Содержание
- 2. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. Agenda The Nature of Price Price and Nonprice
- 3. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. The Nature of Price Price The value exchanged
- 4. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. The Nature of Price (cont’d) The Importance of
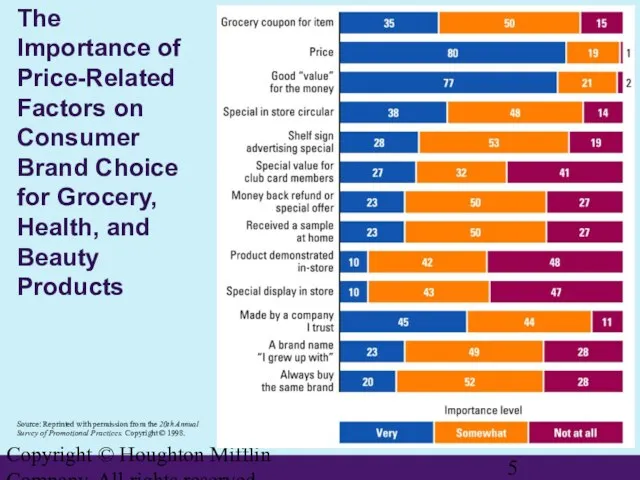
- 5. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. The Importance of Price-Related Factors on Consumer Brand
- 6. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. Price and Nonprice Competition Price Competition Emphasizing price
- 7. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. Price and Nonprice Competition (cont’d) Nonprice Competition Emphasizing
- 8. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. Price and Nonprice Competition (cont’d) Nonprice Competition (cont’d)
- 9. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. Orbitz Allows People to Save Up to 75%
- 10. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. Hertz Emphasizes Its Benefits to Small Businesses
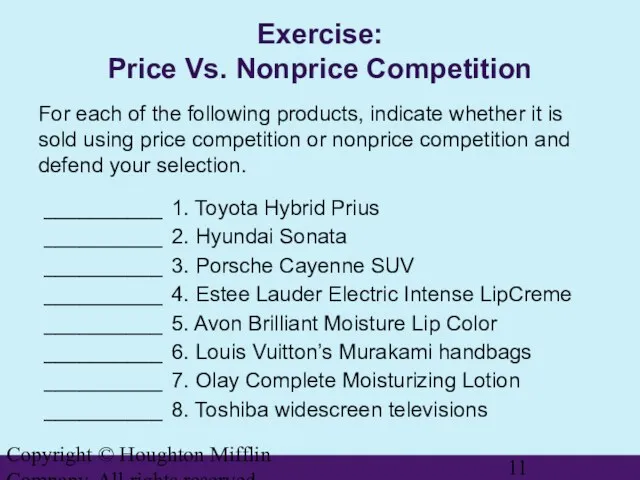
- 11. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. Exercise: Price Vs. Nonprice Competition For each of
- 12. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. Debate Issue Is price competition more effective than
- 13. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. Analysis of Demand The Demand Curve A graph
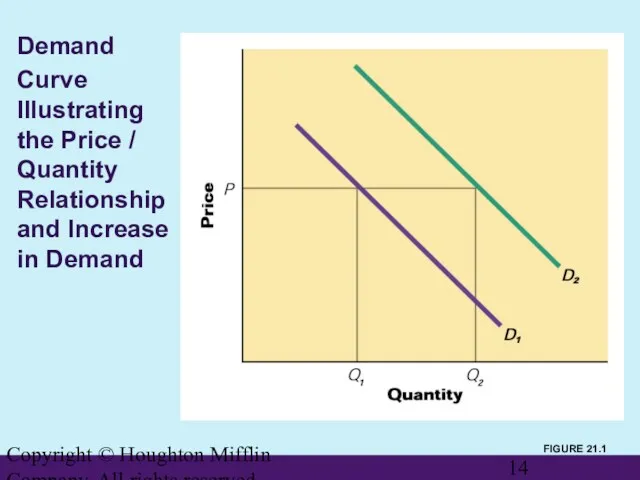
- 14. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. Demand Curve Illustrating the Price / Quantity Relationship
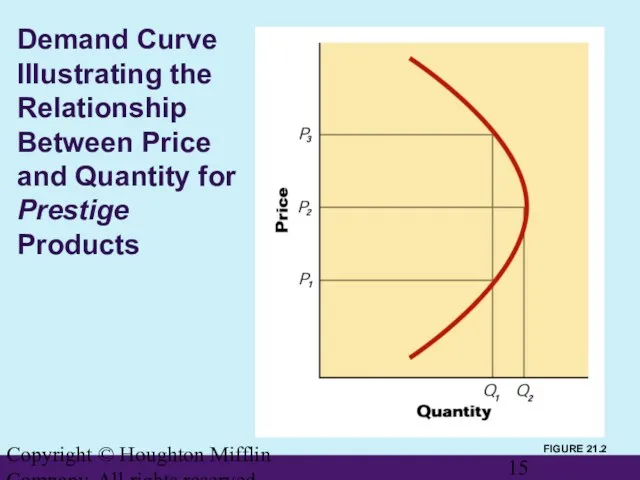
- 15. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. Demand Curve Illustrating the Relationship Between Price and
- 16. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. Analysis of Demand (cont’d) Demand Fluctuations Changes in
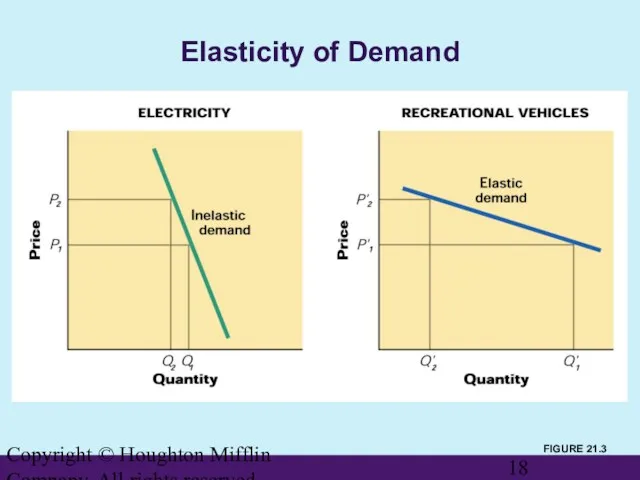
- 17. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. Analysis of Demand (cont’d) Assessing Price Elasticity of
- 18. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. Elasticity of Demand FIGURE 21.3
- 19. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. Demand, Cost, and Profit Relationships Marginal Analysis Examines
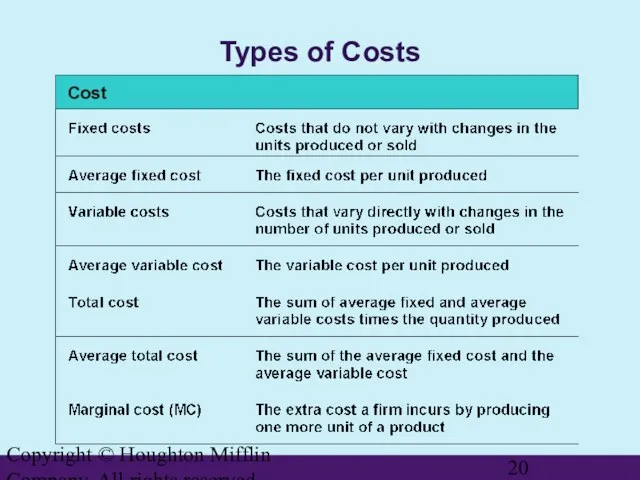
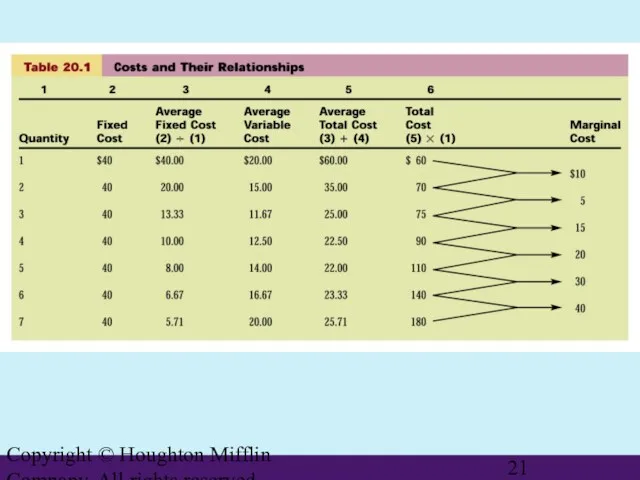
