Chemical reaction rate. Influence of conditions on the rate of chemical reactions. Catalysis. Topic 3.2 презентация
Содержание
- 2. Outline Introduction Main part 1.The concept of the rate of chemical reactions 2. Influence of the
- 3. 1.The concept of the rate of chemical reactions A branch of chemistry that studies the rate
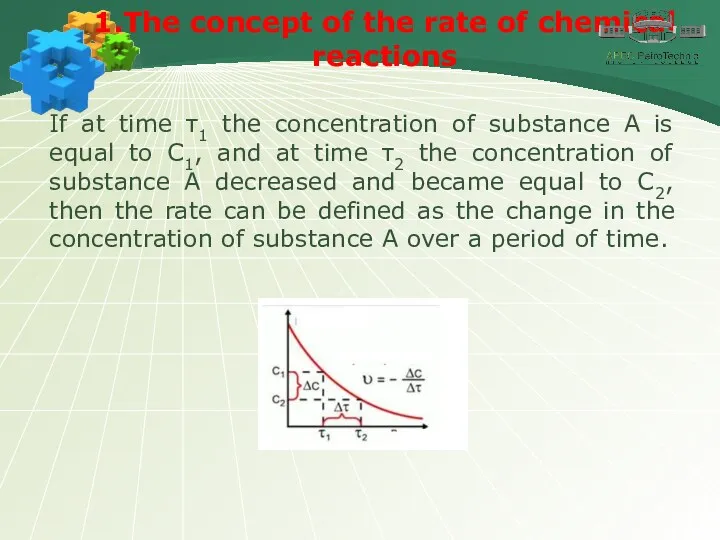
- 5. 1.The concept of the rate of chemical reactions If at time τ1 the concentration of substance
- 6. 1.The concept of the rate of chemical reactions The rate is positive and the concentration of
- 7. 1.The concept of the rate of chemical reactions The rate of a chemical reaction depends on:
- 8. 2.Influence of the nature of reactants on the rate of a chemical reaction In aqueous solutions,
- 9. 2.Influence of the nature of reactants on the rate of a chemical reaction Substances with non-polar
- 10. 3.Influence of the concentration of reactants on the rate of a chemical reaction With an increase
- 11. Law of mass action : the rate of a chemical reaction is directly proportional to the
- 12. The kinetic equation of the reaction is an equation that establishes the dependence of the reaction
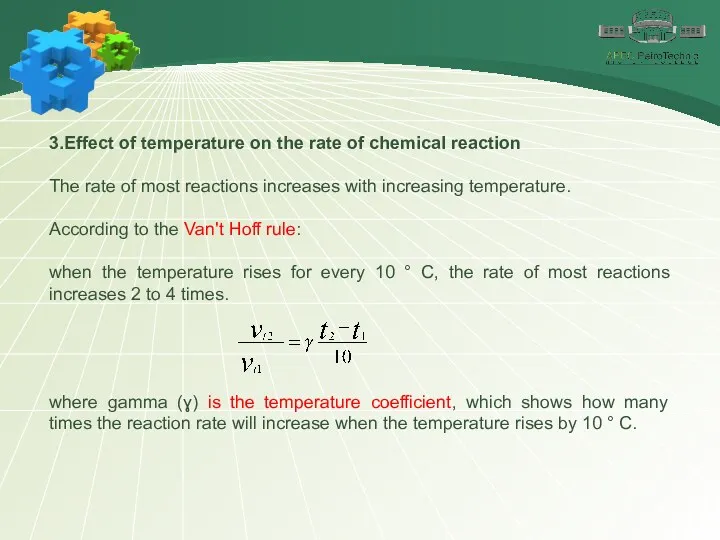
- 13. 3.Effect of temperature on the rate of chemical reaction The rate of most reactions increases with
- 14. An increase in the reaction rate with increasing temperature is associated not only with an increase
- 15. The reaction occurs only as a result of effective collisions (b) of particles with excess energy
- 16. 4.Effect of a catalyst on the rate of a chemical reaction Catalysts are substances that speed
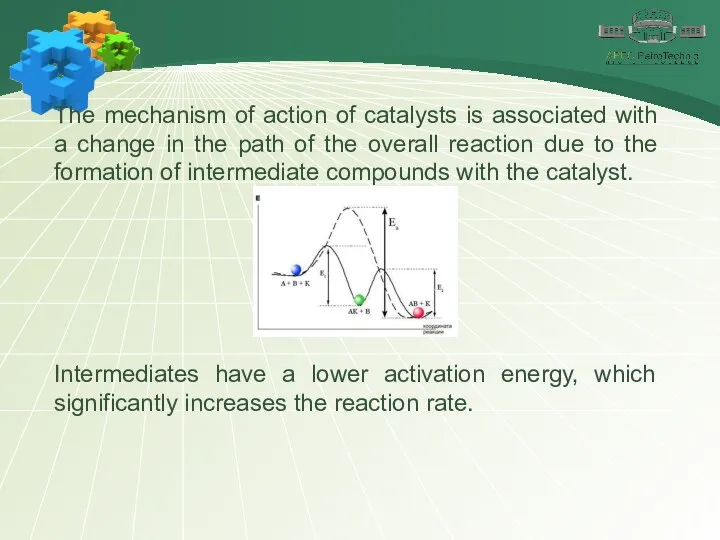
- 17. The mechanism of action of catalysts is associated with a change in the path of the
- 18. Catalysis can be homogeneous or heterogeneous. With homogeneous catalysis, the reactants and the catalyst are in
- 19. Questions for self control 1.Complete the sentence. Chemical reaction rate ... A)independent of temperature B)depends on
- 20. 4.Choose the correct statement for homogeneous catalysis : A)the aggregate state of the catalyst and the
