Содержание
- 2. Lesson objectives Introduce the concept of futures and forward contracts. Consider differences between futures and forwards.
- 3. Introduction Forward and future contracts represent one of the basic types of financial derivatives. Both futures
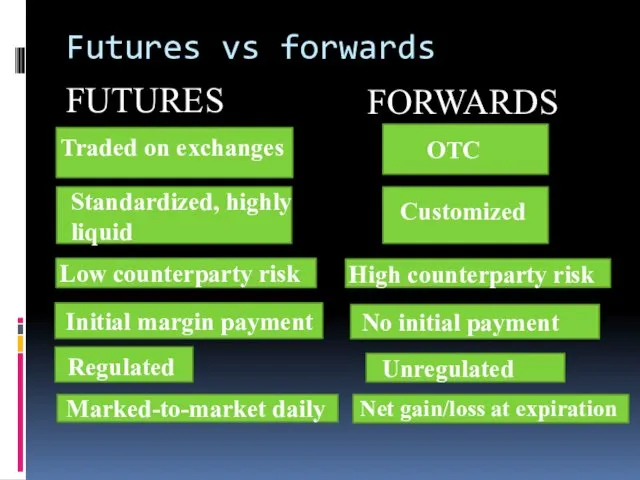
- 4. Futures vs forwards FUTURES FORWARDS Traded on exchanges Regulated Standardized, highly liquid Low counterparty risk Initial
- 5. Example of commodity futures contract NYMEX crude oil futures with delivery in Dec 2008 traded in
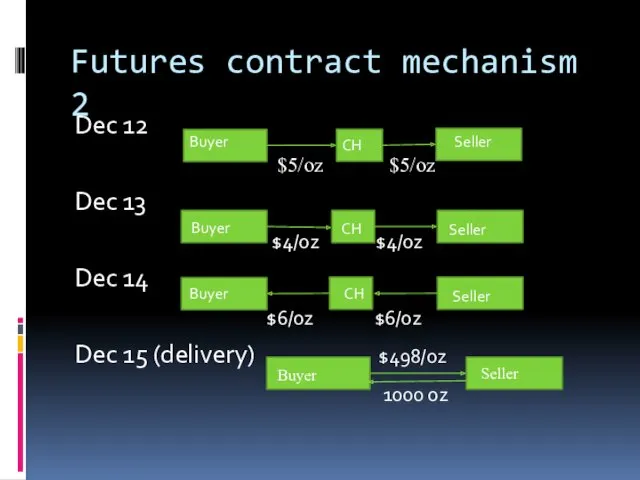
- 6. Futures contract mechanism 1 Example: futures contract for 1000 ounces of gold concluded on Dec 12
- 7. Futures contract mechanism 2 Dec 12 $5/oz $5/oz Dec 13 $4/oz $4/oz Dec 14 $6/oz $6/oz
- 8. Forward contract definition Seller Seller Buyer Buyer
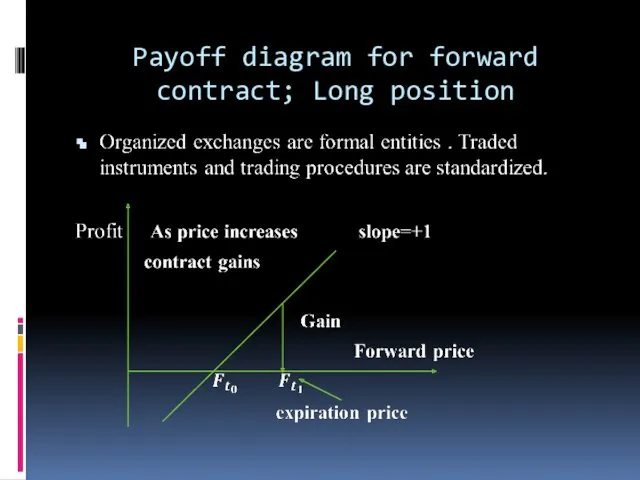
- 9. Payoff diagram for forward contract; Long position
- 10. Types of forward and future contracts Forwards on interest rates Forwards on currencies Futures on commodities
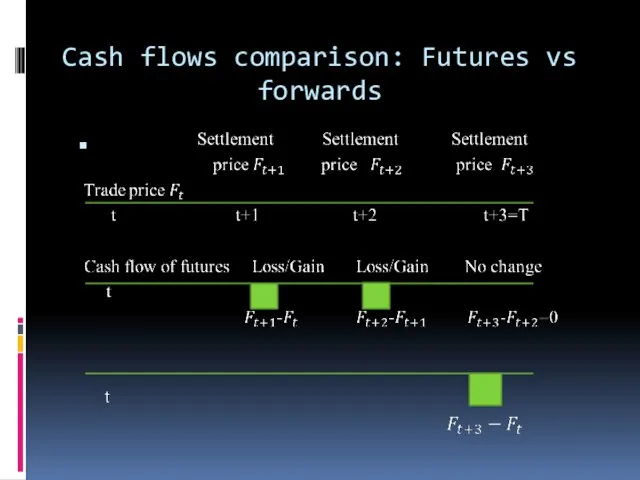
- 11. Cash flows comparison: Futures vs forwards
- 12. Forward and futures prices Forward and futures contract prices can be derived from spot market prices
- 13. Forward and futures prices 2
- 14. Forward and futures prices 3
- 15. Forward and futures prices 4
- 16. Synthetic instrument concept Financial instruments can be visualized as bundles of cash flows, which allows to
- 17. Forward loan
- 18. Forward loan importance Forward loan is successfully used in the following cases: a) Business wants to
