Содержание
- 2. FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING Assessment -evaluation during semester (EDS) 50% -test 80% (week 5) -test quizzes 20% -exam
- 3. References Horngren, C.T., Sundem, G.L., Elliot, J.A., Philbrick, D, Introduction to Financial Accounting, 11th edition, Pearson,
- 4. Course description: Financial statements Recording Transactions Accrual Accounting and Income Balance Sheet: A +B +C A.
- 5. The Financial Statements Course 1 Copyright ©2010 Pearson Education Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall.
- 6. Learning Objective 1 Use accounting vocabulary
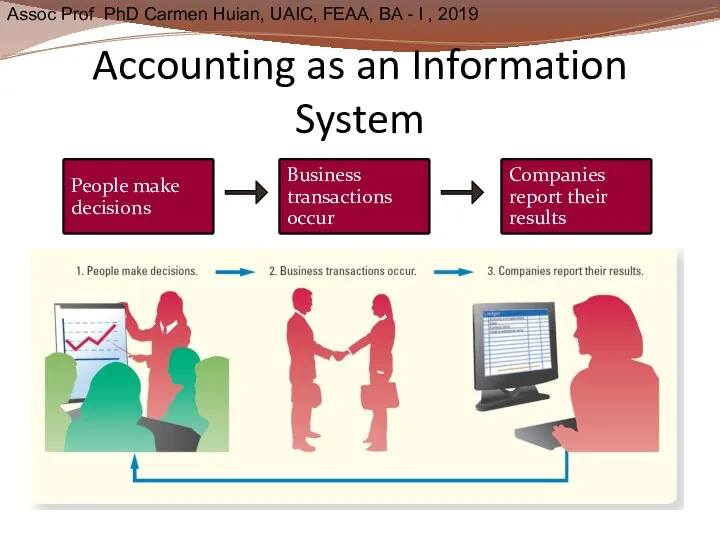
- 7. Accounting as an Information System
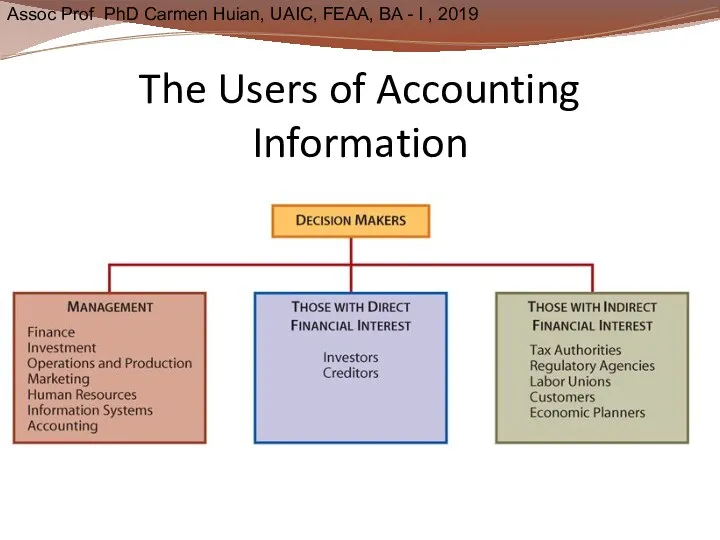
- 8. The Users of Accounting Information
- 9. Match each term with one of the three types of users of accounting information that follow:
- 10. Types of Accounting © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc.
