Содержание
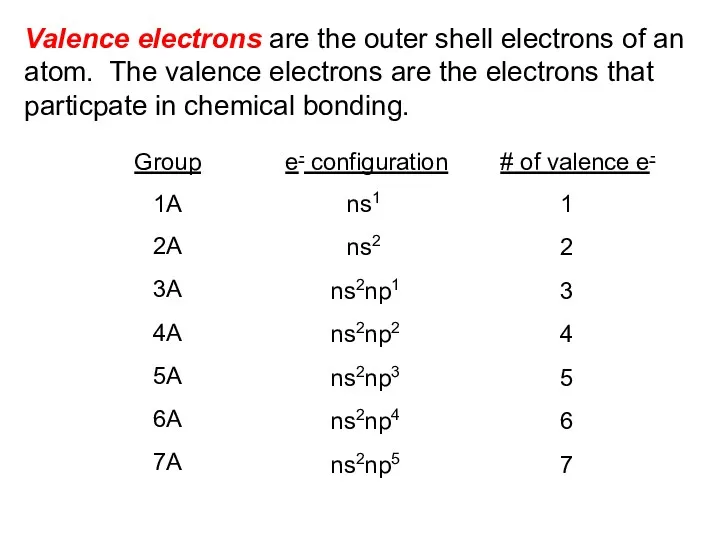
- 2. Valence electrons are the outer shell electrons of an atom. The valence electrons are the electrons
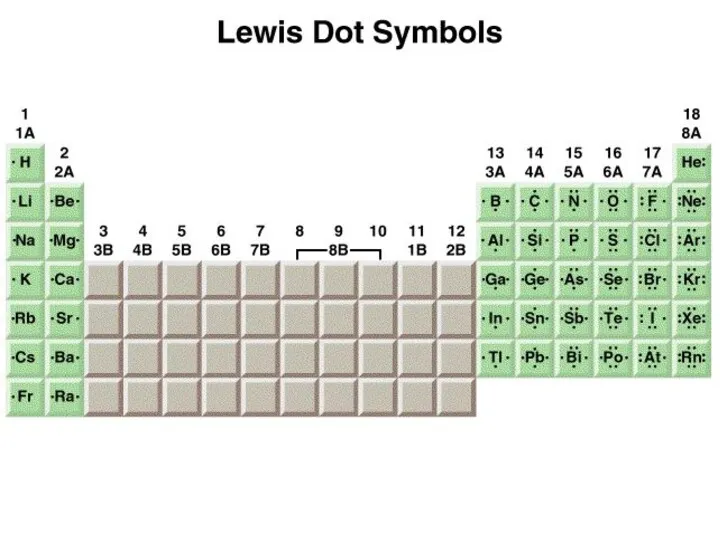
- 4. The Ionic Bond 1s22s1 1s22s22p5 1s2 1s22s22p6 [He] [Ne]
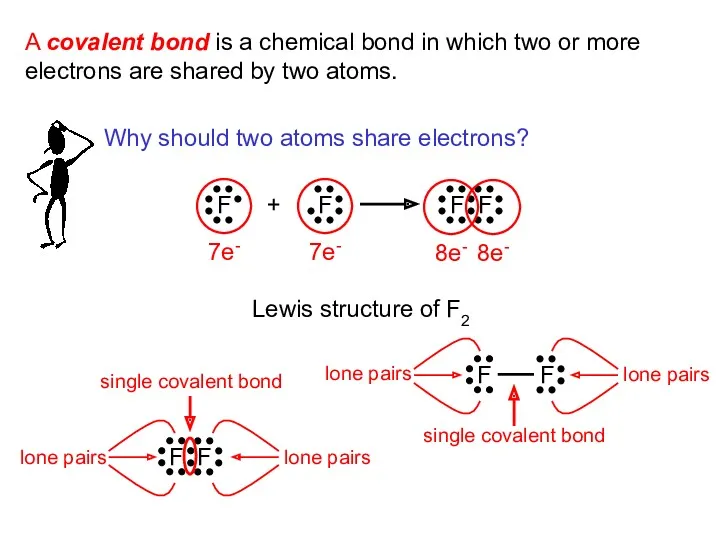
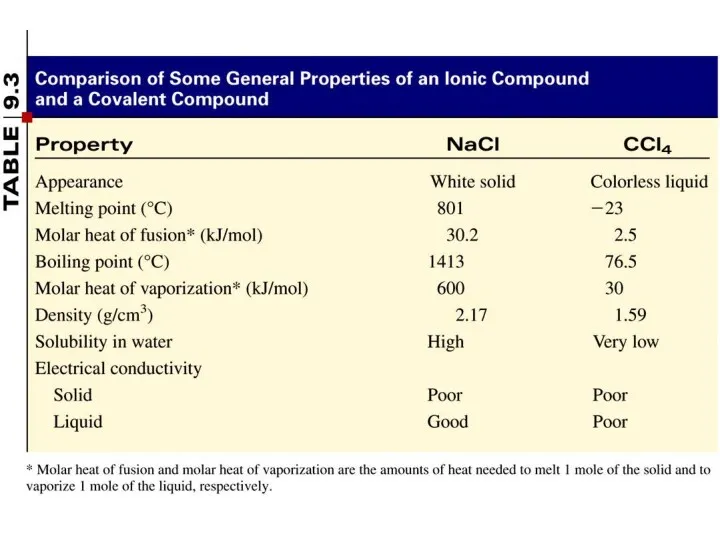
- 5. A covalent bond is a chemical bond in which two or more electrons are shared by
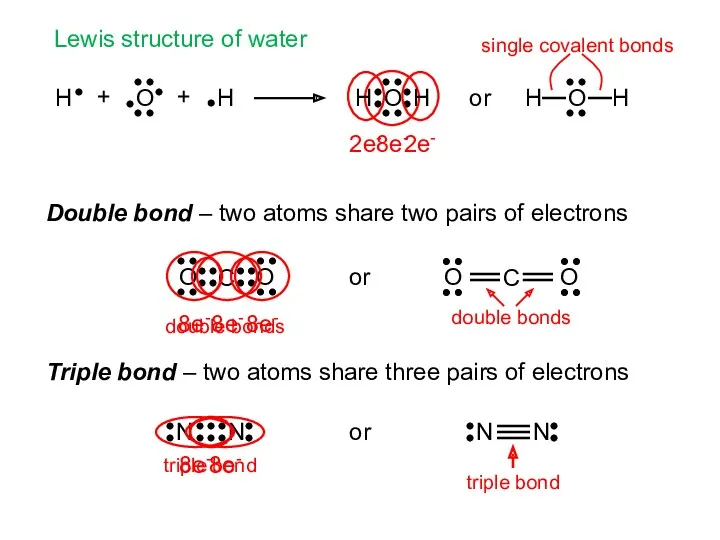
- 6. + + Lewis structure of water Double bond – two atoms share two pairs of electrons
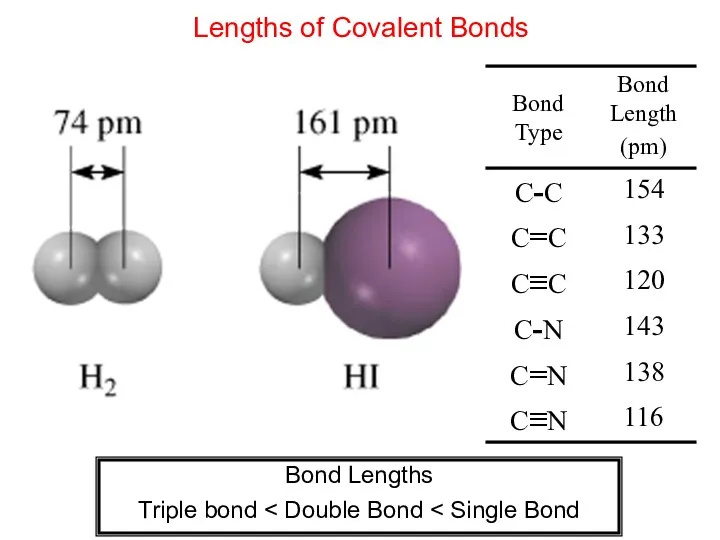
- 7. Lengths of Covalent Bonds Bond Lengths Triple bond
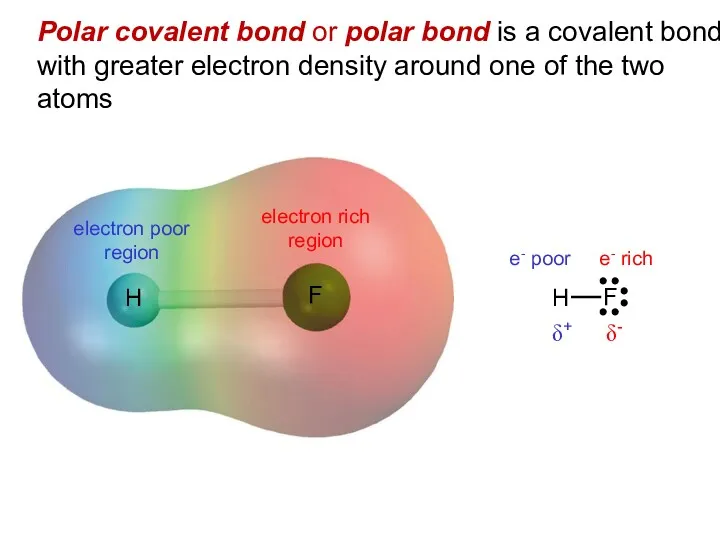
- 9. Polar covalent bond or polar bond is a covalent bond with greater electron density around one