- 20. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. Types of Costs
- 21. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
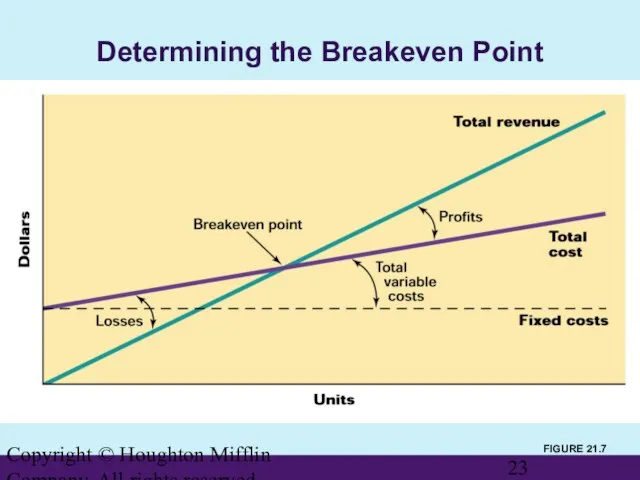
- 22. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. Breakeven Analysis Breakeven Point The point at which
- 23. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. FIGURE 21.7 Determining the Breakeven Point
- 24. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. Exercise Breakeven Analysis Assume you are selling pizzas
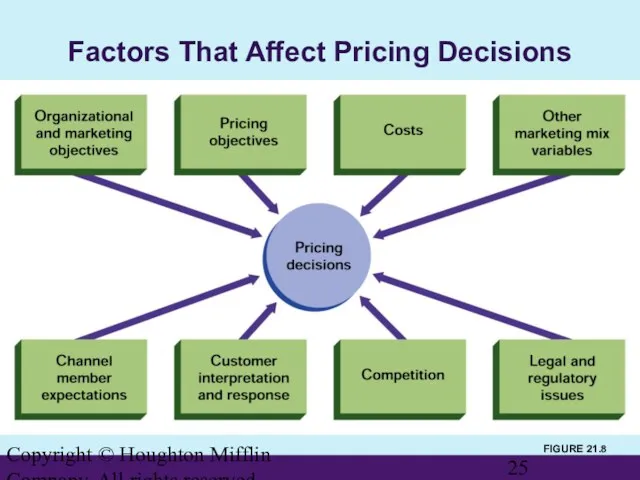
- 25. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. FIGURE 21.8 Factors That Affect Pricing Decisions
- 26. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. Factors Affecting Pricing Decisions Organizational and Marketing Objectives
- 27. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. Factors Affecting Pricing Decisions (cont’d) Costs Set a
- 28. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. Factors Affecting Pricing Decisions (cont’d) Channel Member Expectations
- 29. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. Factors Affecting Pricing Decisions (cont’d) Customers’ Interpretation and
- 30. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. Factors Affecting Pricing Decisions (cont’d) Buyers’ responses to
- 31. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. Factors Affecting Pricing Decisions (cont’d) Competition Pricing to
- 32. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. Selection of a Basis for Pricing (pp. 591-594)
- 33. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved. Exercise Prices of personal computers continue to drop
- 35. Скачать презентацию























 Preparing Financial Statements
Preparing Financial Statements Деловые бумаги
Деловые бумаги Халықаралық қаржылық есеп стандарттары
Халықаралық қаржылық есеп стандарттары Опционные стратегии. Сочетания опционов и акций
Опционные стратегии. Сочетания опционов и акций Финансовоматематические основы инвестиционного проектирования. Тема 3
Финансовоматематические основы инвестиционного проектирования. Тема 3 Проведение операций по потребительскому кредитованию физических лиц
Проведение операций по потребительскому кредитованию физических лиц Индивидуальный лицевой счет застрахованного лица
