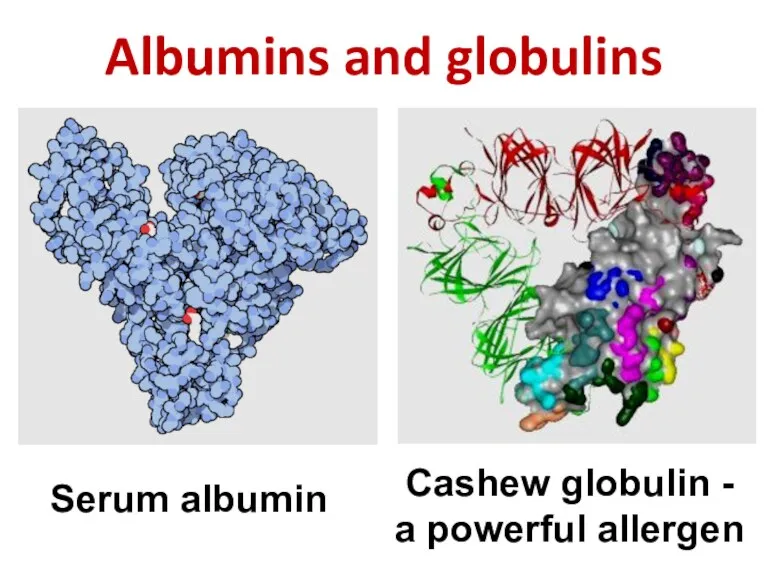
- 20. Albumins and globulins Serum albumin Cashew globulin - a powerful allergen
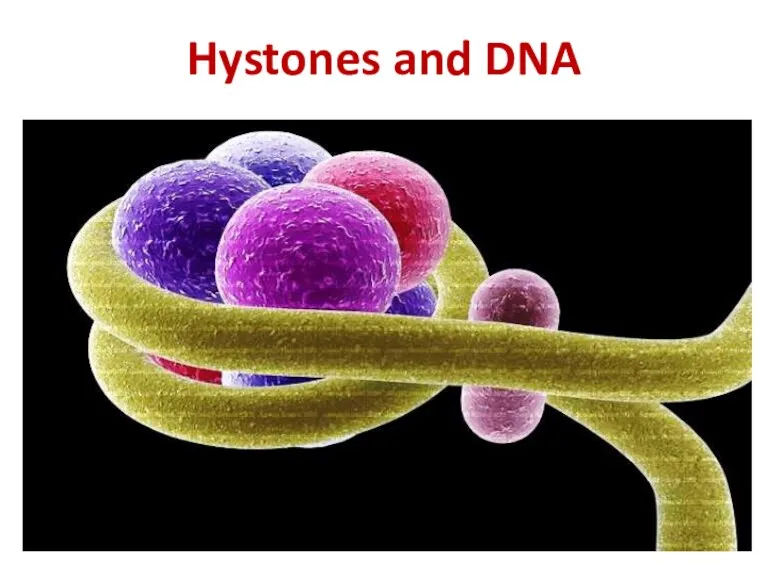
- 21. Hystones and DNA
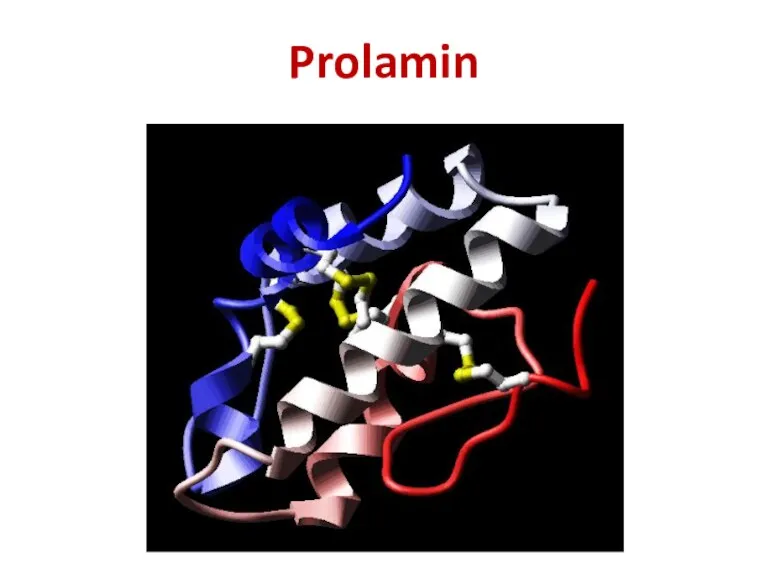
- 22. Prolamin
- 23. Conjugative proteins
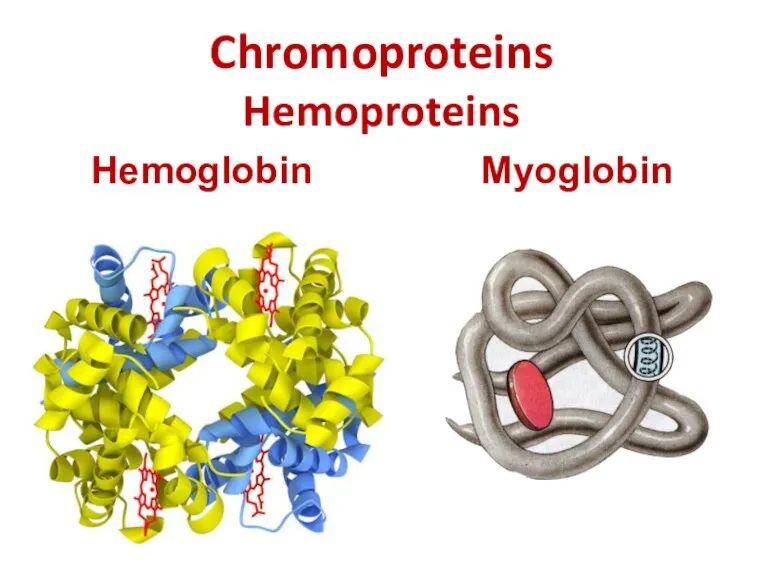
- 24. Chromoproteins Hemoproteins Hemoglobin Myoglobin
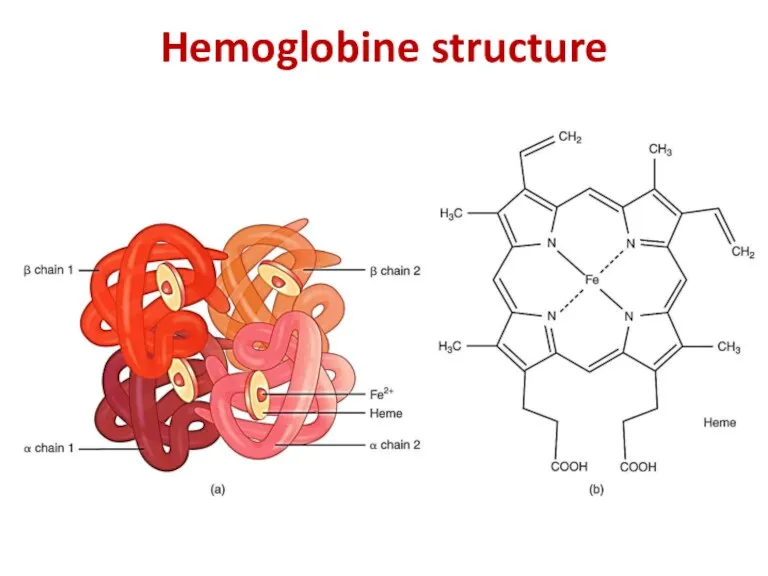
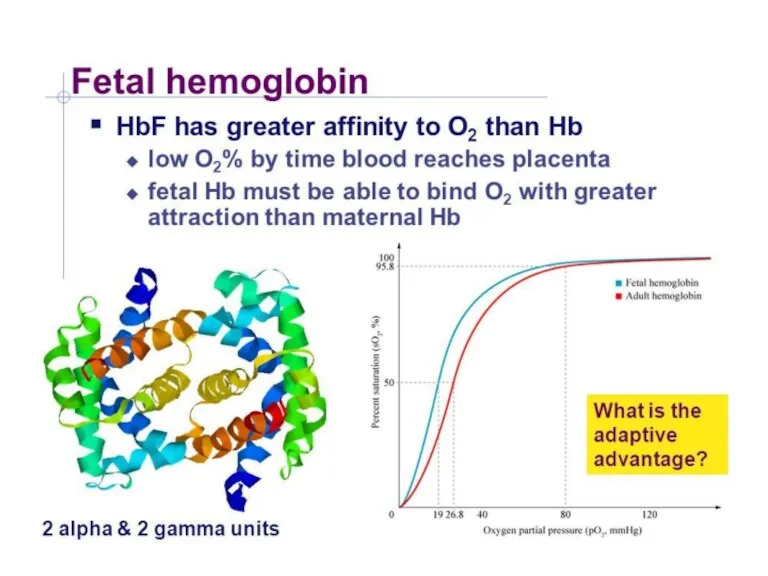
- 25. Hemoglobine structure
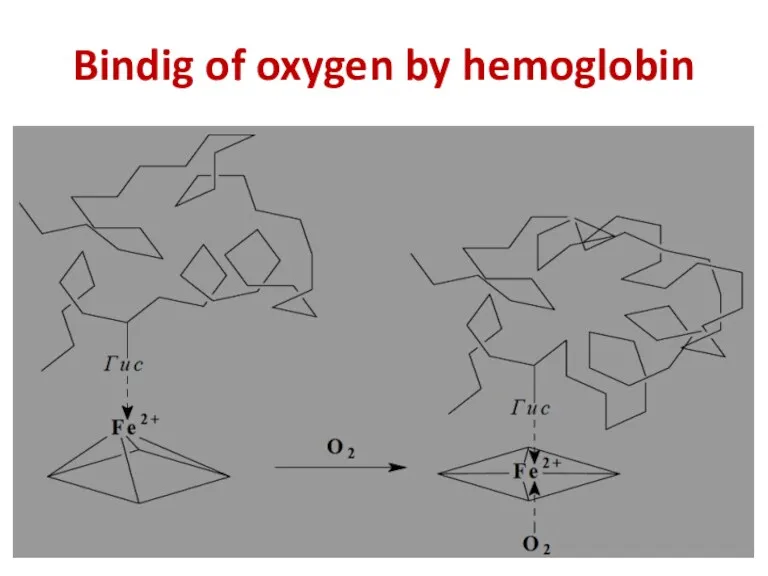
- 26. Bindig of oxygen by hemoglobin
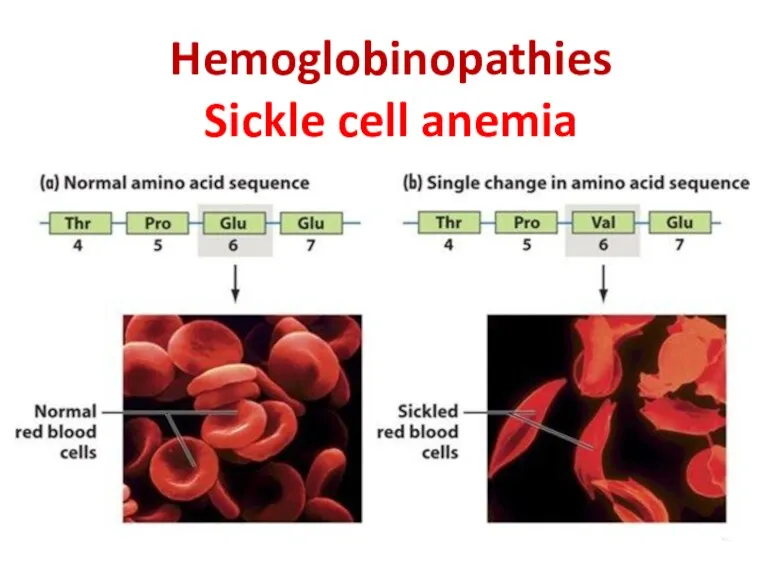
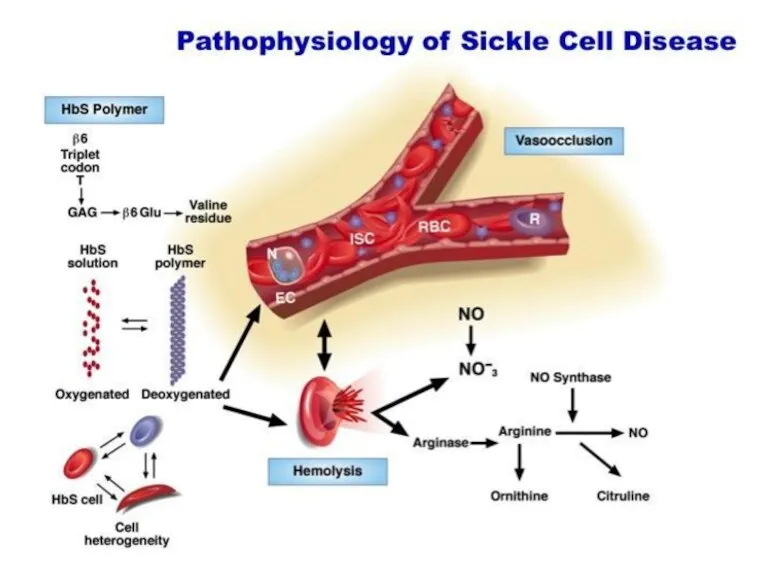
- 28. Hemoglobinopathies Sickle cell anemia
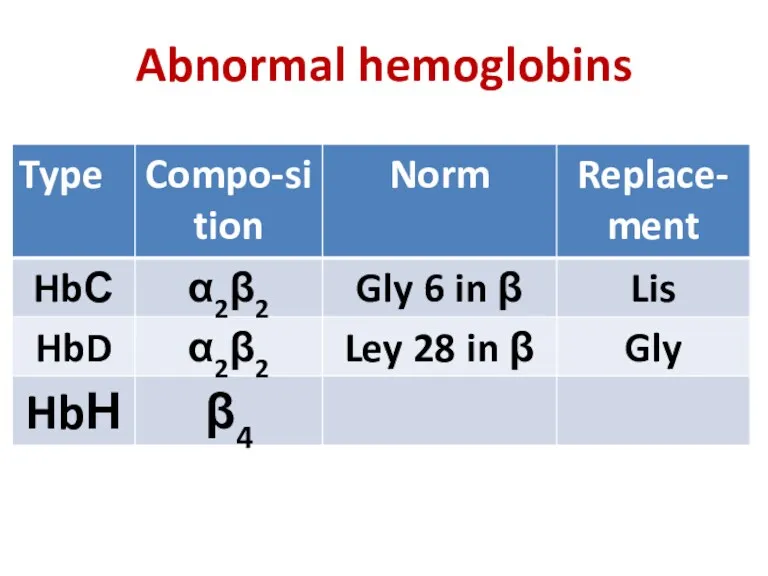
- 30. Abnormal hemoglobins
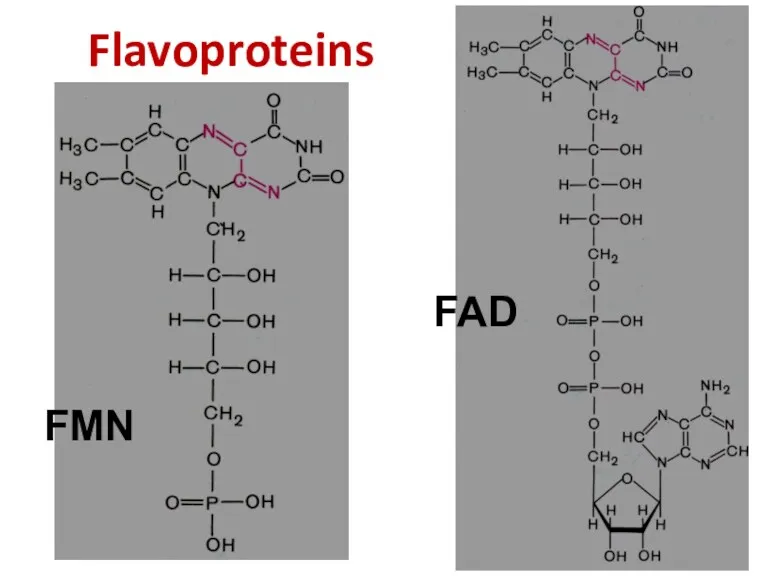
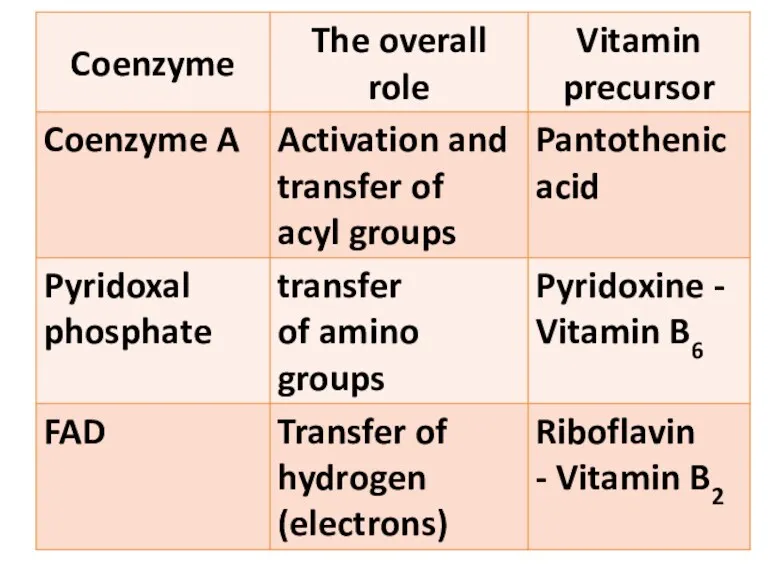
- 31. Flavoproteins FMN FAD
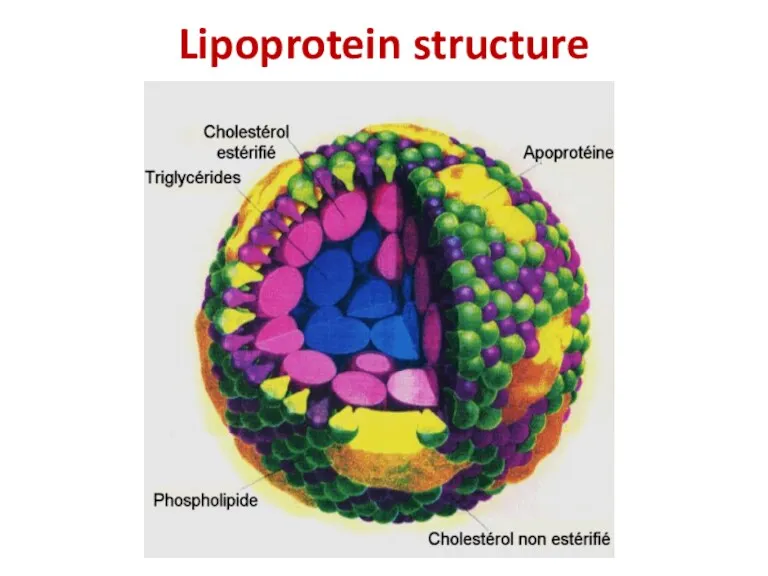
- 32. Lipoprotein structure
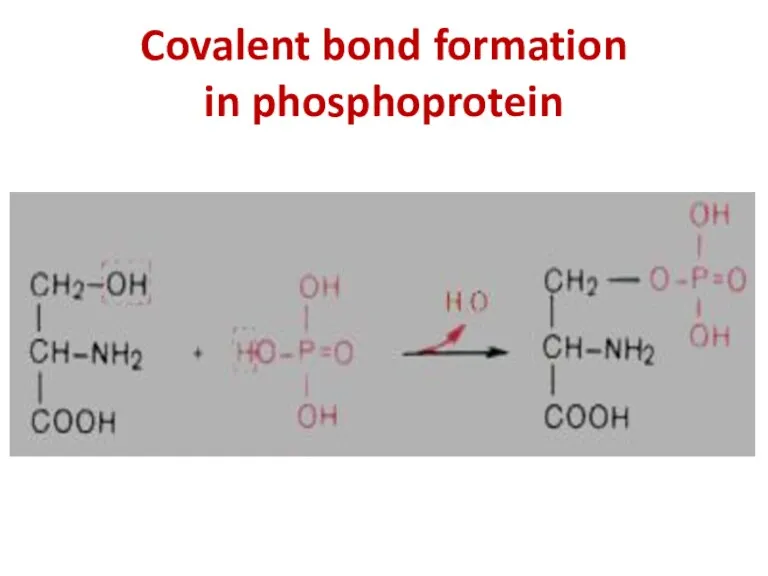
- 33. Covalent bond formation in phosphoprotein
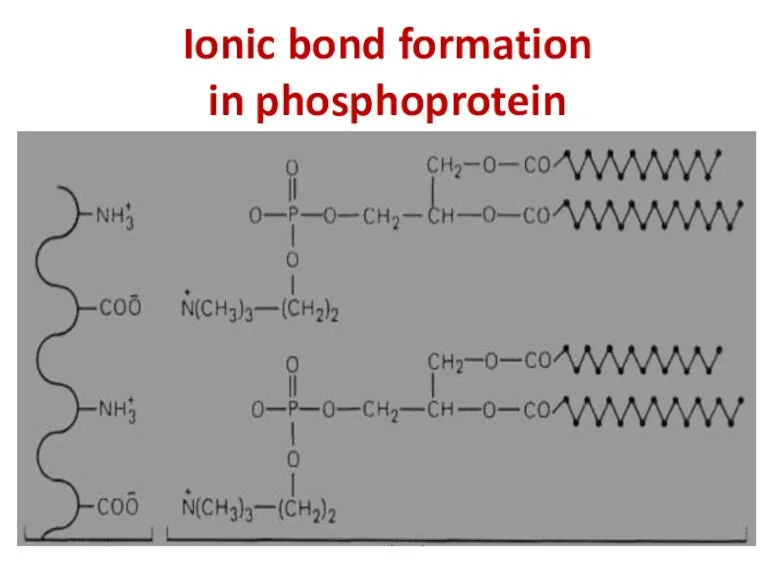
