Содержание
- 2. Chapter 42 – Part I Circulation
- 3. What you need to know: Circulatory vessels, heart chambers, route of mammalian circulation Evolution of the
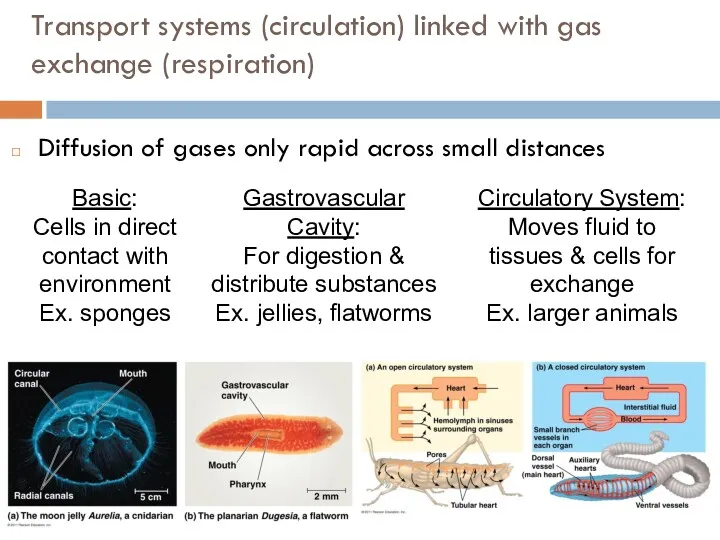
- 4. Transport systems (circulation) linked with gas exchange (respiration) Diffusion of gases only rapid across small distances
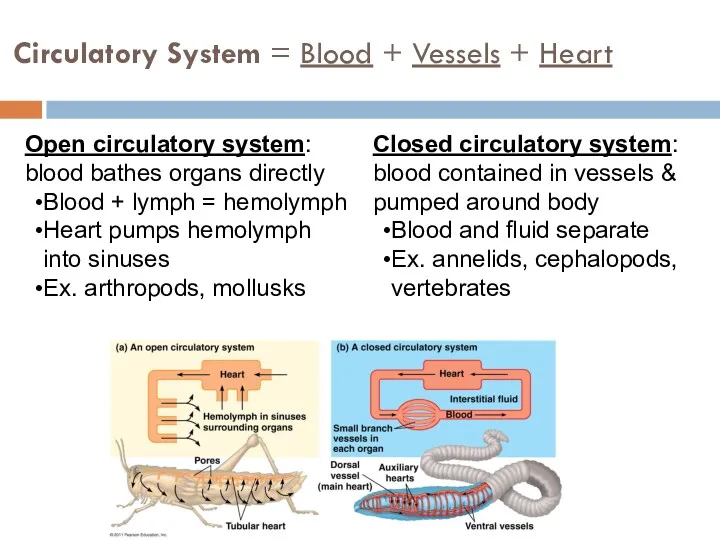
- 5. Circulatory System = Blood + Vessels + Heart Open circulatory system: blood bathes organs directly Blood
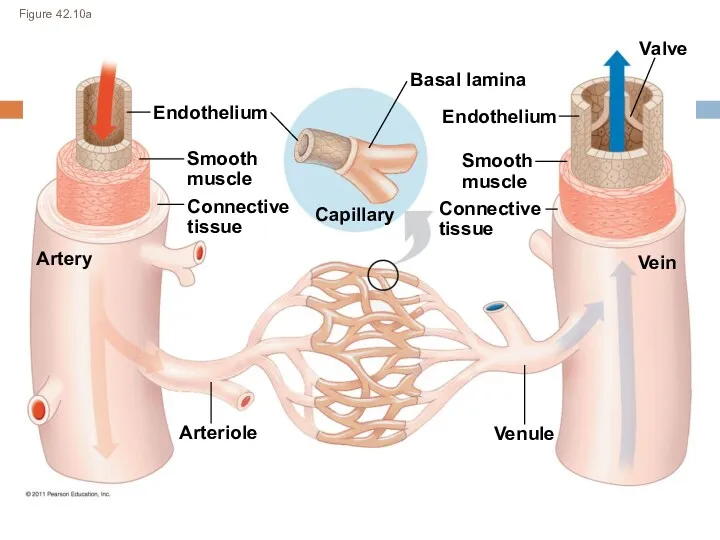
- 6. Figure 42.10a Endothelium Artery Smooth muscle Connective tissue Capillary Valve Vein Basal lamina Endothelium Smooth muscle
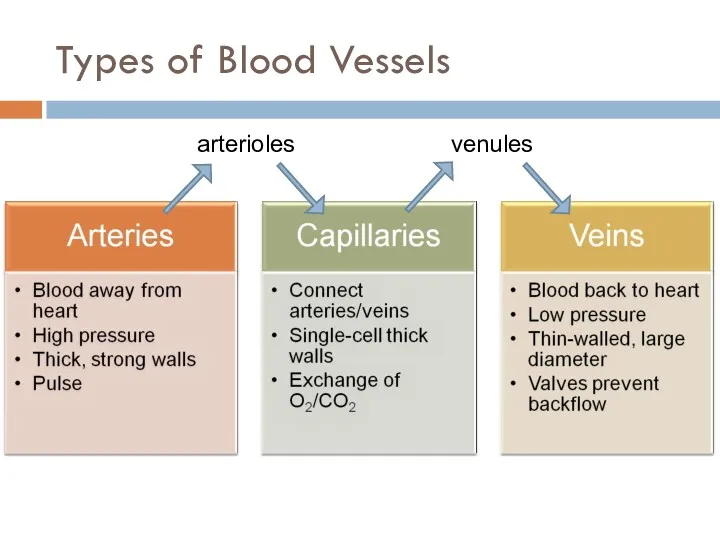
- 7. Types of Blood Vessels arterioles venules