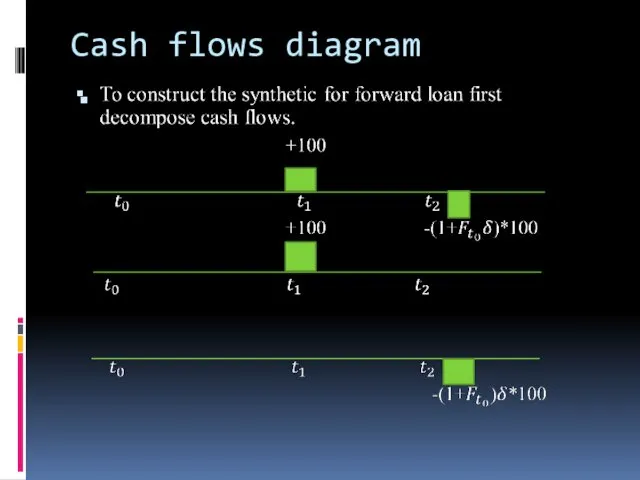
- 19. Cash flows diagram
- 20. Cash flows diagram 2
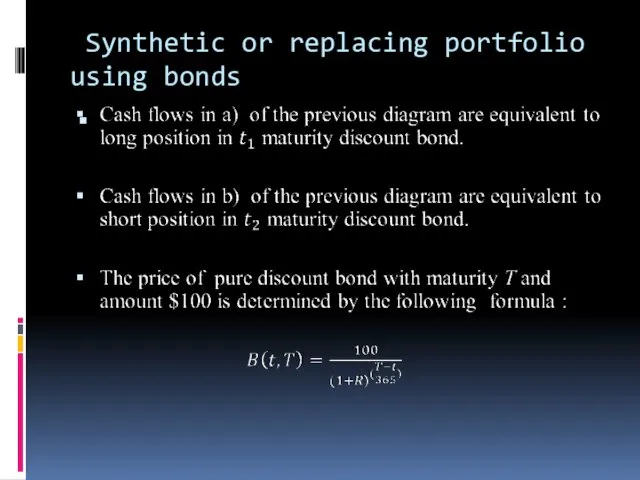
- 21. Synthetic or replacing portfolio using bonds
- 22. Synthetic or replacing portfolio using bonds 2
- 23. Synthetic or replacing portfolio using bonds 3
- 24. Synthetic using money market instrument
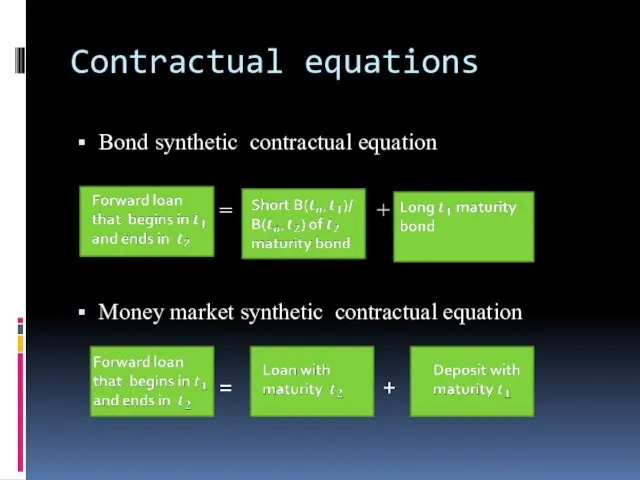
- 25. Contractual equations Bond synthetic contractual equation = + Money market synthetic contractual equation = +
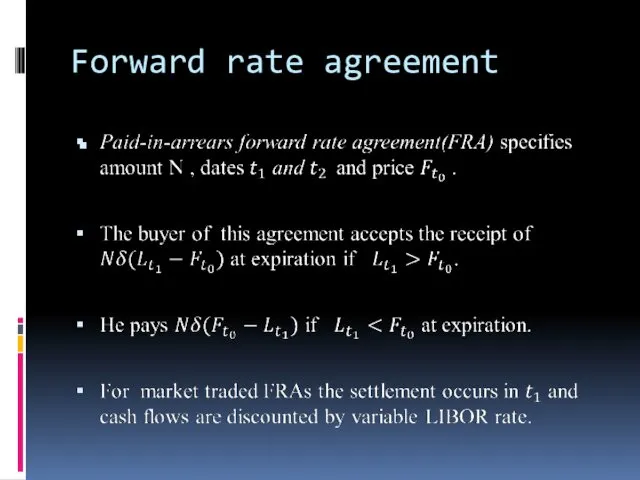
- 26. Forward rate agreement
- 28. Скачать презентацию

















 Institutional developments worldwide and in the EU with regard to financial stability
Institutional developments worldwide and in the EU with regard to financial stability ҚР Ұлттық банкі еңбек қатынастары
ҚР Ұлттық банкі еңбек қатынастары Положения по международной аудиторской практике с использованием КИС в ходе аудита
Положения по международной аудиторской практике с использованием КИС в ходе аудита Налогообложение физических лиц в РФ
Налогообложение физических лиц в РФ ЛЕКЦИЯ № 3
ЛЕКЦИЯ № 3 Стипендиальное обеспечение студентов Южно-Уральского государственного университета
Стипендиальное обеспечение студентов Южно-Уральского государственного университета Загальний огляд системи. Тендерні пропозиціі
Загальний огляд системи. Тендерні пропозиціі Оценка эффективности проекта
Оценка эффективности проекта Налоговый контроль
Налоговый контроль Государственный бюджет
Государственный бюджет Організація обліку розрахунків за виплатами працівникам