- 34. Ionic bond formation in phosphoprotein
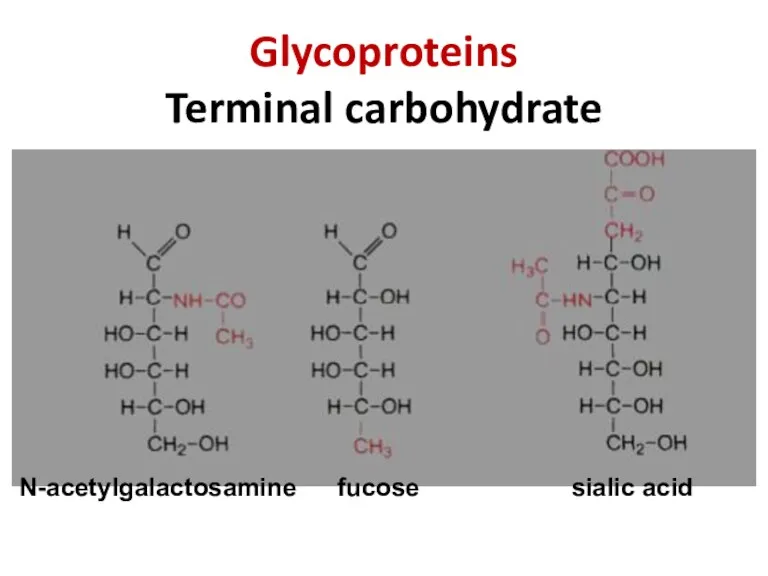
- 35. Glycoproteins Terminal carbohydrate N-acetylgalactosamine fucose sialic acid
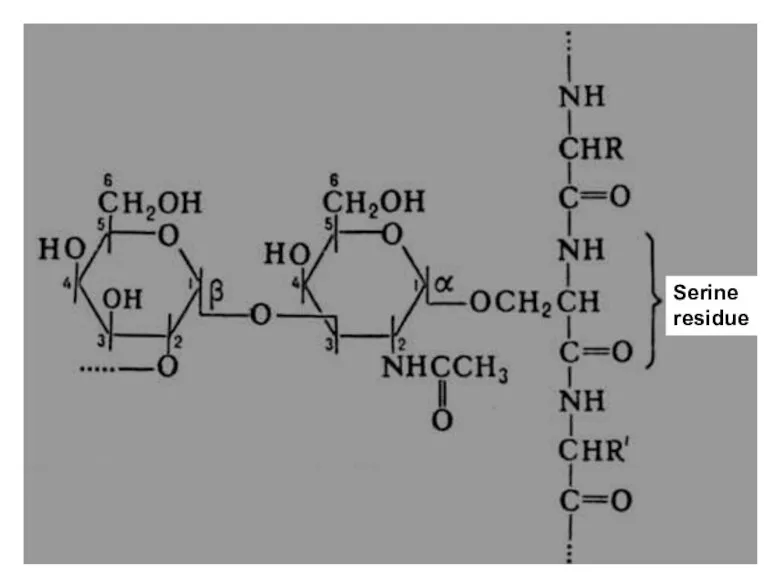
- 36. Bond formation in glycoproteins Serine residue
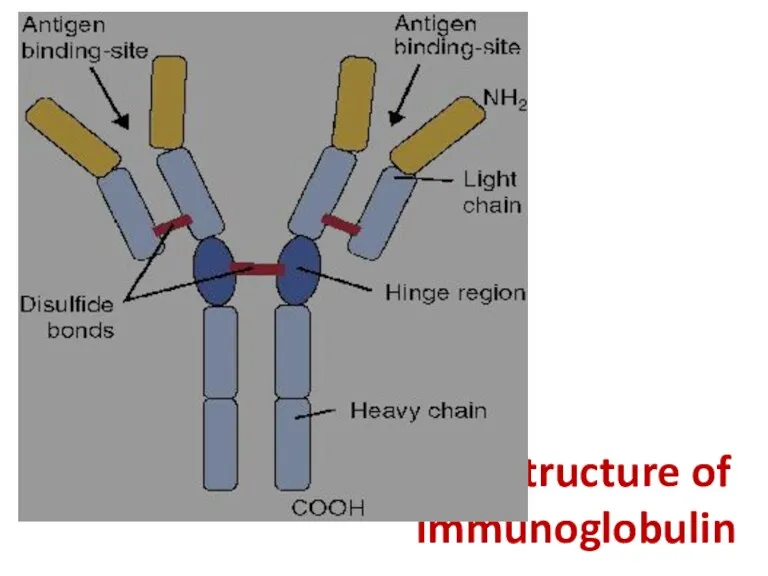
- 37. The structure of immunoglobulin
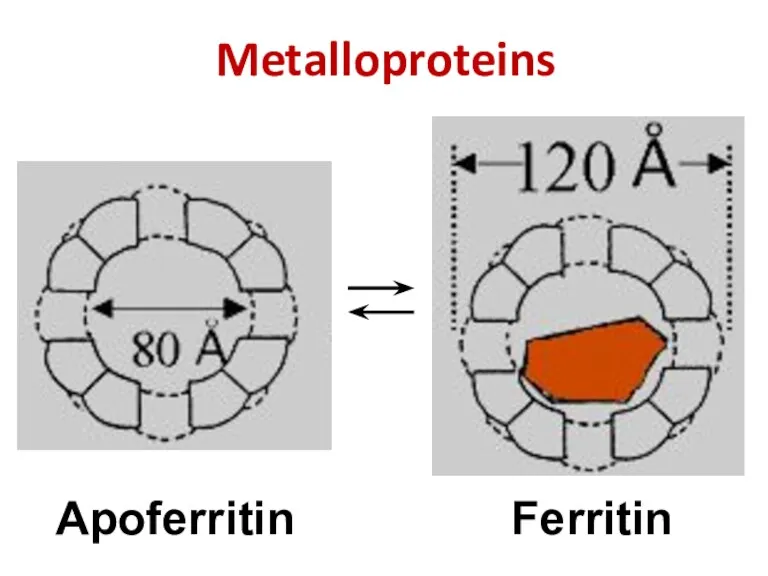
- 38. Metalloproteins Ferritin Apoferritin
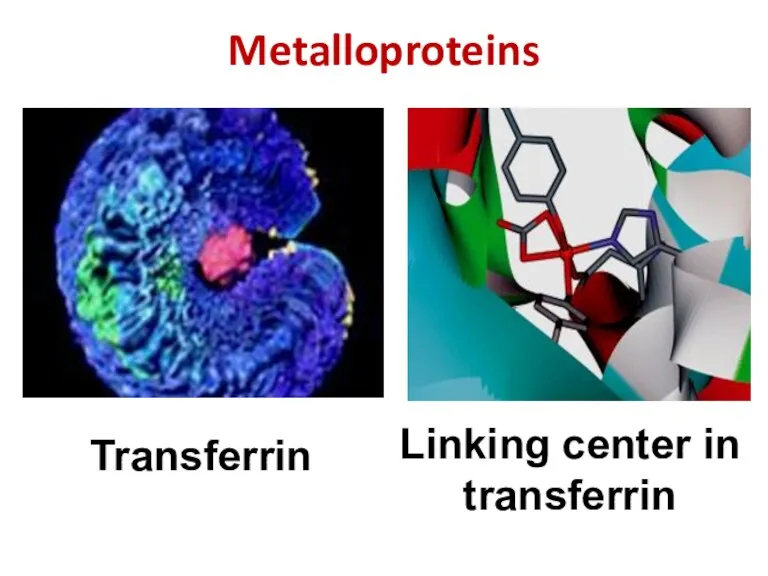
- 39. Metalloproteins Transferrin Linking center in transferrin
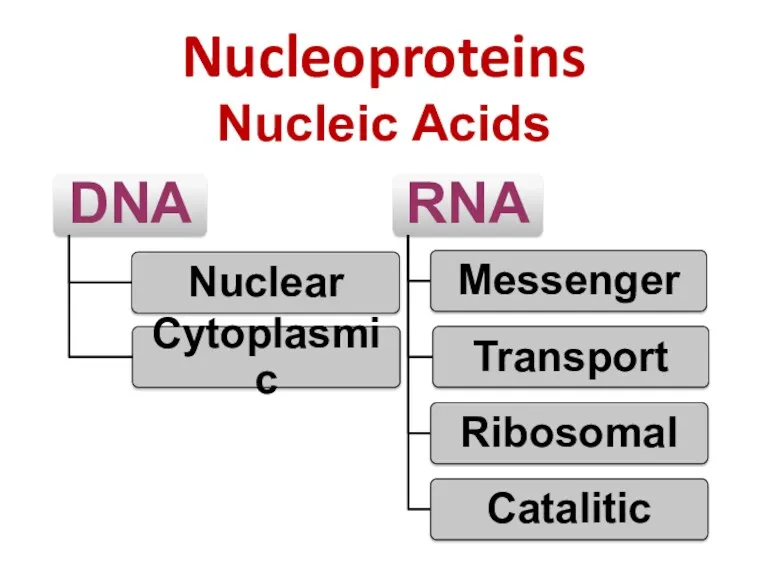
- 40. Nucleoproteins Nucleic Acids
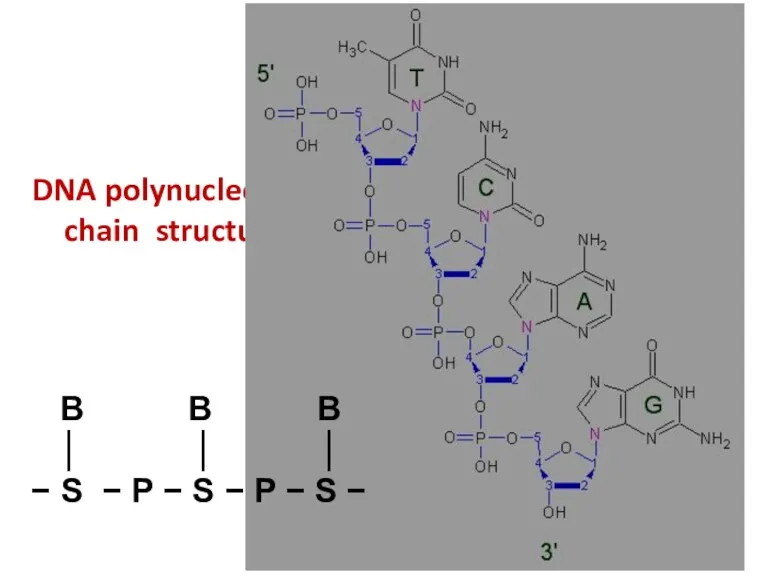
- 41. DNA polynucleotide chain structure B B B │ │ │ − S − P − S
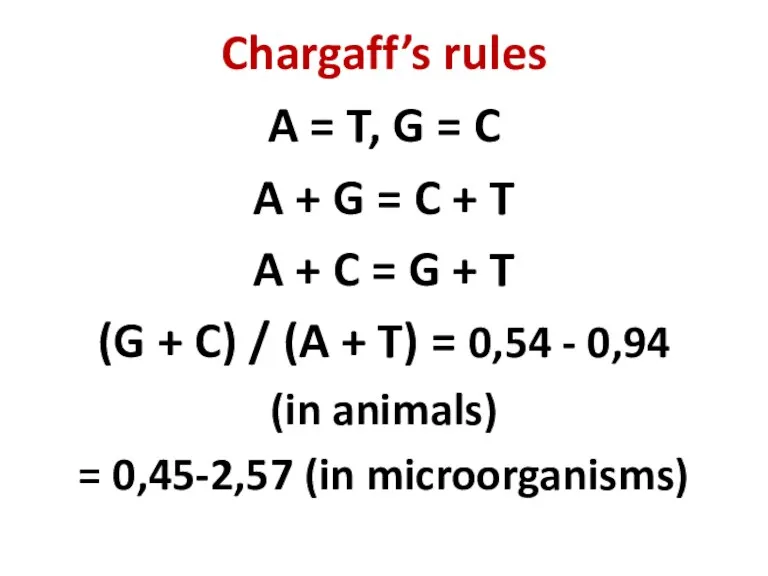
- 42. Chargaff’s rules A = T, G = C A + G = C + T A
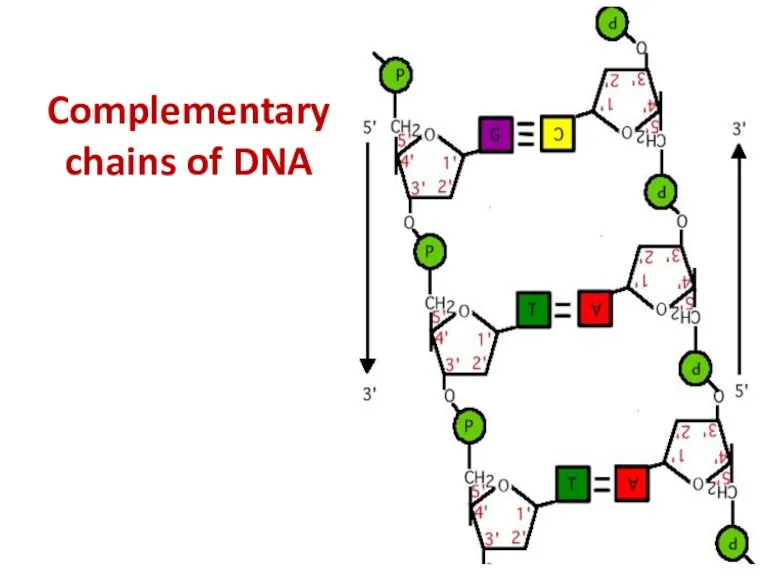
- 43. Complementary chains of DNA
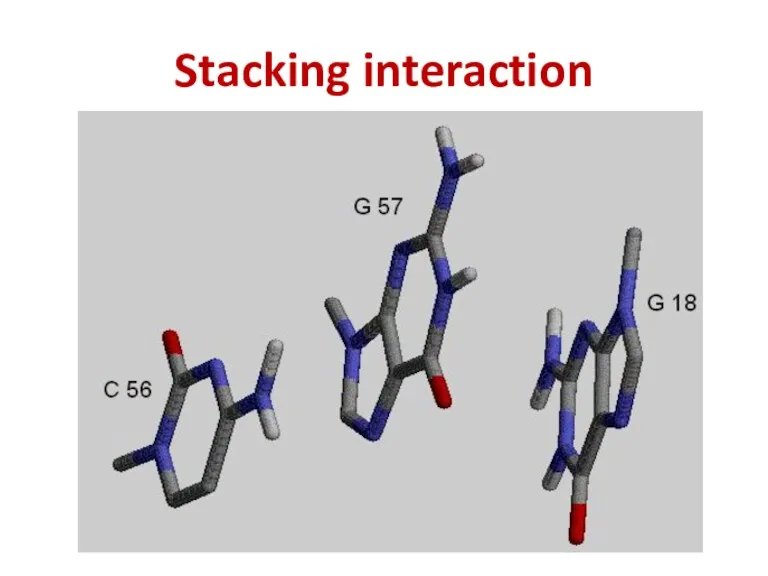
- 44. Stacking interaction
- 45. The intensity of stacking Purine – Purine > > Pyrimidine – Purine > > Pyrimidine –