- 21. Literature 1.Basic literature : 1. Jenkins, Chemistry, ISBN 978-0-17-628930-0 2. Alberta Learning, Chemistry data booklet 2010,
- 22. 2.Additional literature : 1.Б.А.Мансуров «Химия» 10-11 кл., Атамура 2015 г 2.Б.Мансуров., Н.Торшина «Методика преподавания органической химии»
- 24. Скачать презентацию


















 Химические свойства металлов
Химические свойства металлов Золото. Что о нём мы можем рассказать?
Золото. Что о нём мы можем рассказать? d-элементы
d-элементы Подготовка к ВПР по химии. 11 класс
Подготовка к ВПР по химии. 11 класс Метаболизм кетоновых тел. Метаболизм холестерина
Метаболизм кетоновых тел. Метаболизм холестерина Химический потенциал. Фазовые равновесия
Химический потенциал. Фазовые равновесия Кислотные дожди
Кислотные дожди The Molecules of Life
The Molecules of Life Цинк и его соединения
Цинк и его соединения Фосфор и его соединения
Фосфор и его соединения Химия воды
Химия воды Закономірності протікання хімічних реакцій
Закономірності протікання хімічних реакцій Классификация химических элементов
Классификация химических элементов Способы выражения состава раствора. Задача 7
Способы выражения состава раствора. Задача 7 НЮ 2.1.1. Металлы - общая характеристика
НЮ 2.1.1. Металлы - общая характеристика Гониометрическое исследование кристаллов
Гониометрическое исследование кристаллов Сплавы железа с углеродом: стали и чугуны
Сплавы железа с углеродом: стали и чугуны Багатоатомні насичені спирти. Фізичні та хімічні властивості. Добування і застосування
Багатоатомні насичені спирти. Фізичні та хімічні властивості. Добування і застосування Мінерали та гірські породи
Мінерали та гірські породи Серная кислота
Серная кислота Electrolysis
Electrolysis Вещества
Вещества Карбон қышқылдары, жіктелуі, сипаттамалары, таралуы
Карбон қышқылдары, жіктелуі, сипаттамалары, таралуы Аминокислоты 2
Аминокислоты 2 Метаболизм углеводов
Метаболизм углеводов Спектральные методы: атомная спектроскопия
Спектральные методы: атомная спектроскопия Валентность и степень окисления. Химическая связь
Валентность и степень окисления. Химическая связь Альдегіди. Карбонові кислоти. Одержання. Фізичні та хімічні властивості
Альдегіди. Карбонові кислоти. Одержання. Фізичні та хімічні властивості