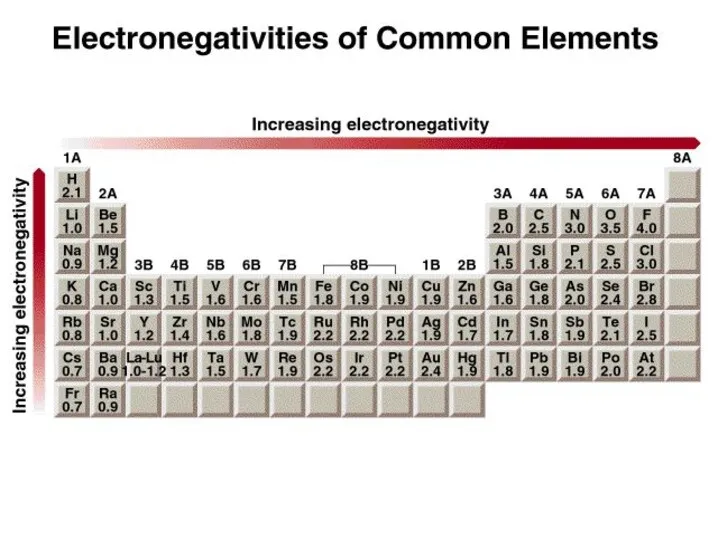
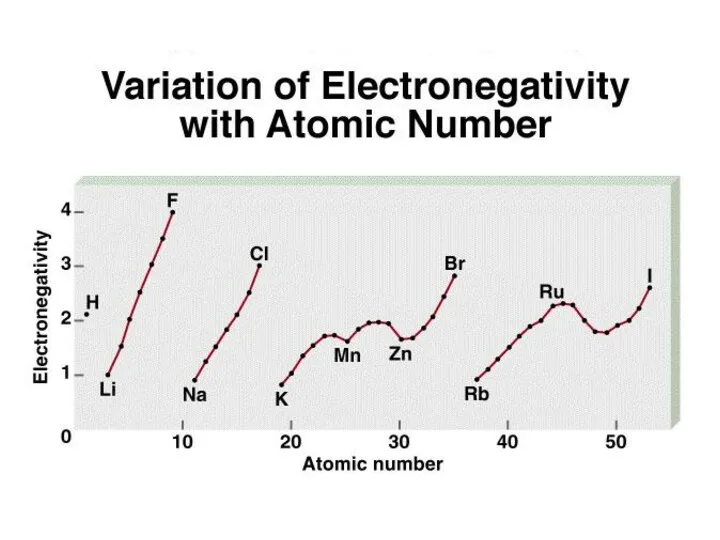
- 10. Electronegativity is the ability of an atom to attract toward itself the electrons in a chemical
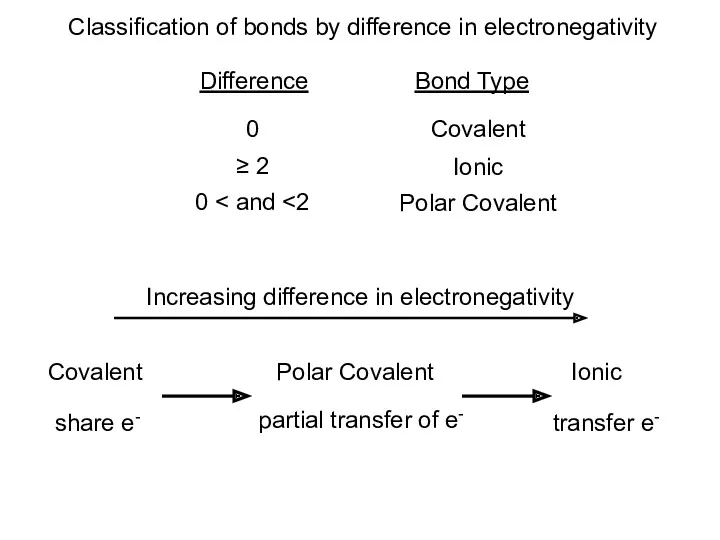
- 13. Classification of bonds by difference in electronegativity Difference Bond Type 0 Covalent ≥ 2 Ionic 0
- 14. Cs – 0.7 Cl – 3.0 3.0 – 0.7 = 2.3 Ionic H – 2.1 S
- 15. Draw skeletal structure of compound showing what atoms are bonded to each other. Put least electronegative
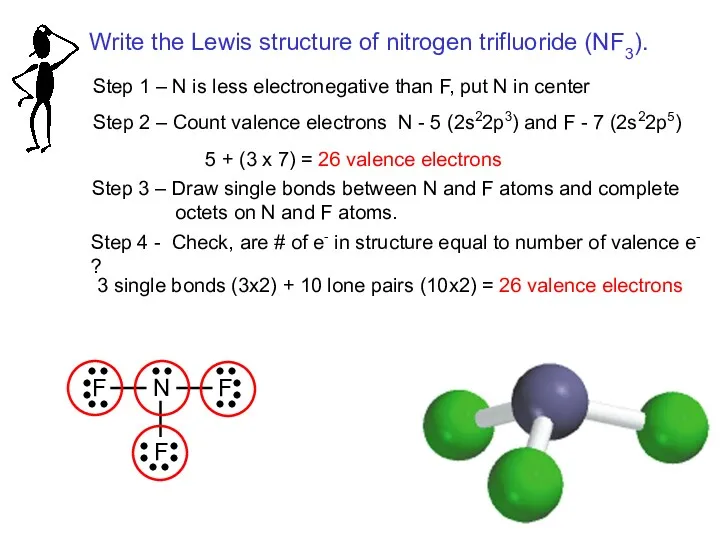
- 16. Step 1 – N is less electronegative than F, put N in center Step 2 –
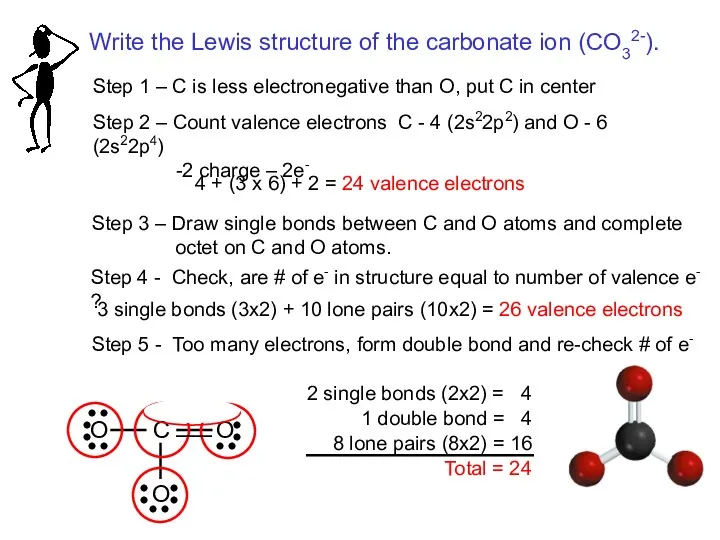
- 17. Step 1 – C is less electronegative than O, put C in center Step 2 –