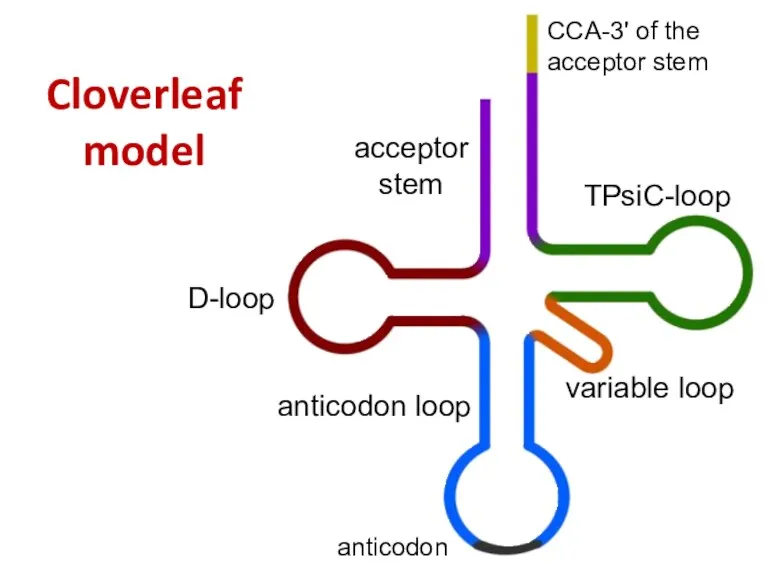
- 46. Cloverleaf model acceptor stem D-loop anticodon loop variable loop TPsiC-loop CCA-3' of the acceptor stem anticodon
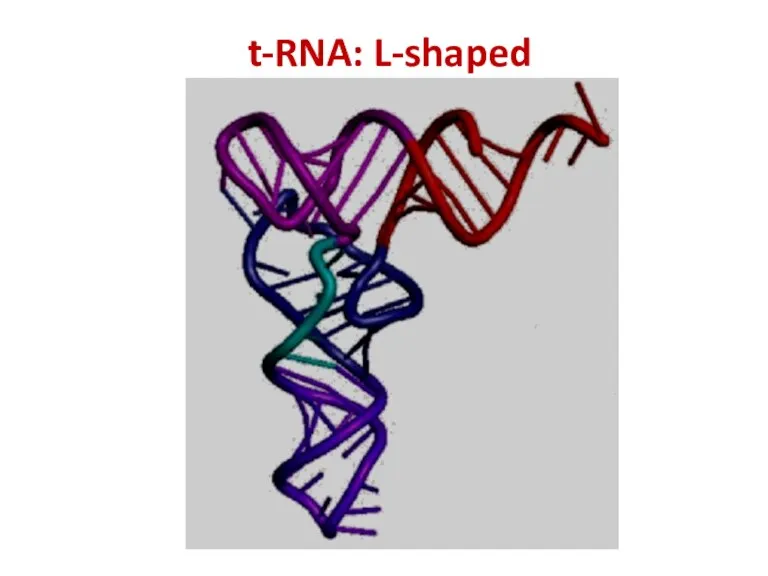
- 47. t-RNA: L-shaped
- 48. Вiochemistry of enzymes
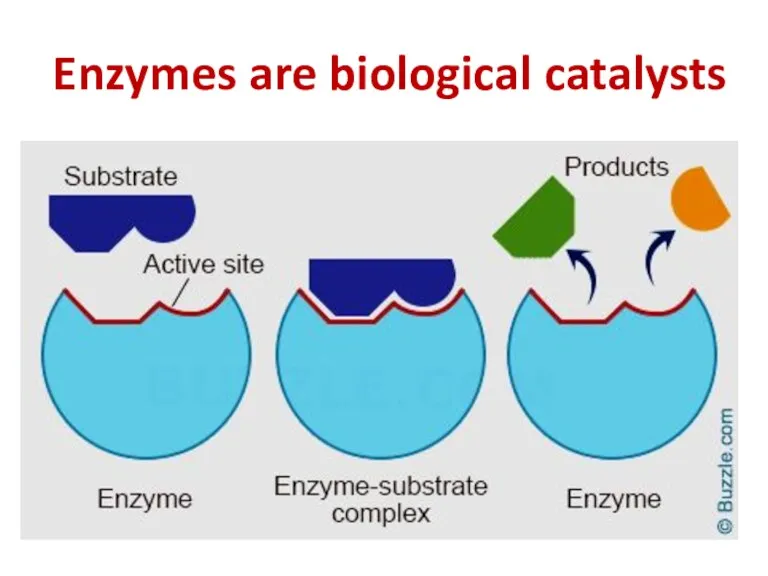
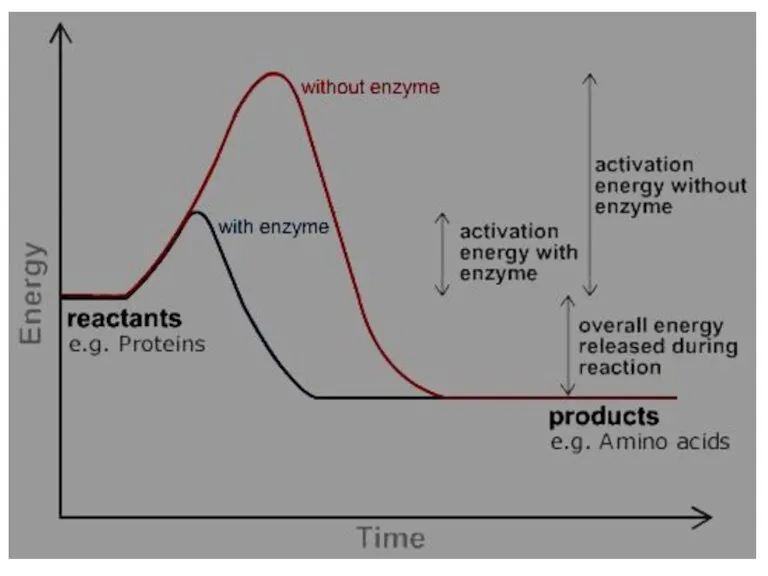
- 49. Enzymes are biological catalysts
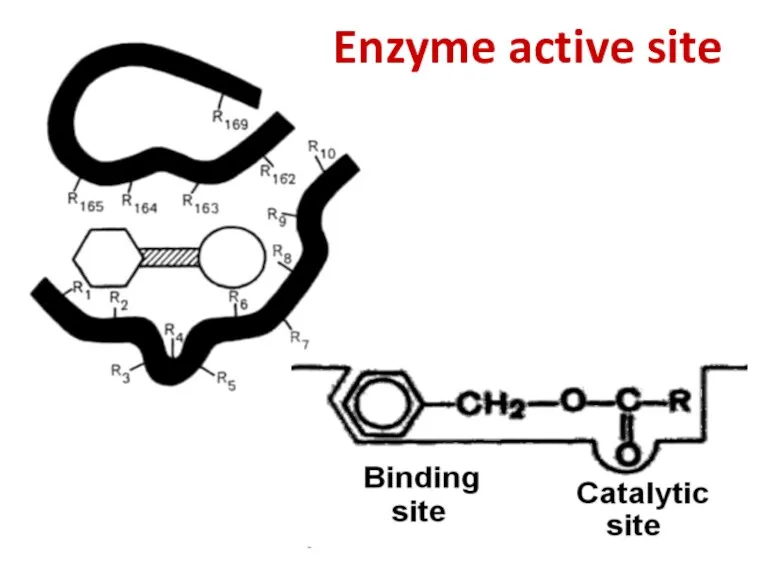
- 50. Enzyme active site
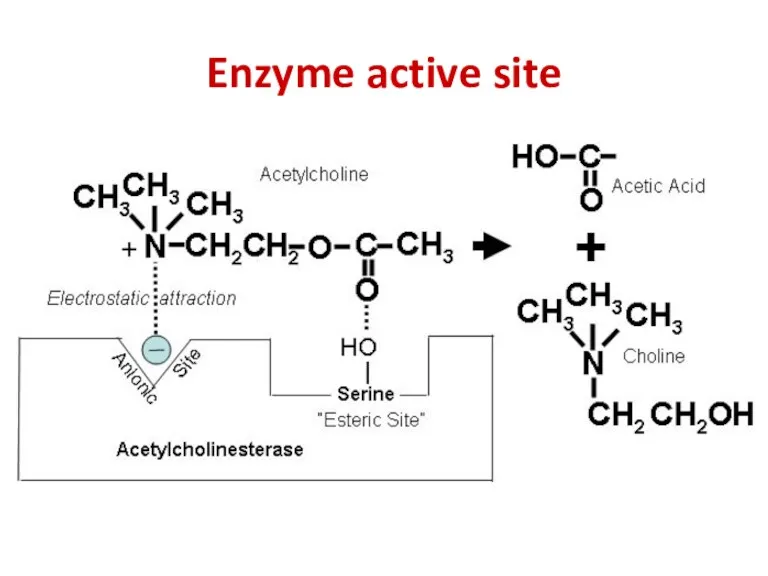
- 51. Enzyme active site
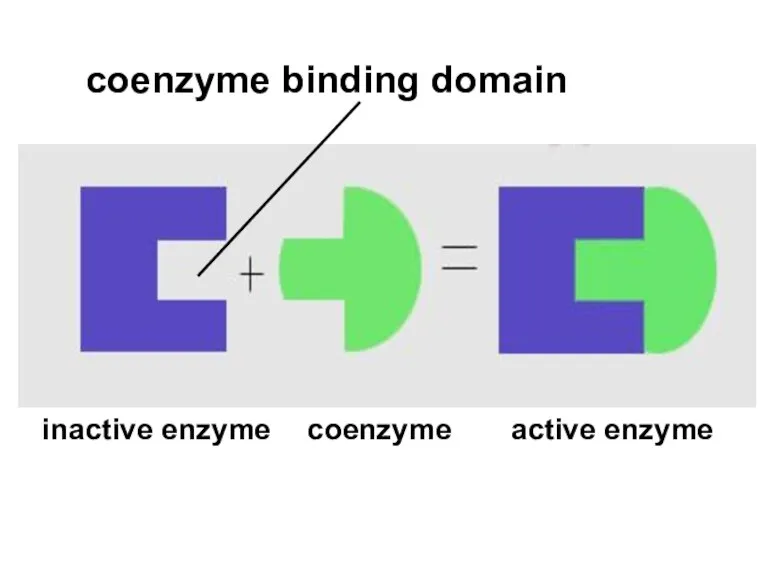
- 52. coenzyme binding domain inactive enzyme active enzyme coenzyme
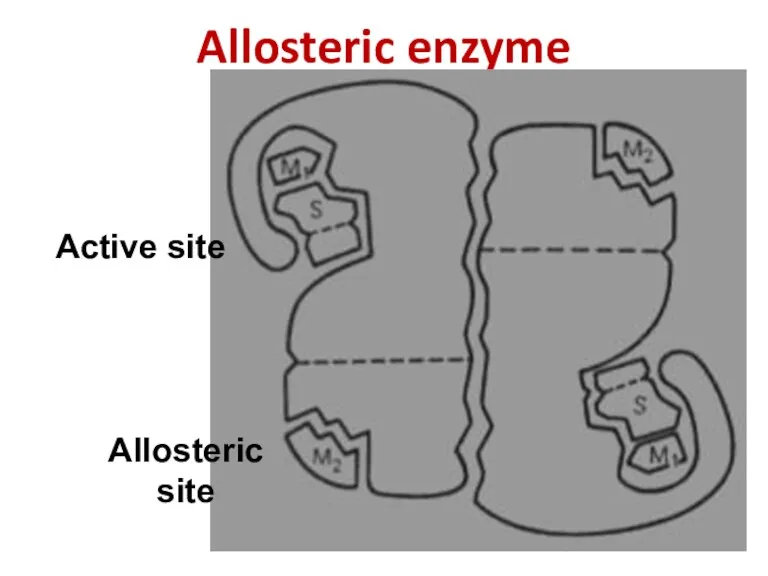
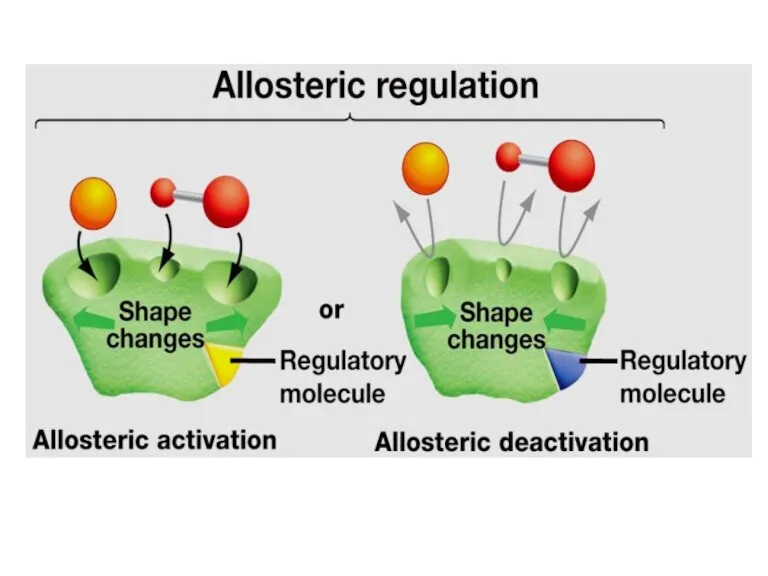
- 54. Allosteric enzyme Active site Allosteric site
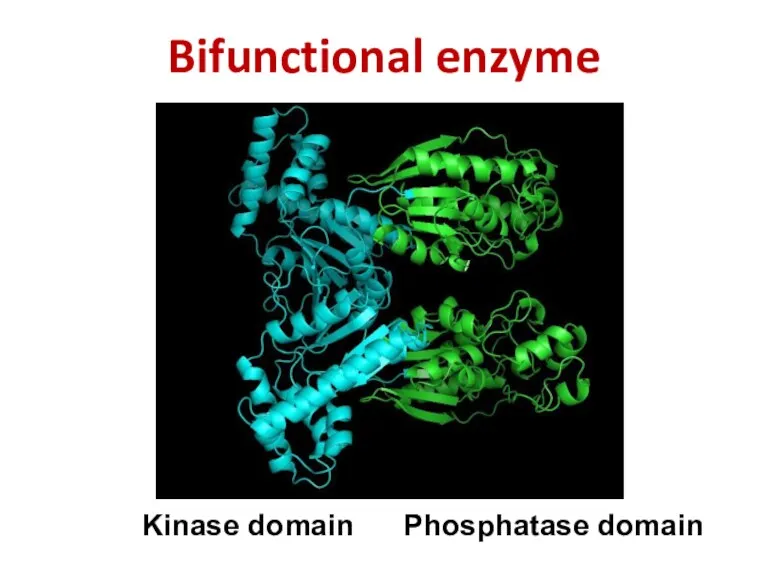
- 55. Bifunctional enzyme Kinase domain Phosphatase domain
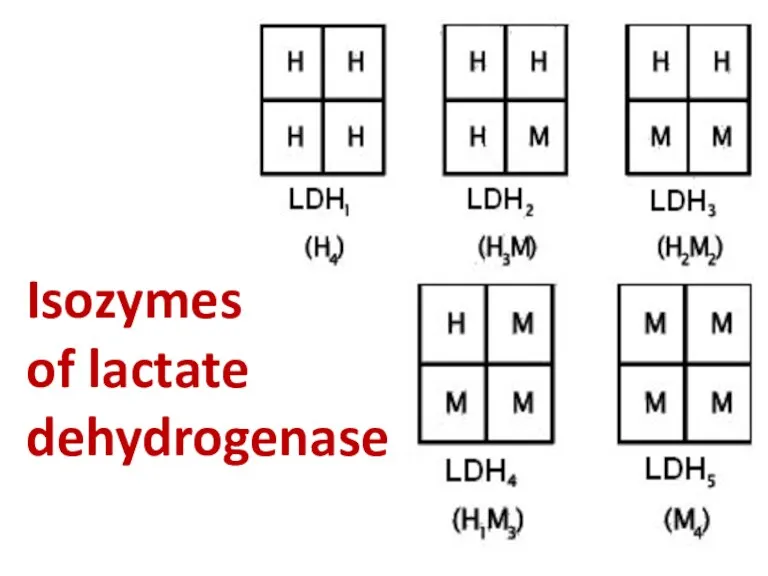
- 56. Isozymes of lactate dehydrogenase
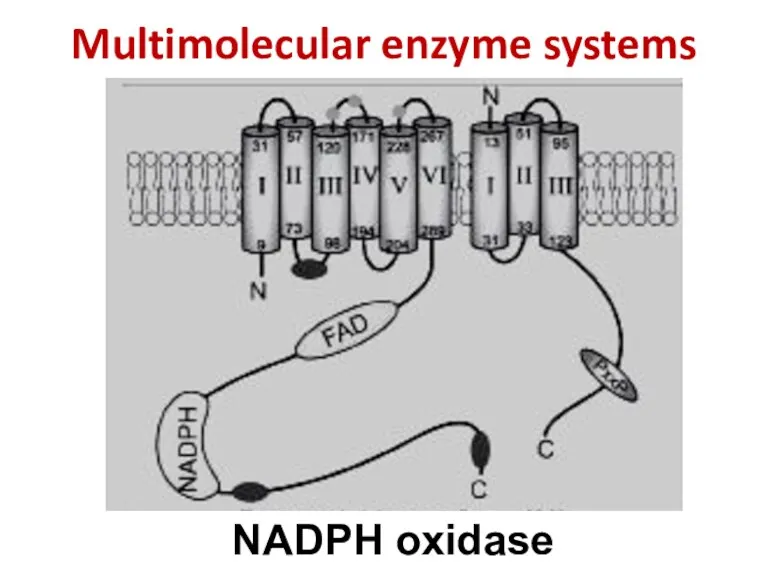
- 57. Multimolecular enzyme systems NADPH oxidase