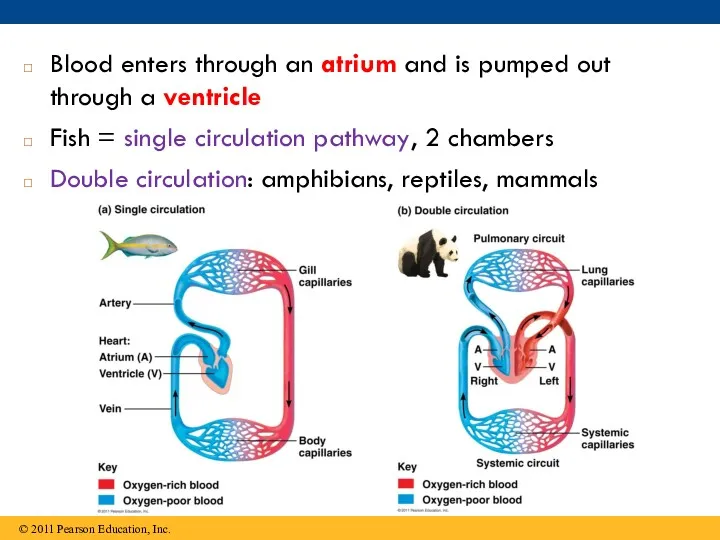
- 8. Blood enters through an atrium and is pumped out through a ventricle Fish = single circulation
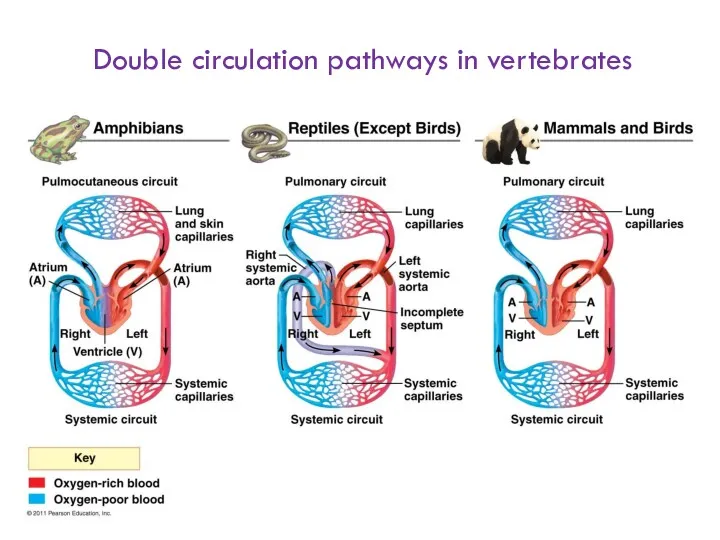
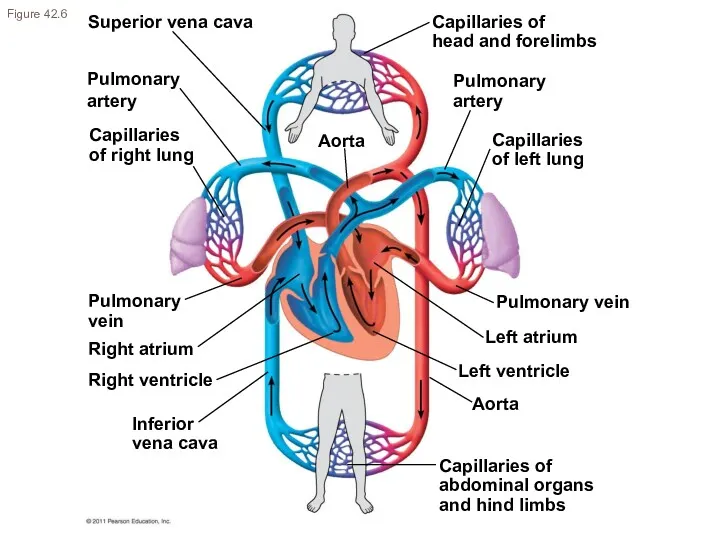
- 9. Double circulation pathways in vertebrates
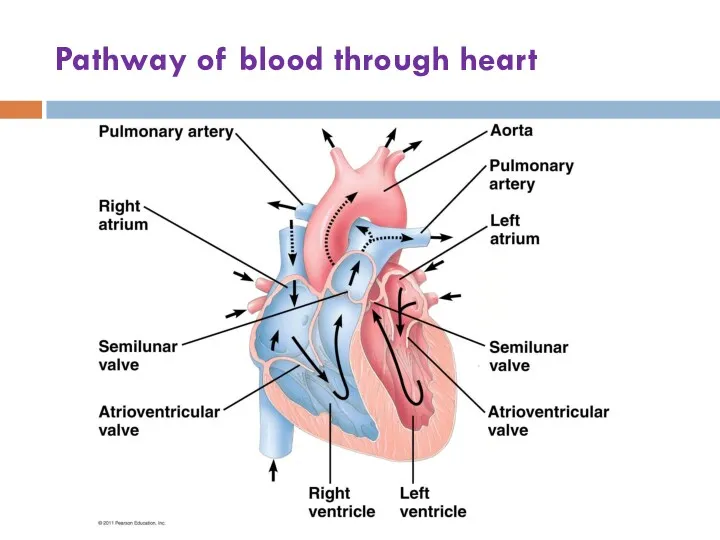
- 10. Pathway of blood through heart
- 11. Superior vena cava Pulmonary artery Capillaries of right lung Pulmonary vein Aorta Inferior vena cava Right
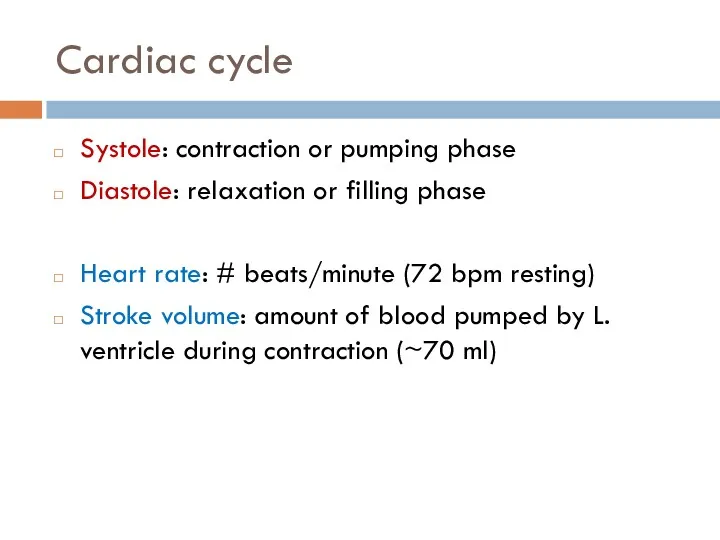
- 12. Cardiac cycle Systole: contraction or pumping phase Diastole: relaxation or filling phase Heart rate: # beats/minute
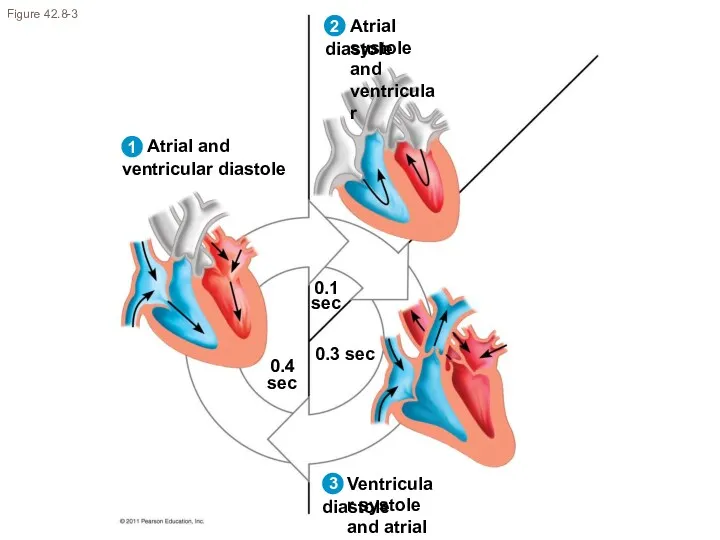
- 13. Figure 42.8-3 0.1 sec 0.4 sec 0.3 sec 2 1 3