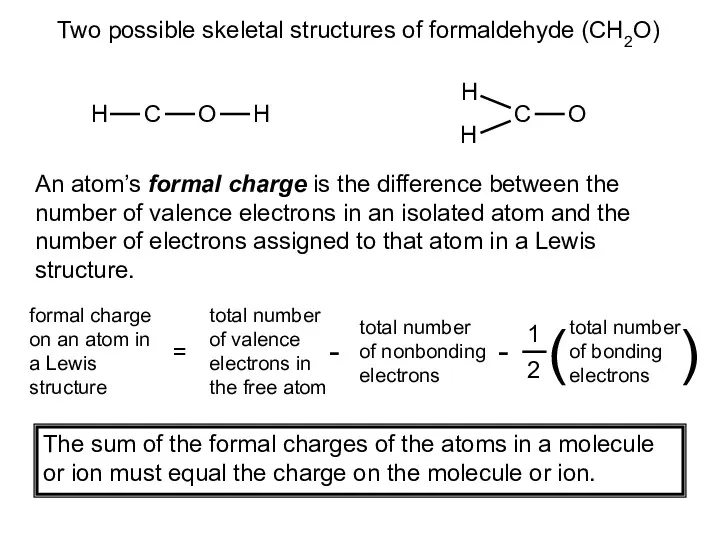
- 18. Two possible skeletal structures of formaldehyde (CH2O) An atom’s formal charge is the difference between the
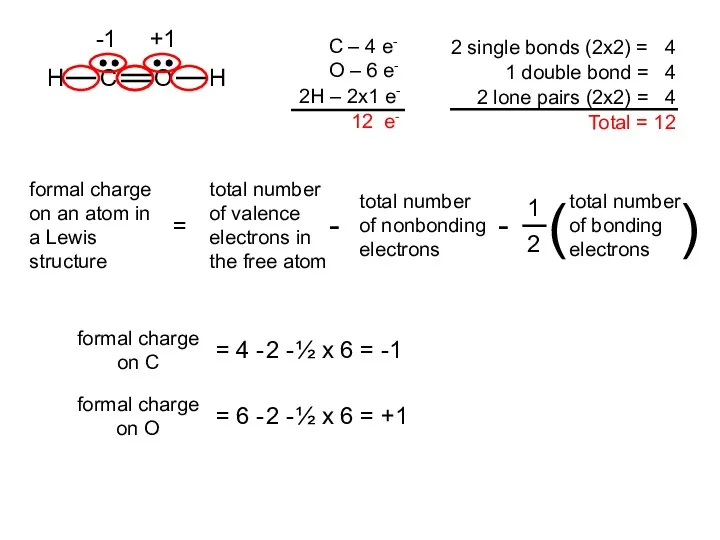
- 19. formal charge on C = 4 - 2 - ½ x 6 = -1 formal charge
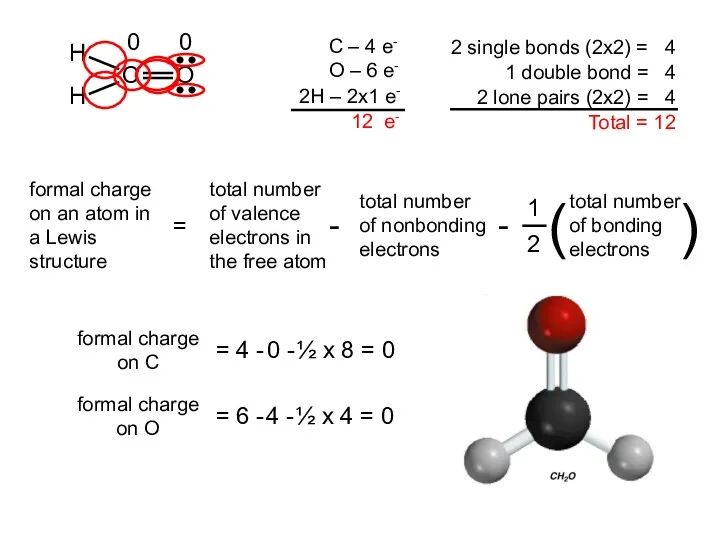
- 20. formal charge on C = 4 - 0 - ½ x 8 = 0 formal charge
- 22. Скачать презентацию
![The Ionic Bond 1s22s1 1s22s22p5 1s2 1s22s22p6 [He] [Ne]](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/267522/slide-3.jpg)



 Основы коррозии и защиты металлов
Основы коррозии и защиты металлов Антибиотики как ЛС
Антибиотики как ЛС Сера. Аллотропия серы. Физические и химические свойства серы. Применение серы
Сера. Аллотропия серы. Физические и химические свойства серы. Применение серы Аналитическая химия