- 58. I, II, III and IV – mitochondrial respiratory chain complexes (the electron transport chain) Fumarate Succinate
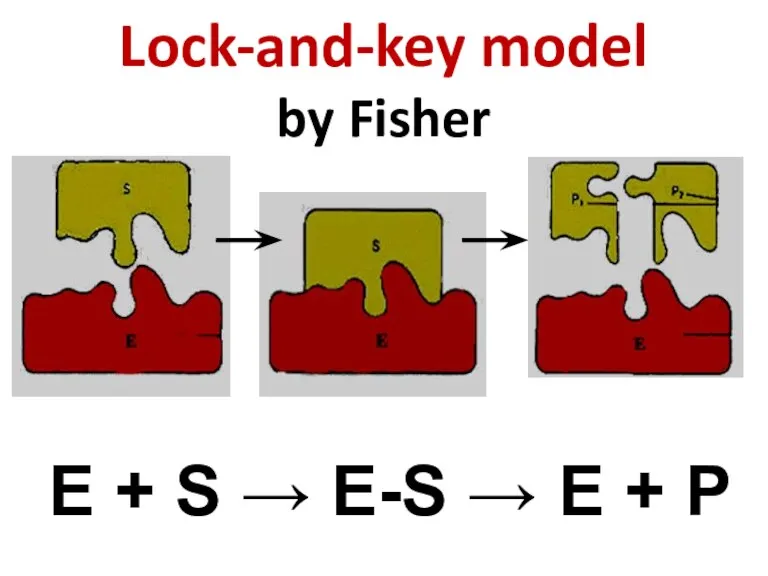
- 59. Hermann Emil Fischer (1852 - 1919)
- 60. Lock-and-key model by Fisher E + S → E-S → E + P
- 61. Daniel Koshland (1920 - 2007)
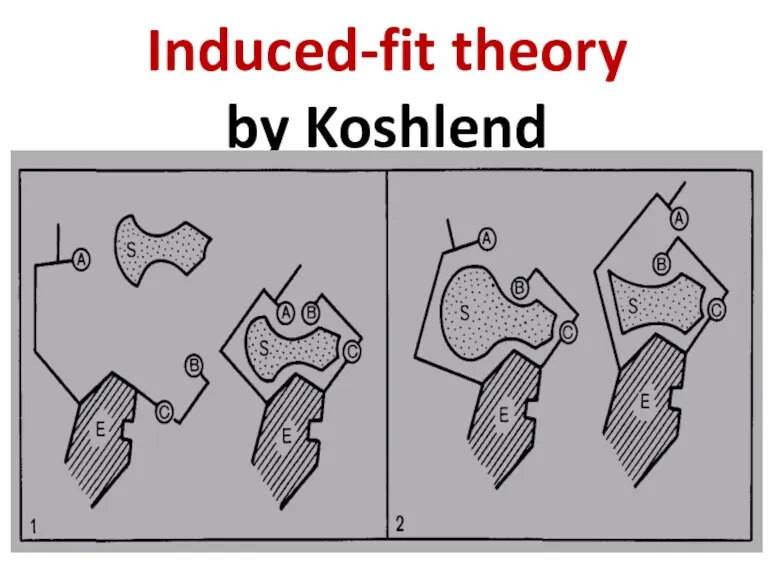
- 62. Induced-fit theory by Koshlend
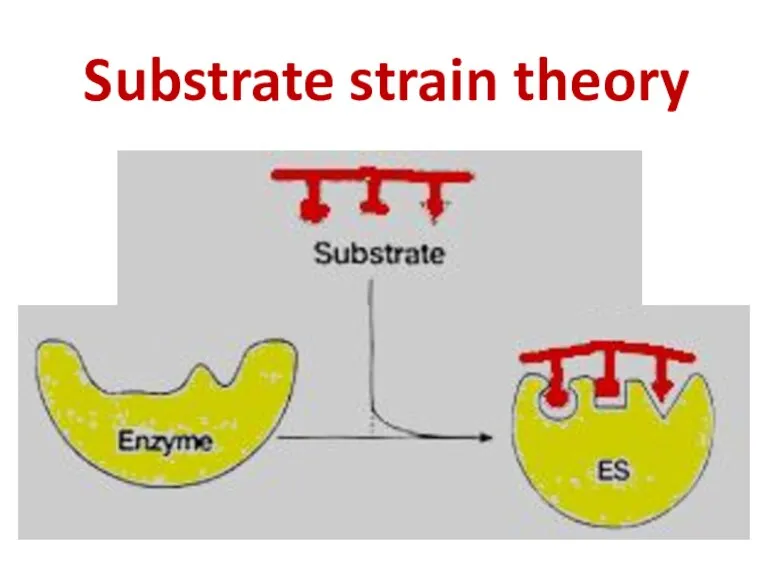
- 63. Substrate strain theory
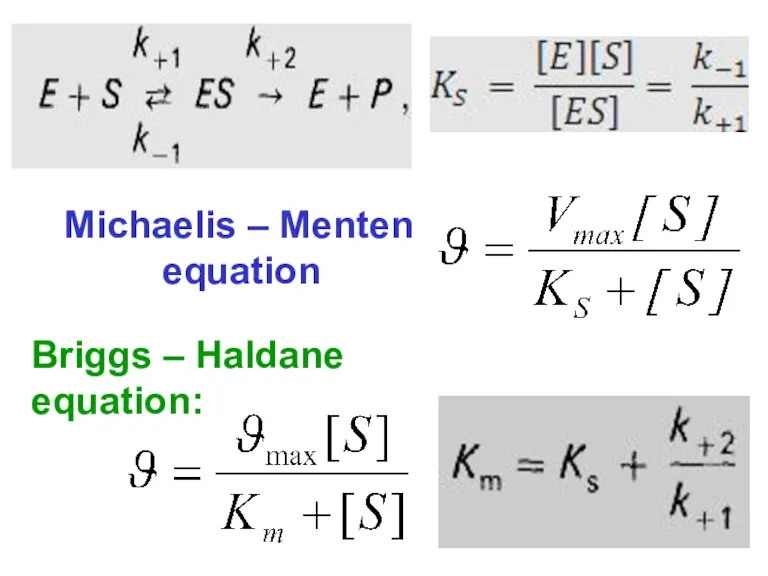
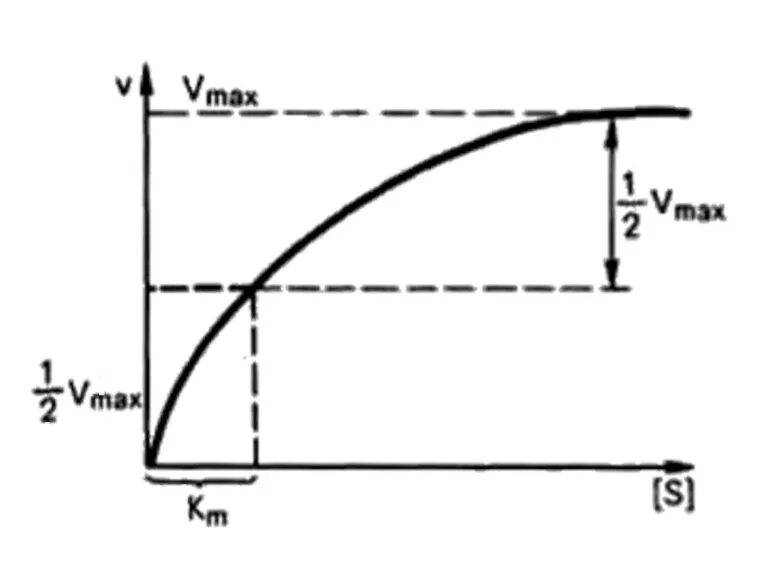
- 65. Leonor Michaelis Maud Leonora Menten Enzyme kinetics
- 66. Michaelis – Menten equation Briggs – Haldane equation:
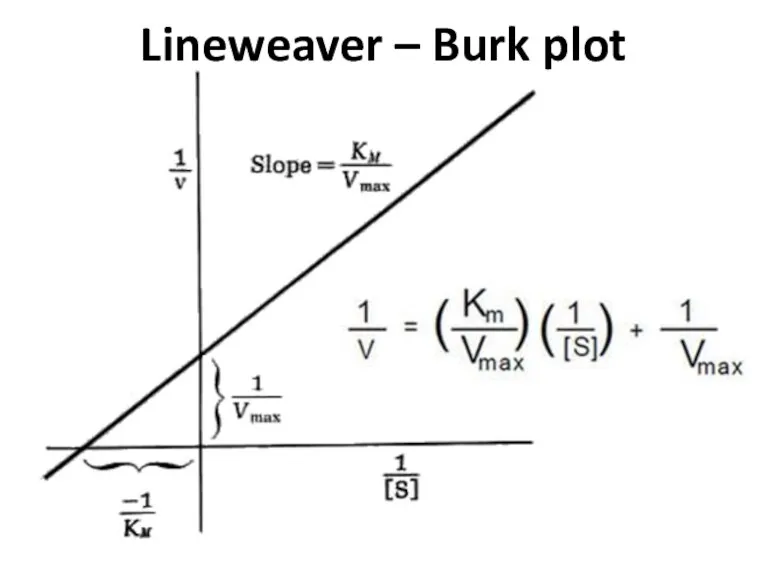
- 68. Lineweaver – Burk plot
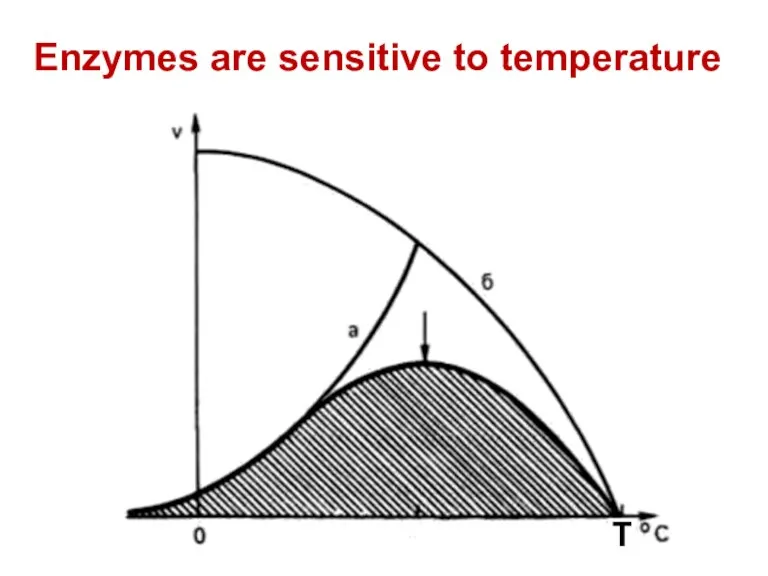
- 69. Enzymes are sensitive to temperature
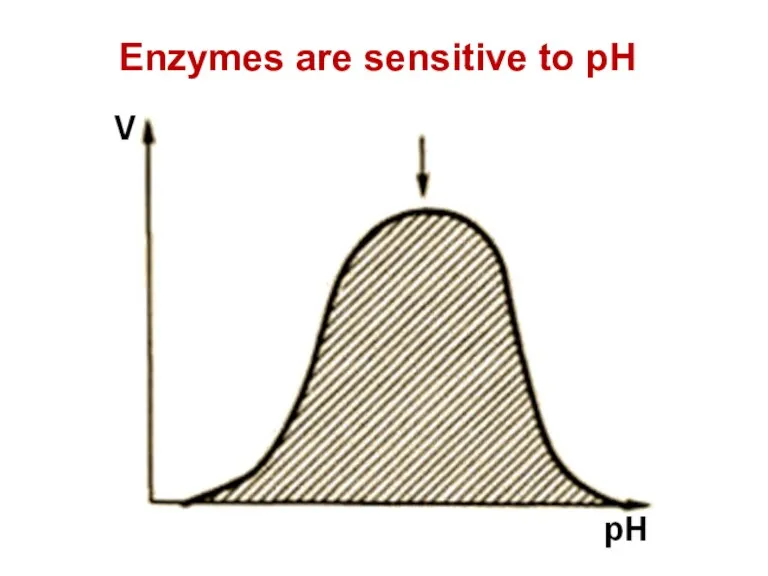
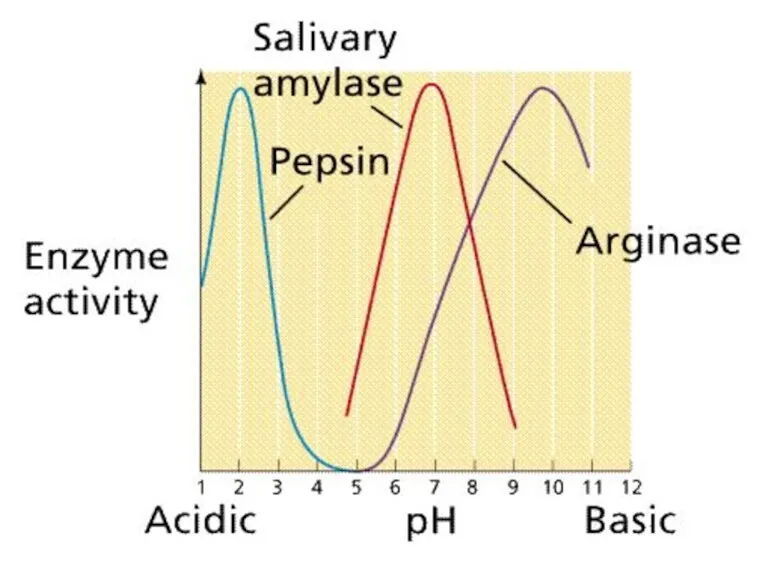
- 70. Enzymes are sensitive to pH
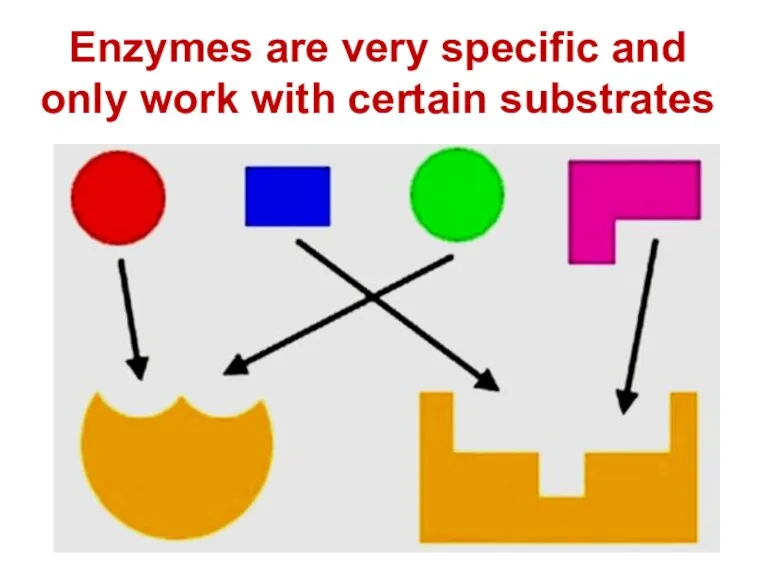
- 72. Enzymes are very specific and only work with certain substrates
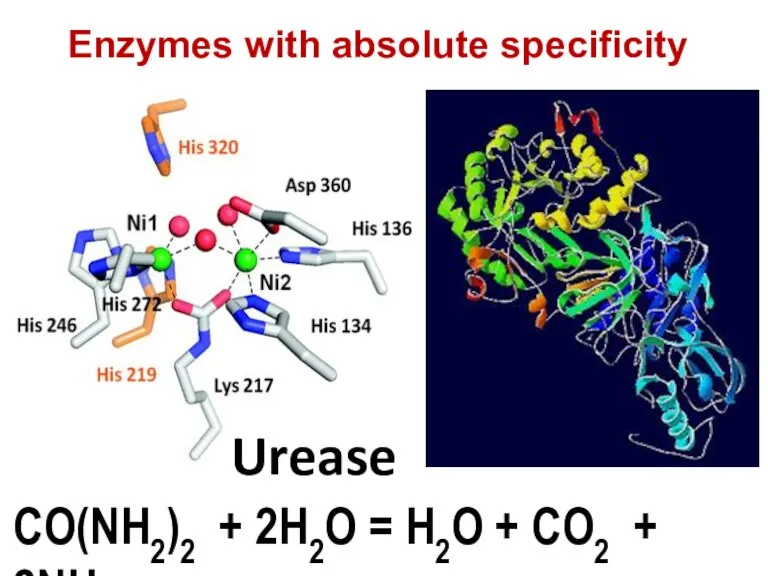