Индивидуальный лицевой счет застрахованного лица Тема 8. Концепція управління ефективністю бізнесу в системі стратегічного фінансового контролінгу
Тема 8. Концепція управління ефективністю бізнесу в системі стратегічного фінансового контролінгу Основные итоги и ключевые задачи в сфере развития бюджетной методологии
Основные итоги и ключевые задачи в сфере развития бюджетной методологии Кәсіпорын активтерін басқару жүйесін әзірлеу
Кәсіпорын активтерін басқару жүйесін әзірлеу Методы оценки коммерческой эффективности инвестиционных проектов
Методы оценки коммерческой эффективности инвестиционных проектов Фундаментальный анализ финансовых рынков
Фундаментальный анализ финансовых рынков Денежные фонды и резервы организации
Денежные фонды и резервы организации Информационные технологии в управлении фирмой. Бизнес-решения. Рыночное окружение. (Лекция 2)
Информационные технологии в управлении фирмой. Бизнес-решения. Рыночное окружение. (Лекция 2) Кредитование аптечных организаций и их безналичные расчеты
Кредитование аптечных организаций и их безналичные расчеты Студенческий совет факультета ПМ-ПУ. Информационное собрание на тему: Повышенная академическая стипендия
Студенческий совет факультета ПМ-ПУ. Информационное собрание на тему: Повышенная академическая стипендия Реквизиты при уплате налогов в бюджет
Реквизиты при уплате налогов в бюджет Сущность и формы кредита
Сущность и формы кредита Доходы, расходы и прибыль организации
Доходы, расходы и прибыль организации Дополнительное материальное обеспечение гражданам за выдающие достижения и особые заслуги РФ
Дополнительное материальное обеспечение гражданам за выдающие достижения и особые заслуги РФ Электронные платежные системы в таможенном деле
Электронные платежные системы в таможенном деле هزینه های قابل قبول
هزینه های قابل قبول Аудит издержек производства
Аудит издержек производства Пенсия по случаю потери кормильца
Пенсия по случаю потери кормильца Затраты и расходы предприятия. Тема 5
Затраты и расходы предприятия. Тема 5 Валютная система и валютная политика государства
Валютная система и валютная политика государства Упрощенные формы бухгалтерской отчетности (законодательно-обоснованные)
Упрощенные формы бухгалтерской отчетности (законодательно-обоснованные) Предоставление субсидий субъектам МСП в 2019 году
Предоставление субсидий субъектам МСП в 2019 году