Аналитическая химия Сполуки нітрогену з оксигеном
Сполуки нітрогену з оксигеном Органическая химия. Подготовка к контрольной работе № 2
Органическая химия. Подготовка к контрольной работе № 2 λ-MnO2 as material with pseudocapacitive properties
λ-MnO2 as material with pseudocapacitive properties Магній. Знаходження в періодичній системі і основні характеристики
Магній. Знаходження в періодичній системі і основні характеристики Особенности организации обучения химии в рамках компетентностно-ориентированной модели образования
Особенности организации обучения химии в рамках компетентностно-ориентированной модели образования Теоретическая электрохимия
Теоретическая электрохимия Серная кислота и её свойства
Серная кислота и её свойства Аналитические методы
Аналитические методы Гетерофункциональные производные бензольного ряда как лекарственные средства. Гетероциклические соединения. Алкалоиды
Гетерофункциональные производные бензольного ряда как лекарственные средства. Гетероциклические соединения. Алкалоиды Значення періодичного закону
Значення періодичного закону Превращение (S)-бутанол-2 в другие соединения
Превращение (S)-бутанол-2 в другие соединения Химия. 6я группа элементов. 9 класс
Химия. 6я группа элементов. 9 класс Химическая связь
Химическая связь Арены. Бензол. Урок химии. 10 класс
Арены. Бензол. Урок химии. 10 класс Коррозия металлов
Коррозия металлов БАЗ-ды алу. БАЗ өндірудегі шикізат базасы. 2 Лекция
БАЗ-ды алу. БАЗ өндірудегі шикізат базасы. 2 Лекция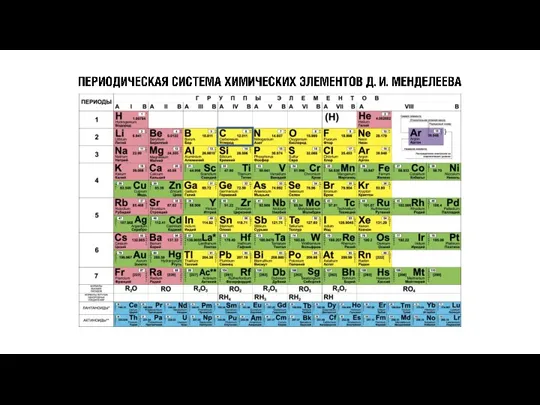 Периодическая система химических элементов Д.И. Менделеева
Периодическая система химических элементов Д.И. Менделеева Химические свойства кислот как электролитов
Химические свойства кислот как электролитов Силикаты. Гранат. Берилл
Силикаты. Гранат. Берилл Прочность полимеров
Прочность полимеров Химические элементы IV группы главной подгруппы
Химические элементы IV группы главной подгруппы Алкадиены. Гомологический ряд, номенклатура и изомерия
Алкадиены. Гомологический ряд, номенклатура и изомерия Классификация органических соединений
Классификация органических соединений Theories of acids and bases. Ionic equilibria in electrolyte solutions. Buffer solutions (topic 3.4)
Theories of acids and bases. Ionic equilibria in electrolyte solutions. Buffer solutions (topic 3.4)