- 73. CO(NH2)2 + 2H2O = H2O + CO2 + 2NH3 Urease Enzymes with absolute specificity
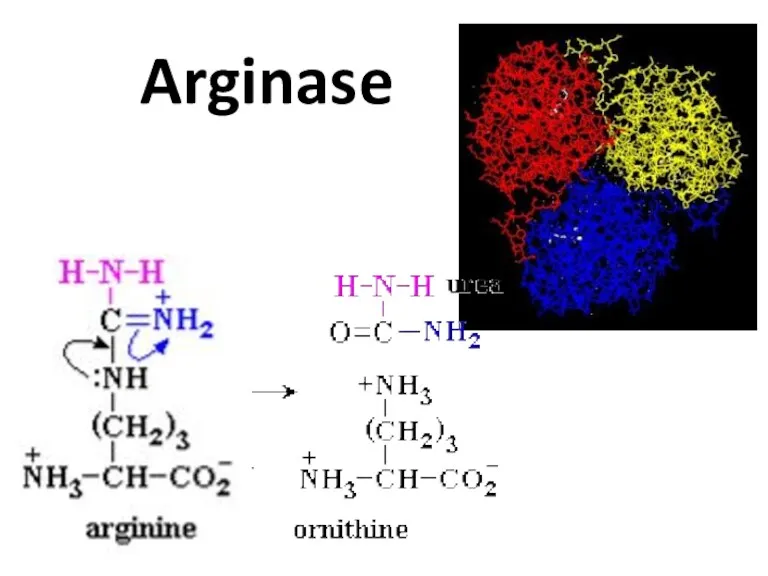
- 74. Arginase
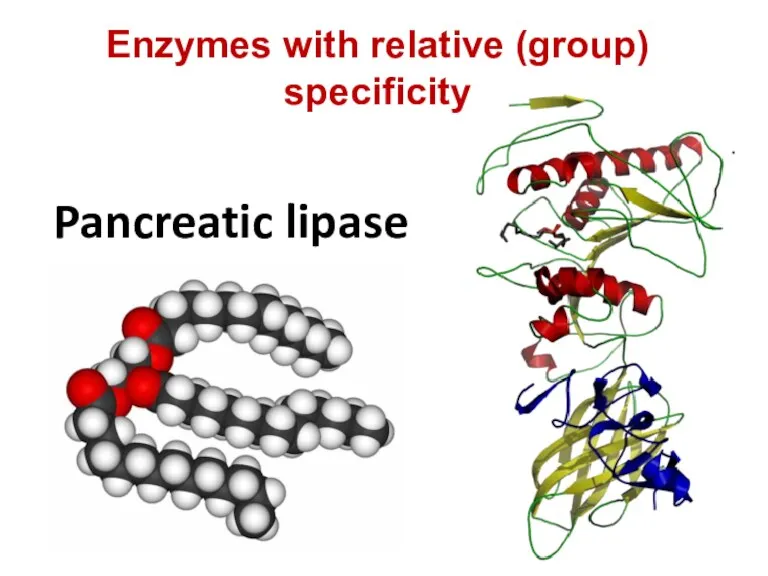
- 75. Pancreatic lipase Enzymes with relative (group) specificity
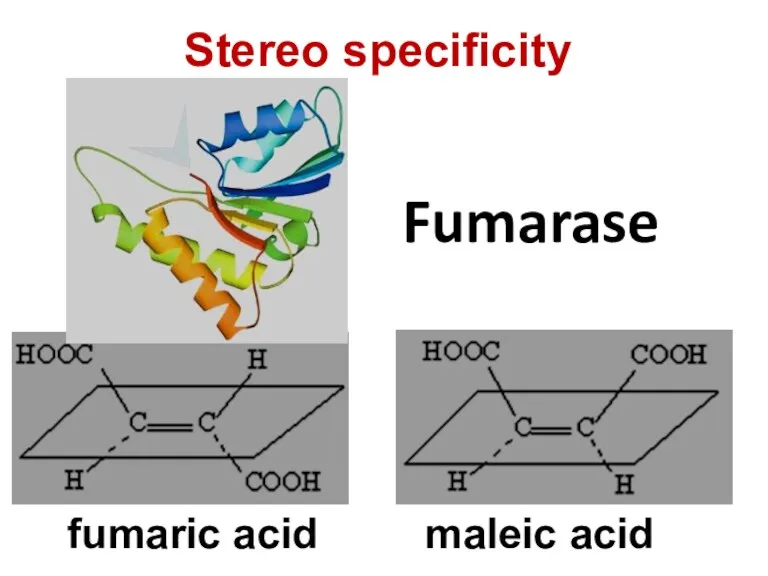
- 76. Fumarase fumaric acid maleic acid Stereo specificity
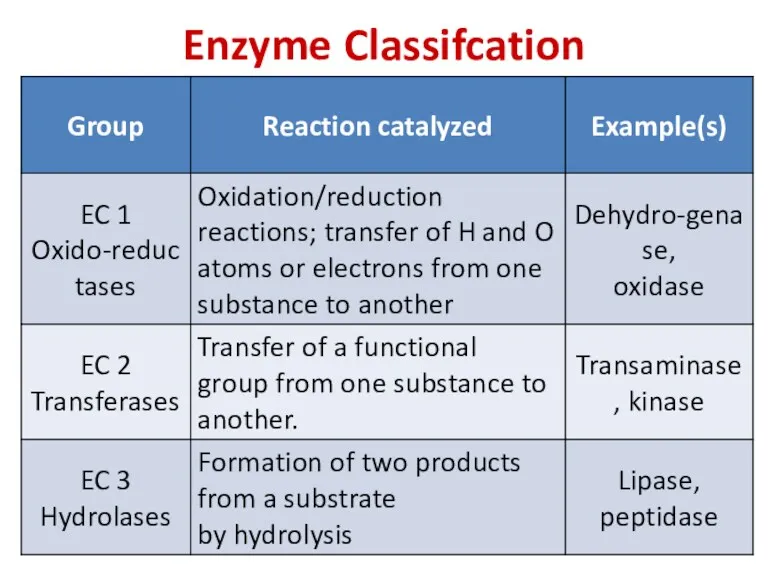
- 77. Enzyme Classifcation
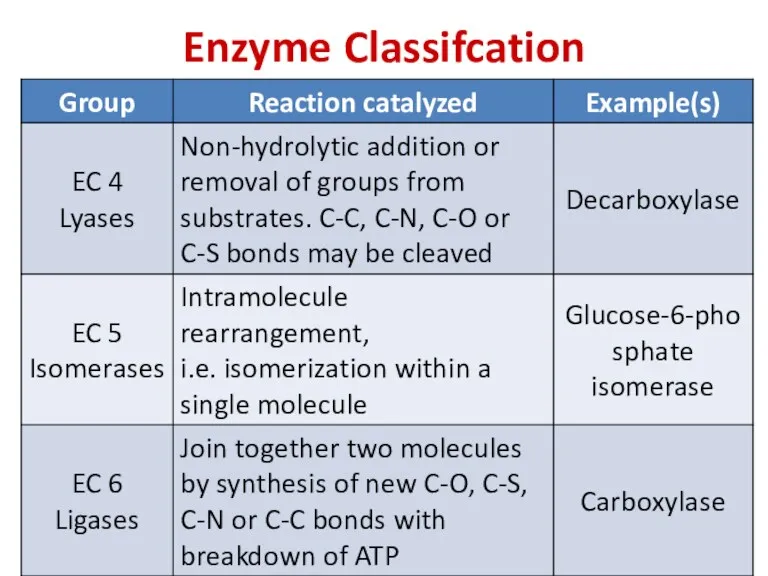
- 78. Enzyme Classifcation
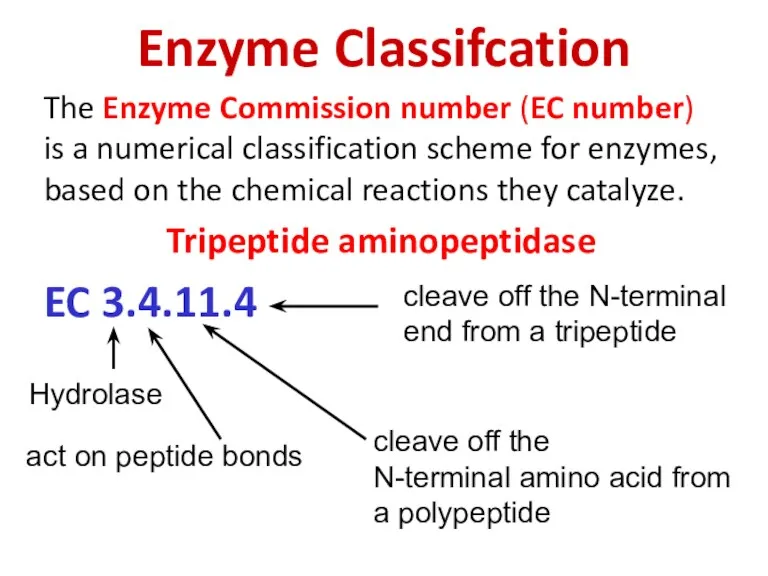
- 79. Enzyme Classifcation The Enzyme Commission number (EC number) is a numerical classification scheme for enzymes, based
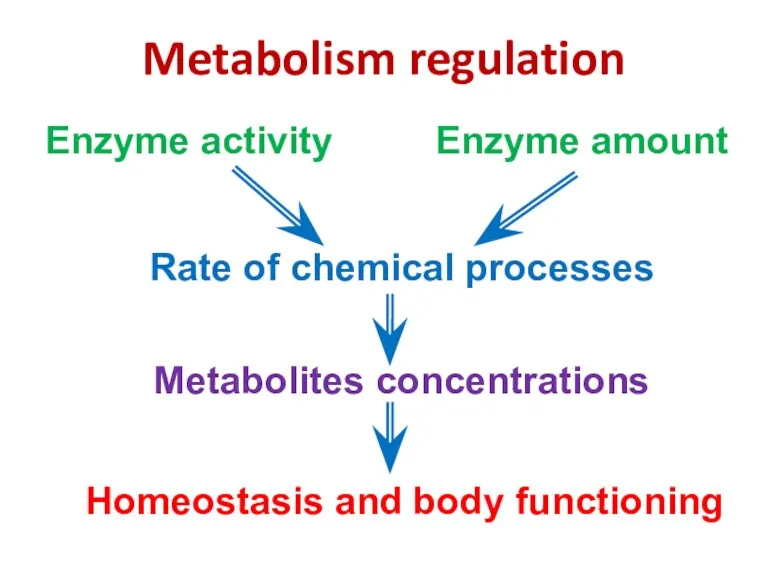
- 80. Metabolism regulation Rate of chemical processes Metabolites concentrations Enzyme activity Enzyme amount Homeostasis and body functioning
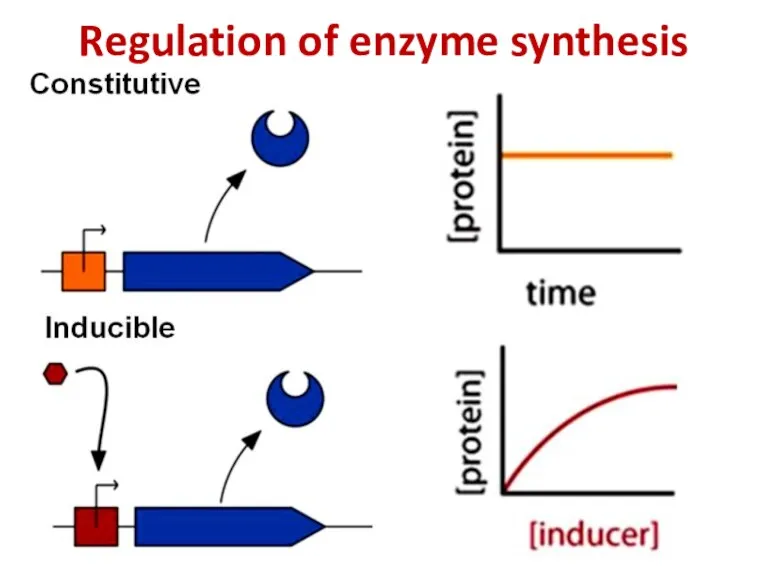
- 81. Regulation of enzyme synthesis
- 82. Regulation of enzyme activity
- 83. Enzymatic activity IU = 1mcmole/min 1 kat = 1 mole/sec 1 IU = 16.67 nkat
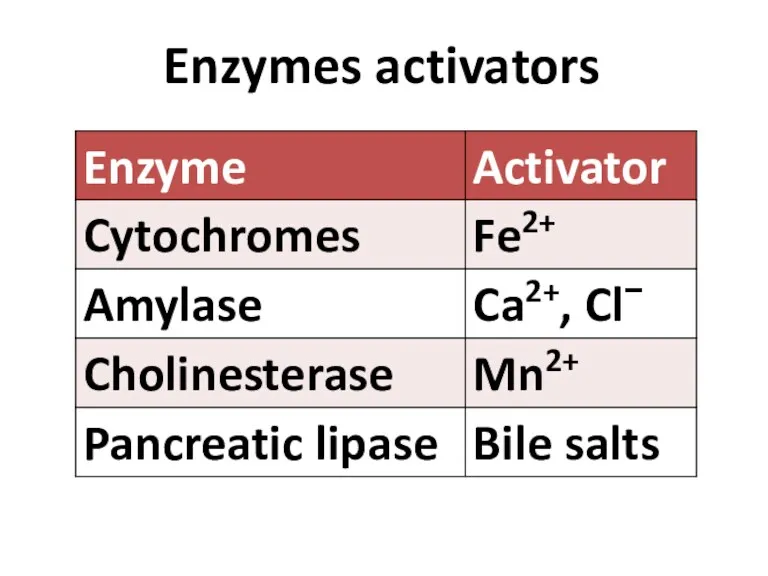
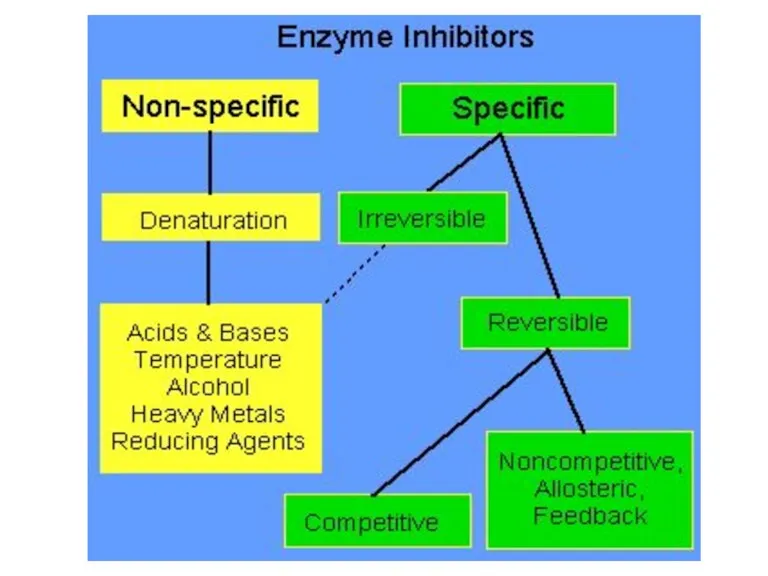