Організація обліку розрахунків за виплатами працівникам Matryoshka. Annual Report. Эффективность собственных каналов продаж
Matryoshka. Annual Report. Эффективность собственных каналов продаж Банковские гарантии
Банковские гарантии ОСНОВНЫЕ СРЕДСТВА
ОСНОВНЫЕ СРЕДСТВА Особенности развития аудита в Южной Корее
Особенности развития аудита в Южной Корее Рекомендации по составлению финансового отчета в рамках социального проекта
Рекомендации по составлению финансового отчета в рамках социального проекта Расчеты, сбережения, кредиты
Расчеты, сбережения, кредиты Всеобщее декларирование доходов и имущества физических лиц
Всеобщее декларирование доходов и имущества физических лиц Аналіз джерел формування капіталу. Лекція 5
Аналіз джерел формування капіталу. Лекція 5 Управление рисками на инвестиционной фазе
Управление рисками на инвестиционной фазе Бюджетное устройство
Бюджетное устройство Инвестиционный паспорт Котласского муниципального округа Архангельской области
Инвестиционный паспорт Котласского муниципального округа Архангельской области Учет и аудит расчетов с персоналом по оплате труда
Учет и аудит расчетов с персоналом по оплате труда Меншікті капитал-корпорация
Меншікті капитал-корпорация Отчет по экологическому проекту инициативного бюджетирования
Отчет по экологическому проекту инициативного бюджетирования Несостоятельность (банкротство) коммерческих организаций
Несостоятельность (банкротство) коммерческих организаций Бухгалтерлік есептің нысандары
Бухгалтерлік есептің нысандары Облік фінансових інвестицій
Облік фінансових інвестицій