Содержание
- 2. 1. Read and translate the international words Analysis, analytical, separation, identification, component, indication, classical, instrumental, extraction,
- 3. 3. Match the English word combinations in column A to their Russian equivalents in column B
- 4. 4. Read and translate Analytical Chemistry Analytical chemistry is the study of the separation, identification, and
- 5. Classical Methods Qualitative analysis determines the presence or absence of a particular compound, but not its
- 6. Instrumental Methods Spectroscopy measures the interaction of the molecules with electromagnetic radiation. Mass spectrometry measures mass-to-charge
- 7. 5. Answer the questions 1. What does analytical chemistry study? 2. What are the main classifications
- 8. 6. Read and translate An optical spectrometer is an instrument used to measure properties of light
- 9. 7. Read and translate the text into the English language using the diagrams of atomic force
- 10. 8. Find the Russian equivalents for the following phrases 9. Find the English equivalents for the
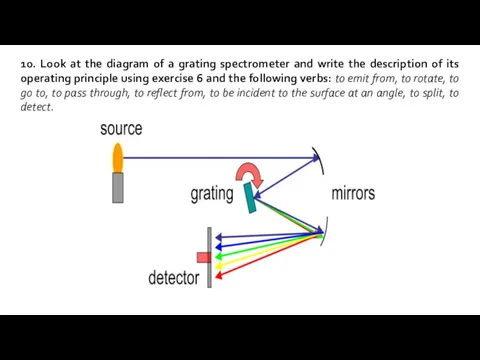
- 11. 10. Look at the diagram of a grating spectrometer and write the description of its operating
- 12. 11. Complete the description of nuclear magnetic resonance using the following words and phrases: equilibrium, range,
- 13. 12. Match the English word combinations in column A to their Russian equivalents in column B
- 14. 13. Read the text using the terminology from exercise 12 and describe the main principles of
- 15. Electrical properties can be expressed also through the quantity, inverse to the resistance, conductivity. Its unit
- 17. Briefly describe the experimental process. Describe the main parts of the conductometer. What are the modes
- 19. Скачать презентацию















 Газовые законы. Расчетные задачи
Газовые законы. Расчетные задачи Photocatalysts based on AgCl / Ag nanocomposites
Photocatalysts based on AgCl / Ag nanocomposites Альдегиды и кетоны
Альдегиды и кетоны Спирты: общая характеристика
Спирты: общая характеристика Материаловедение в полиграфическом и упаковочном производстве
Материаловедение в полиграфическом и упаковочном производстве B13. Задачи на концентрацию и сплавы
B13. Задачи на концентрацию и сплавы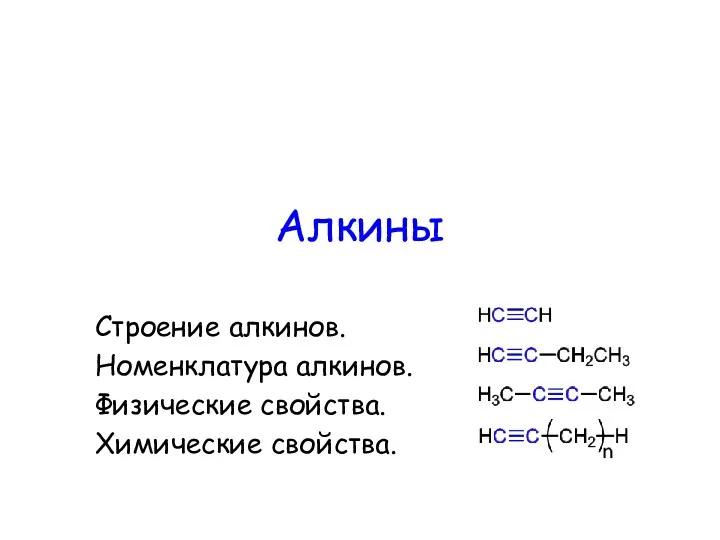 Алкины. Строение алкинов. Номенклатура алкинов. Физические свойства. Химические свойства
Алкины. Строение алкинов. Номенклатура алкинов. Физические свойства. Химические свойства Основания
Основания Кислород. Атом кислорода
Кислород. Атом кислорода Простые и сложные эфиры
Простые и сложные эфиры Расчет реактора установки гидроочистки бензина
Расчет реактора установки гидроочистки бензина Електронні і графічні електронні формули атомів s-, p-, d- елементів. Принцип Мінімальної енергії
Електронні і графічні електронні формули атомів s-, p-, d- елементів. Принцип Мінімальної енергії Альдегиды и кетоны
Альдегиды и кетоны Карбоновые кислоты (часть 1)
Карбоновые кислоты (часть 1) Химическая технология органических веществ
Химическая технология органических веществ Сложные эфиры. Жиры
Сложные эфиры. Жиры Атом. Химический элемент. Изотопы. Простые и сложные вещества
Атом. Химический элемент. Изотопы. Простые и сложные вещества Кислородсодержащие соединения азота
Кислородсодержащие соединения азота Биологически важные окислительно-восстановительные реакции органических соединений
Биологически важные окислительно-восстановительные реакции органических соединений Классификация химических реакций
Классификация химических реакций Анализ качества лекарственных средств органической природы из группы галогенпроизводных углеводородов жирного ряда
Анализ качества лекарственных средств органической природы из группы галогенпроизводных углеводородов жирного ряда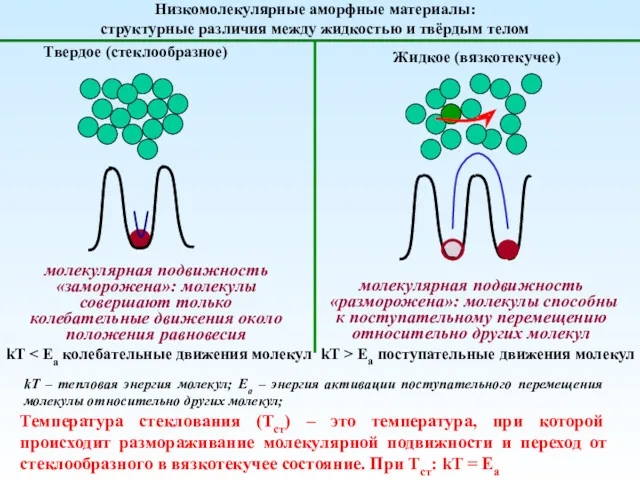 Механика полимеров
Механика полимеров Основные понятия и законы химии. Тема1
Основные понятия и законы химии. Тема1 Механические свойства минералов
Механические свойства минералов Строение атома
Строение атома Геохимия, как наука
Геохимия, как наука Обчислення за хімічними рівняннями відносного виходу продукту реакції
Обчислення за хімічними рівняннями відносного виходу продукту реакції Синтетические моющие средства, порошки, омыление, выпадение в осадок мыла, жиров
Синтетические моющие средства, порошки, омыление, выпадение в осадок мыла, жиров