- 84. Enzymes activators
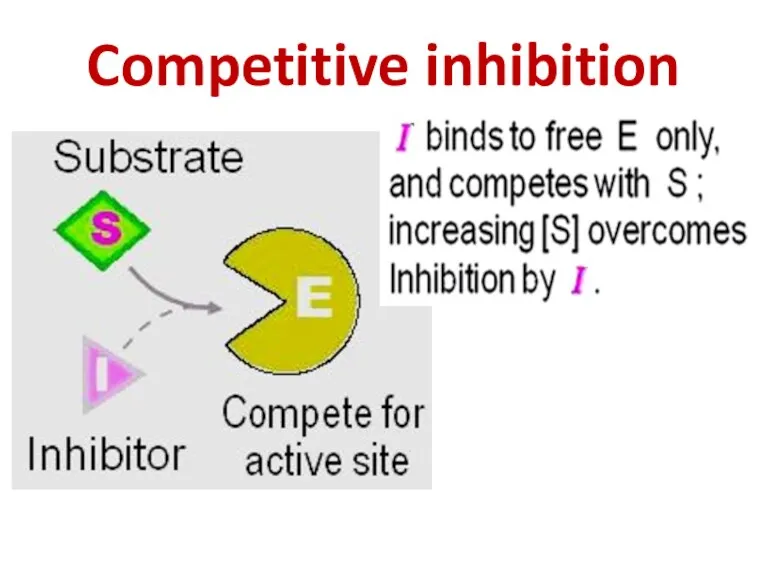
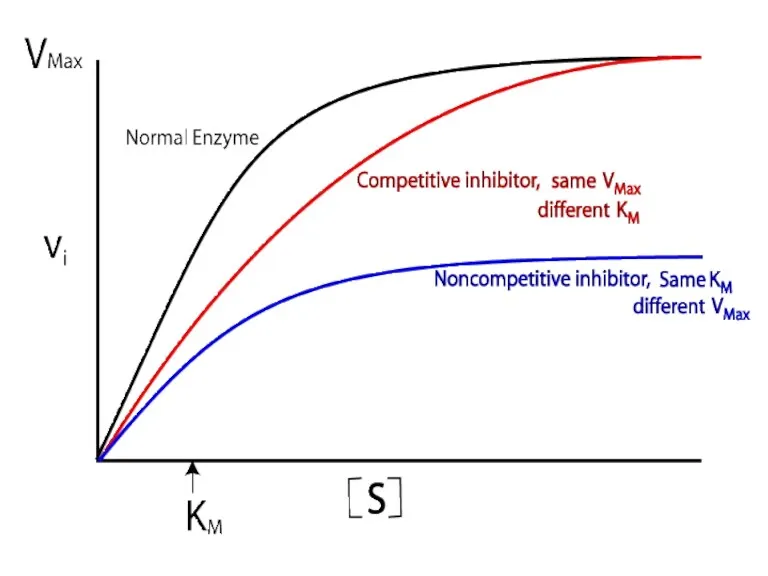
- 86. Competitive inhibition
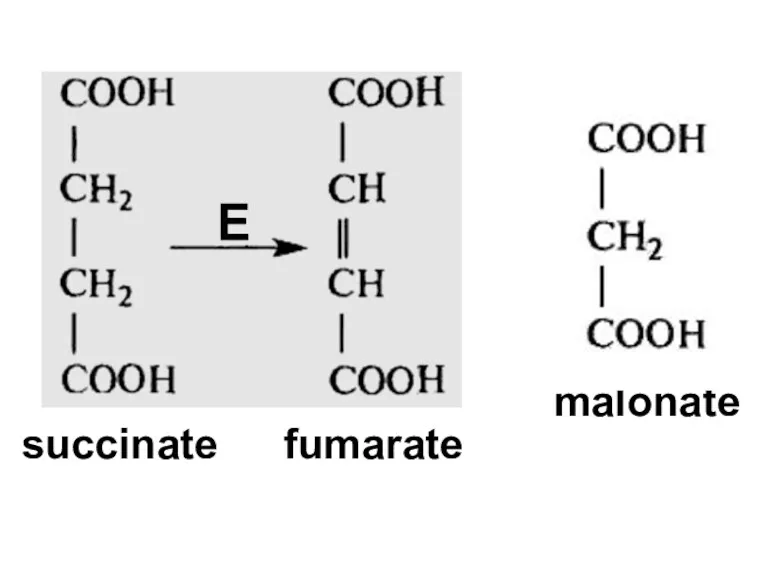
- 87. succinate fumarate malonate
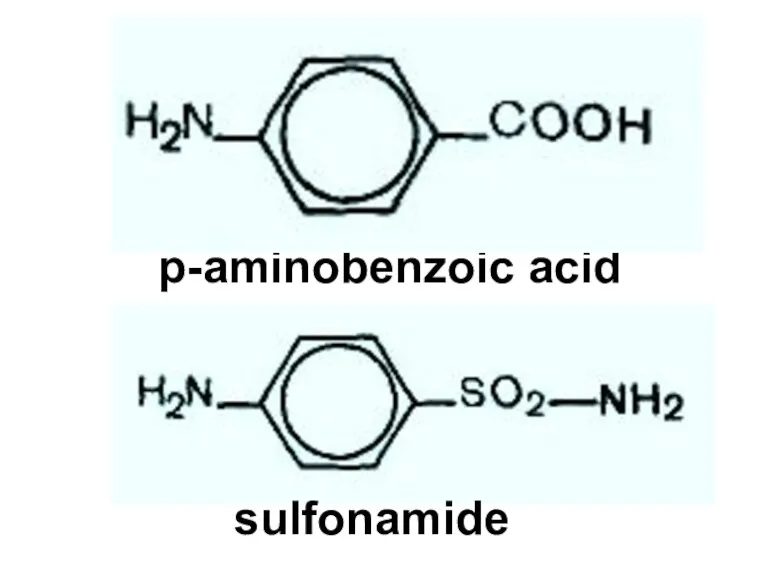
- 88. p-aminobenzoic acid sulfonamide
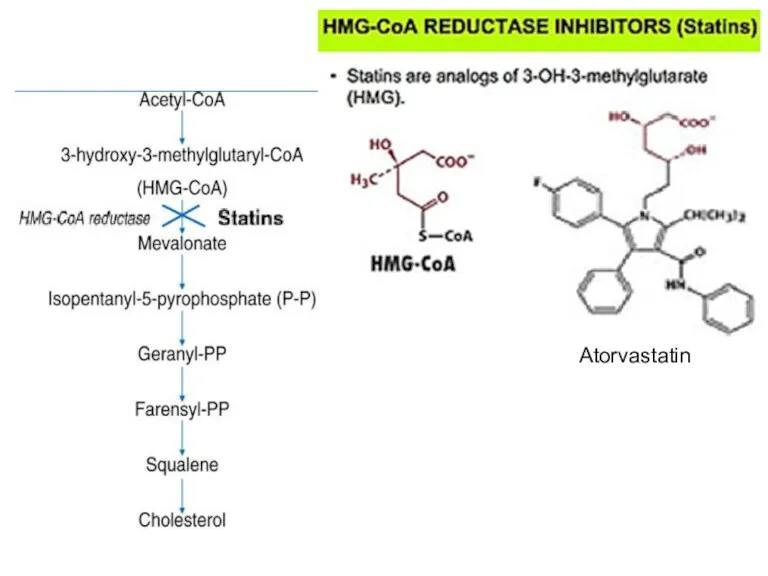
- 89. Atorvastatin
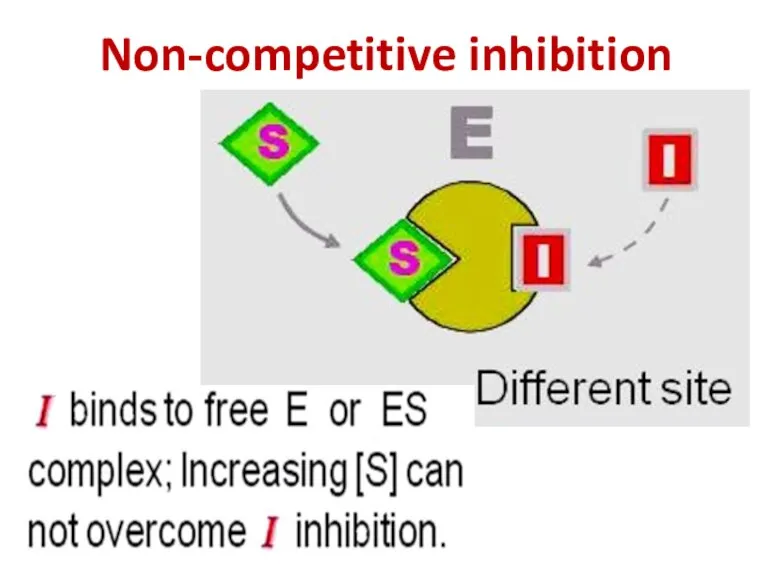
- 90. Non-competitive inhibition
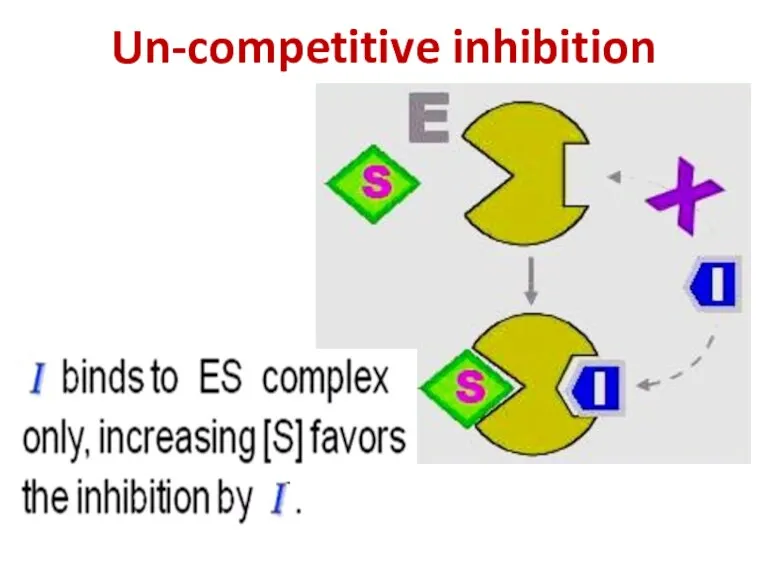
- 92. Un-competitive inhibition
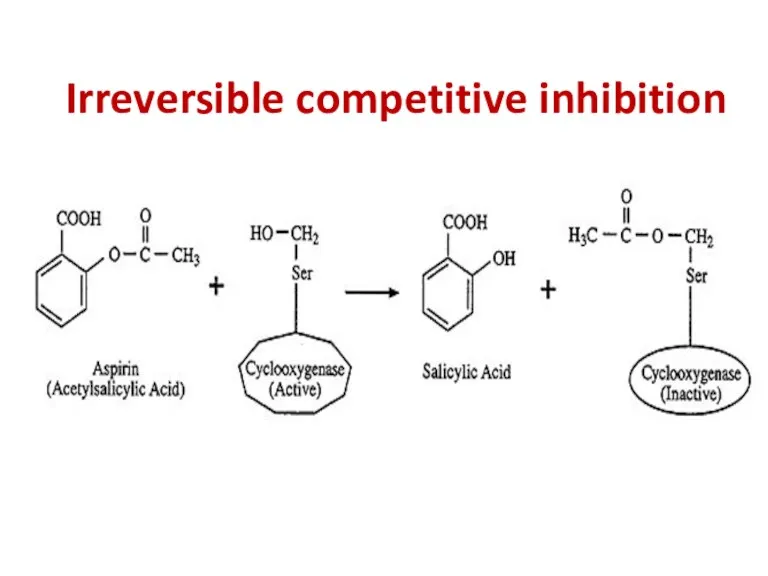
- 93. Irreversible competitive inhibition
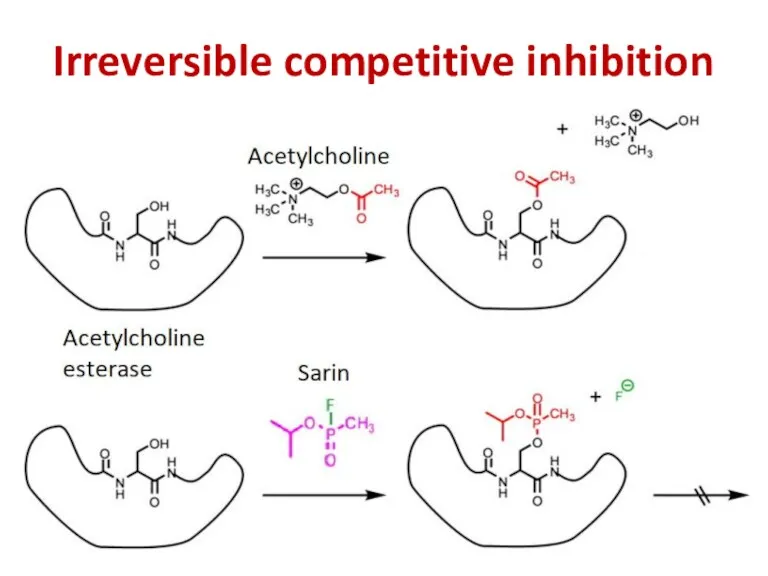
- 94. Irreversible competitive inhibition
- 97. Скачать презентацию











 Обратимость химических реакций. Обратимые и необратимые химические реакции. Химическое равновесие
Обратимость химических реакций. Обратимые и необратимые химические реакции. Химическое равновесие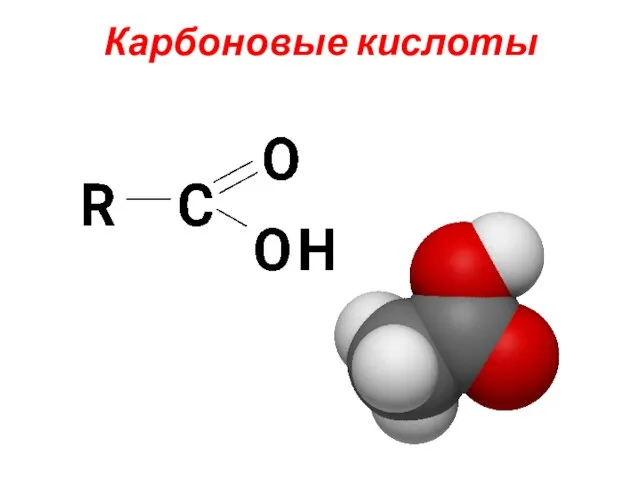 Карбоновые кислоты. Классификация карбоновых кислот
Карбоновые кислоты. Классификация карбоновых кислот Классы неорганических веществ (лекция № 4)