- 14. Valves: prevent backflow of blood The atrioventricular (AV) valves (tricuspid, bicuspid) separate each atrium and ventricle
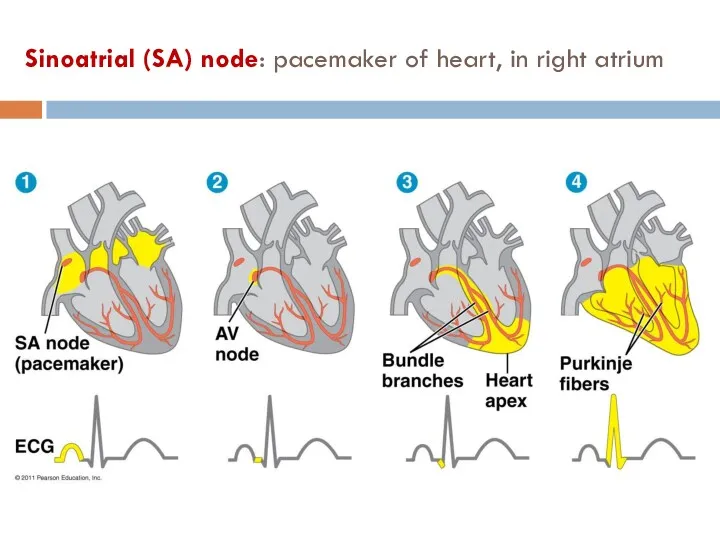
- 15. Sinoatrial (SA) node: pacemaker of heart, in right atrium
- 16. The pacemaker is regulated by two portions of the nervous system: the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions
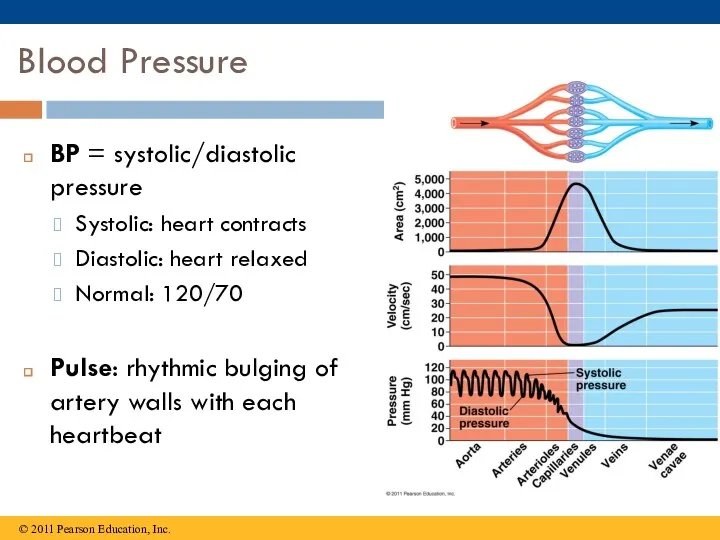
- 17. Blood Pressure BP = systolic/diastolic pressure Systolic: heart contracts Diastolic: heart relaxed Normal: 120/70 Pulse: rhythmic
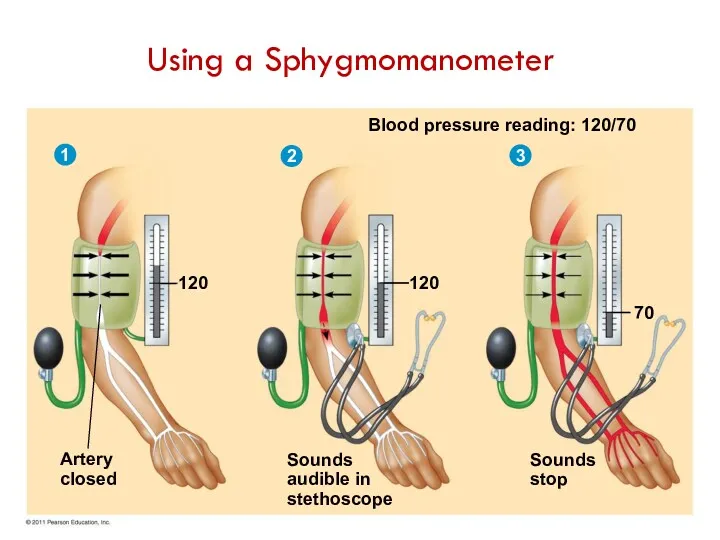
- 18. Blood pressure reading: 120/70 120 70 Sounds stop Sounds audible in stethoscope 120 Artery closed 1
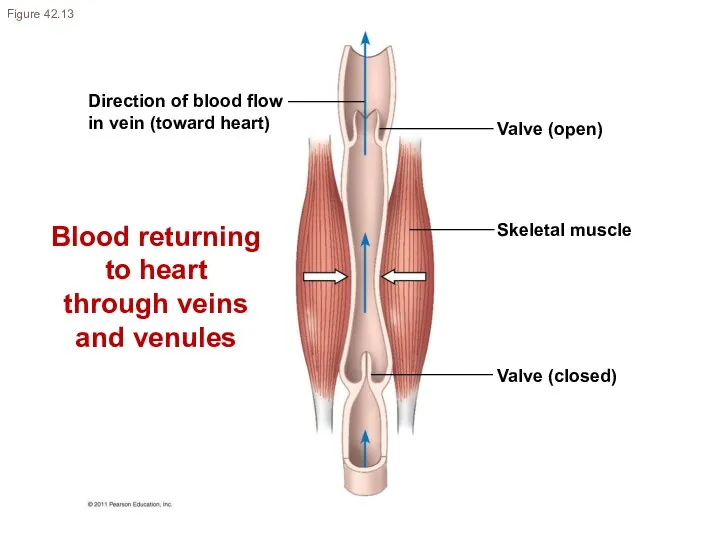
- 19. Direction of blood flow in vein (toward heart) Valve (open) Skeletal muscle Valve (closed) Figure 42.13
