Содержание
- 2. Banks Provide to the money launderer multiple services for placement, layering and integration
- 3. The Money Laundering Process Placement Layering Integration
- 4. Placement The initial movement of criminally derived currency or other proceeds of crime, to initially change
- 5. Forms of Placement Depositing into accounts via tellers, ATMs, or night deposits Changing currency to cashiers
- 6. Layering The process of separating the proceeds of criminal activity from their origin.. Disguising the origin
- 7. Integration The process of using an apparent legitimate transaction to disguise the illicit proceeds allowing the
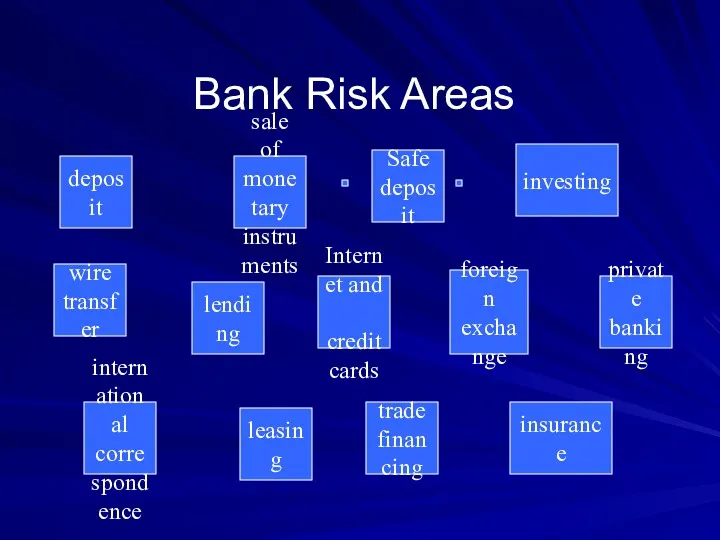
- 8. Bank Risk Areas wire transfer lending investing private banking international correspondence trade financing Safe deposit insurance
- 9. High Risk Countries Countries in which the production or transportation of illegal drugs may be taking
- 10. Depositing Laundered Funds Use of third parties (SMURFS) Deposits under reporting requirements Deposits from front businesses
- 11. Suspicious Signs in Banks Increase in cash shipments without increase in number of accounts Cash on
- 12. Suspicious Signs in Bank Cash shipments which appear large in comparison to dollar volume of currency
- 13. Suspicious Sale of Monetary Instruments When large volume of cashiers checks, money orders or travelers checks
- 14. Suspicious Currency Exchange Large volume of currency exchange for cash When the need for foreign currency
- 15. Safe Deposit Frequent trips to safe deposit prior to movement of funds out of the bank
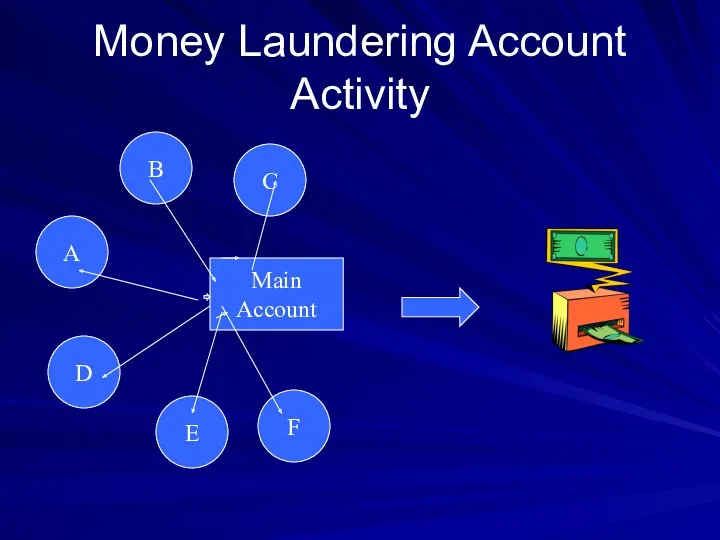
- 16. Money Laundering Account Activity A B C D E F Main Account
- 17. Offshore Funds are wired to: Europe, US and to bank secrecy countries shell corporations Back to
- 18. Wire Transfer Launderers wire funds: form bank to bank from bank to shell companies overseas from
- 19. International Correspondent Accounts Banks enter into agreement with larger international banks to process and complete transactions
- 20. International Correspondent Accounts Problems Banks don't conduct sufficient due diligence review of their foreign bank clients,
- 21. Private Banking Offers money launderers full line of bank services More privacy and more confidentiality Less
- 22. Trusts Trust departments create fiduciary relationship in which bank maintains little control Trustee must follow customers
- 23. Payable Through Account Payable through accounts also known as pass through or pass by accounts are
- 24. Payable Through Accounts Foreign banks provide checks to sub account holders to draw on foreign banks
- 25. Lending Launderers often: use cash or certificates of deposits as collateral for loans Payoff loans early
- 26. Lending Possible money laundered loans are: Request to borrower against assets held by the bank or
- 27. Suspicious Lending Request for loans to offshore commercial companies, or loans secured by obligations of offshore
- 28. Letters of Credit Launderers use: bogus letters of credit Letters of credit for bogus services Letters
- 29. Discount brokerage, Securities and Investment Larger or unusual settlements of security with no discernable purpose or
- 30. Securities Request by Customer for investment management services(either foreign currency or securities) where the source of
- 31. Securities Derivatives trading using two accounts which take from one account and pass the proceeds to
- 32. Insurance Launderers purchase for quick turnaround Arrange payment to a third party Cancel policies early Make
- 33. Bank Involvement Examiners and bank management must be aware of this extremely sensitive area. Nevertheless, there
- 34. Leasing Examples
- 35. Credit card Loading up card
- 36. Internet Funds transfers
- 37. Bank Employees and Agents Lavish lifestyle which cannot be supported by an employees salary Absence of
- 38. Lavish Lifestyle Appearance that doesn't fit the norm designer clothes, expensive watches, expensive automobiles But Could
- 39. Systems and Controls Particular staff having a history of failing to obtain necessary approvals, or over-riding
- 40. New Money Laundering Schemes Each Year the Financial Action Task Force Shares information on new money
- 41. Securities dealers, managers and other markets
- 42. Multiple entities brokers dealers, funds managers, markets For example introducing broker and clearing broker Markets vs.