Классы неорганических веществ (лекция № 4) Взрывоопасные грузы
Взрывоопасные грузы Кремний и его соединения
Кремний и его соединения Коллоидная химия
Коллоидная химия Вывод формул веществ по массовым долям элементов. 10 класс
Вывод формул веществ по массовым долям элементов. 10 класс Чистые вещества и смеси. Способы разделения смесей
Чистые вещества и смеси. Способы разделения смесей Лекция_3_Химические_и_физические_свойства_алканов_и_циклоалканов (1)
Лекция_3_Химические_и_физические_свойства_алканов_и_циклоалканов (1) Азотная кислота
Азотная кислота Типы химических реакций
Типы химических реакций Оксиды, их классификация и свойства
Оксиды, их классификация и свойства Кристаллы и минералы
Кристаллы и минералы Знатоки химии. Викторина
Знатоки химии. Викторина Особенности строения, реакционной способности и методы синтеза карбоновых кислот и функциональных производных
Особенности строения, реакционной способности и методы синтеза карбоновых кислот и функциональных производных Свойства смесей ПАВ
Свойства смесей ПАВ Реологические свойства полимеров
Реологические свойства полимеров Камни и Телец
Камни и Телец Химическая связь
Химическая связь Основные понятия и законы химии
Основные понятия и законы химии Основные положения теории растворов электролитов, используемых в аналитической химии
Основные положения теории растворов электролитов, используемых в аналитической химии Химические профессии на стройках Олимпиады
Химические профессии на стройках Олимпиады Гибридизация атомных орбиталей
Гибридизация атомных орбиталей Көмірсутектерді пиролиздеу арқылы қарапайым олефиндерді алу
Көмірсутектерді пиролиздеу арқылы қарапайым олефиндерді алу Номенклатура органических соединений
Номенклатура органических соединений Қышқылдар мен сілтілер тепе-теңдігі
Қышқылдар мен сілтілер тепе-теңдігі Открытие Д.И. Менделеевым периодического закона. Периодическая система химических элементов
Открытие Д.И. Менделеевым периодического закона. Периодическая система химических элементов Неметаллические и композиционные материалы
Неметаллические и композиционные материалы