- 20. Lymphatic System: returns lost fluid and proteins to blood as lymph Lymph Nodes: filter lymph, house
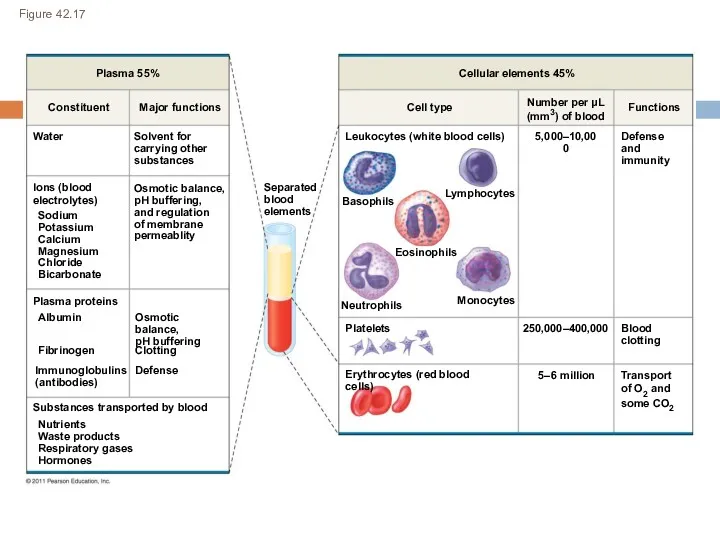
- 21. Blood Plasma (55%) – water, ions, proteins, gases, nutrients, wastes, hormones Cells (45%) – RBC, WBC,
- 22. Figure 42.17 Plasma 55% Constituent Major functions Water Ions (blood electrolytes) Sodium Potassium Calcium Magnesium Chloride
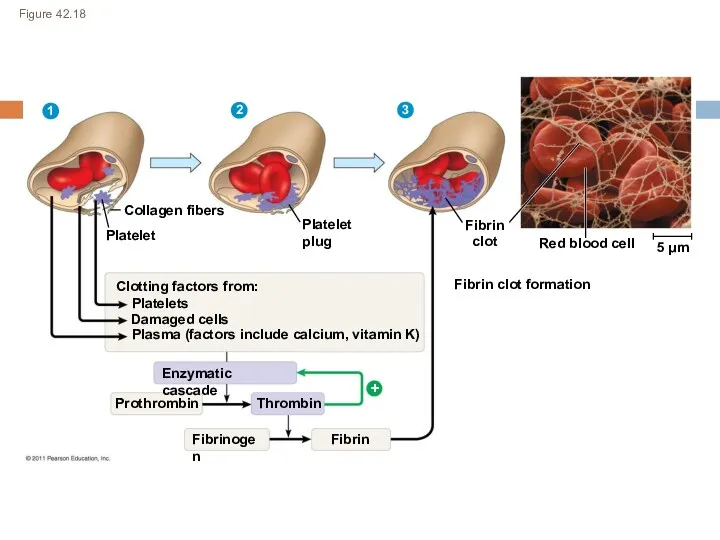
- 23. Figure 42.18 Collagen fibers 1 2 3 Platelet Platelet plug Fibrin clot Fibrin clot formation Red
- 24. Cardiovascular Disease Atherosclerosis: buildup of plaque deposits within arteries Heart attack (myocardial infarction): blockage of one
- 26. Скачать презентацию