- 43. Approach is same as banking Regulations and inspections Compliance program for entities
- 44. Layering and Integration phase Most entities don’t deal in cash Use bank transfers Cash sometimes used
- 45. Securities Commission Inspections Money laundering inspections conducted in concert with inspections for violations of regulations or
- 46. Risk Areas Account opening Cash handling Wire transfer operations Margin accounts
- 47. Advantages for money launderers Launder money Make a profit Commit other securities fraud
- 48. Money laundering examples Purchase of securities for short period of time with no discernable purpose. Selling
- 49. Insurance products, agents and companies
- 50. Product Distribution makes for difficult regulation and compliance Direct marketing Intermediaries Independents Associated with companies
- 51. Risk Areas Customer identification and sales Pay out on policies
- 52. Same approach Regulation Compliance program
- 54. Скачать презентацию
















































 LCCI
LCCI Кредитование
Кредитование Правовое регулирование бюджетного процесса. Тема 5
Правовое регулирование бюджетного процесса. Тема 5 Управление оборотным капиталом
Управление оборотным капиталом Негосударственные пенсионные фонды
Негосударственные пенсионные фонды Валюта. Валютные курсы
Валюта. Валютные курсы О бюджете на 2020-2022 гг. Главное
О бюджете на 2020-2022 гг. Главное Субсидиарная ответственность
Субсидиарная ответственность Эффективность деятельности предприятия
Эффективность деятельности предприятия Учет основного капитала предприятия
Учет основного капитала предприятия Лекции по дисциплине Аудит. Стандарты аудита. Организация аудиторской деятельности. Лекции по дисциплине АУДИТ
Лекции по дисциплине Аудит. Стандарты аудита. Организация аудиторской деятельности. Лекции по дисциплине АУДИТ Vērtspapīri
Vērtspapīri Банк туралы түсінік, оның түрлері, қызметтері. Қазақстандағы банк жүйесі
Банк туралы түсінік, оның түрлері, қызметтері. Қазақстандағы банк жүйесі Виды кредитов
Виды кредитов Реализация проектов инициативного бюджетирования в Чайковском городском поселении
Реализация проектов инициативного бюджетирования в Чайковском городском поселении Роль биржи на финансовом рынке
Роль биржи на финансовом рынке ООО ЗооГрад Хабаровск. Система скидок на продукцию 2018 года
ООО ЗооГрад Хабаровск. Система скидок на продукцию 2018 года Оценка финансового состояния предприятия
Оценка финансового состояния предприятия Положения Банка России №383-П, №384-П (или платежные и расчетные системы)
Положения Банка России №383-П, №384-П (или платежные и расчетные системы) Управление проектам. Финансирование инвестиционных проектов
Управление проектам. Финансирование инвестиционных проектов Анализ учета труда и заработной платы
Анализ учета труда и заработной платы Споживче кредитування
Споживче кредитування Финансовый менеджмент
Финансовый менеджмент Общая характеристика региональных налогов в РФ
Общая характеристика региональных налогов в РФ Мәдениет саласындағы баға белгілеу
Мәдениет саласындағы баға белгілеу Управление портфелем ценных бумаг. Портфельные стратегии
Управление портфелем ценных бумаг. Портфельные стратегии Охрана труда. Финансирование
Охрана труда. Финансирование Пособие по временной нетрудоспособности (ПВН)
Пособие по временной нетрудоспособности (ПВН)