 Биогенді (s.p.d) элементтермен олардың қосылыстарының медициналық және биологиялық маңызы
Биогенді (s.p.d) элементтермен олардың қосылыстарының медициналық және биологиялық маңызы Кислоты, их состав и названия
Кислоты, их состав и названия Карбоновые кислоты и их функциональные производные
Карбоновые кислоты и их функциональные производные Ароматические углеводороды
Ароматические углеводороды Гетерофазный катализ. (Лекция 20)
Гетерофазный катализ. (Лекция 20) Горение топлива
Горение топлива Використання радіоактивних ізотопів, як індикаторів у тваринництві і археології
Використання радіоактивних ізотопів, як індикаторів у тваринництві і археології Основные классы неорганических соединений
Основные классы неорганических соединений Соли, их классификация и свойства
Соли, их классификация и свойства Органічна хімія
Органічна хімія Розв’язування задач за рівняннями реакцій з використанням розчинів із певною масовою часткою розчиненої речовини. Урок 13-14
Розв’язування задач за рівняннями реакцій з використанням розчинів із певною масовою часткою розчиненої речовини. Урок 13-14 Жёсткость воды
Жёсткость воды Полисахариды: крахмал и целлюлоза
Полисахариды: крахмал и целлюлоза Растворы. Часть 2. Лекция №7
Растворы. Часть 2. Лекция №7 Химия атмосферы. Химические процессы в тропосфере
Химия атмосферы. Химические процессы в тропосфере Буферные системы
Буферные системы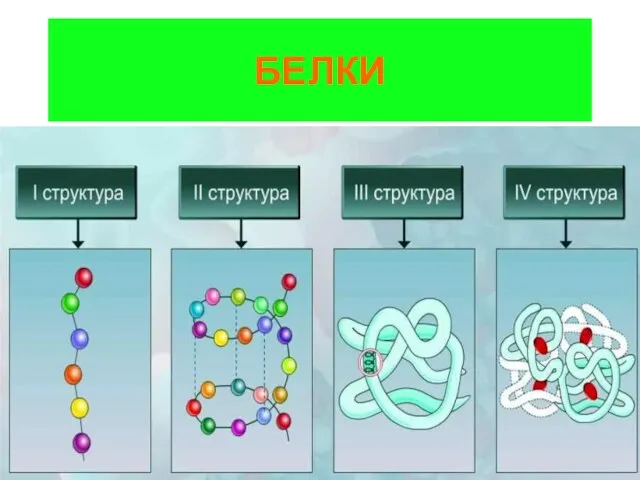 Белки. Строение
Белки. Строение Классификация химических элементов. Составитель. 8 класс
Классификация химических элементов. Составитель. 8 класс Минералы для ИЗБ
Минералы для ИЗБ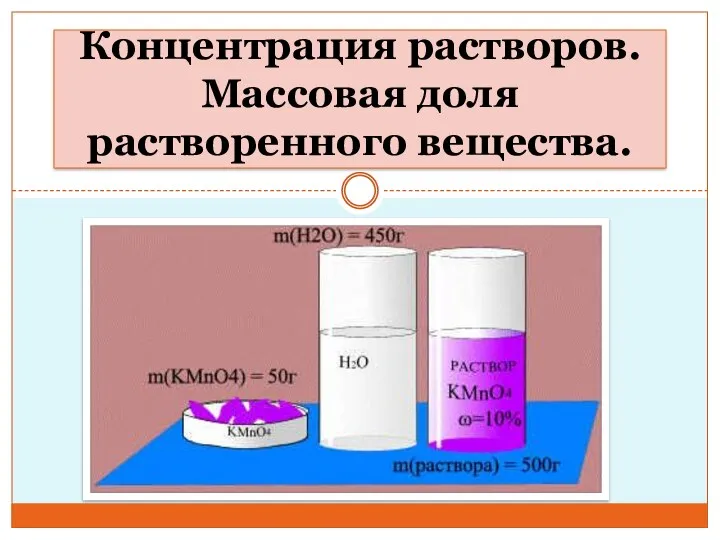 Концентрация растворов. Массовая доля растворенного вещества. Урок 1
Концентрация растворов. Массовая доля растворенного вещества. Урок 1 Химический элемент медь
Химический элемент медь Кинетика химических реакций
Кинетика химических реакций Кремний и его соединения
Кремний и его соединения Галогены. Расположите галогены в порядке их открытия
Галогены. Расположите галогены в порядке их открытия Важнейшие реакции в органической химии
Важнейшие реакции в органической химии Технология производства аминоальдегидных смол
Технология производства аминоальдегидных смол Углерод. Физические и химические свойства
Углерод. Физические и химические свойства Гидролиз солей
Гидролиз солей