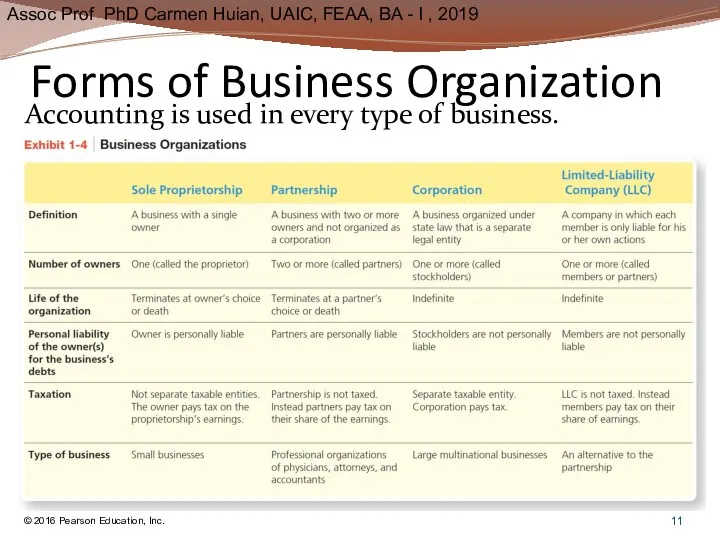
- 11. Forms of Business Organization © 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Accounting is used in every type of
- 12. Match each of the descriptions with the terms that follow: ____ 1. Issues stock a. Sole
- 13. Learning Objective Two Learn the underlying concepts, assumptions and principles of accounting
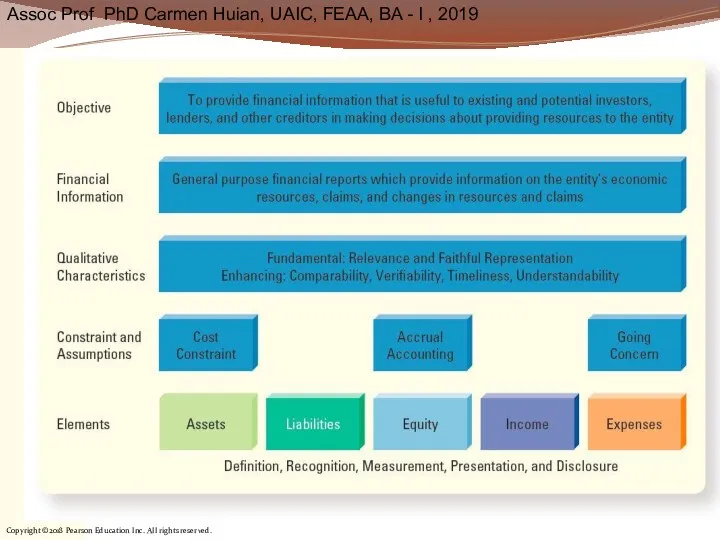
- 14. The Conceptual Framework Generally the “Why, Who, What, How” of financial reporting, it: lays the foundation
- 15. Copyright ©2018 Pearson Education Inc. All rights reserved.
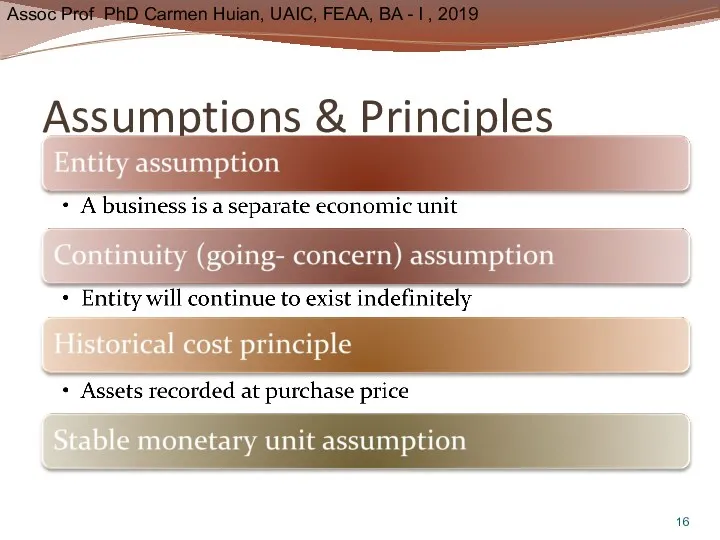
- 16. Assumptions & Principles
- 17. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) Applies to all broad concepts and detailed practices to be followed
- 18. GAAP U.S. GAAP: published by FASB Applies to financial reporting in the U.S. Used by companies
- 19. Learning Objective Three Apply the accounting equation to business organizations
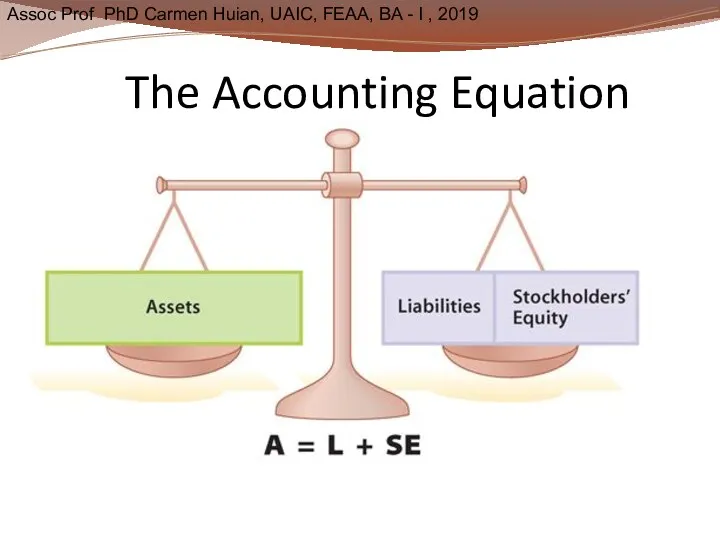
- 20. The Accounting Equation
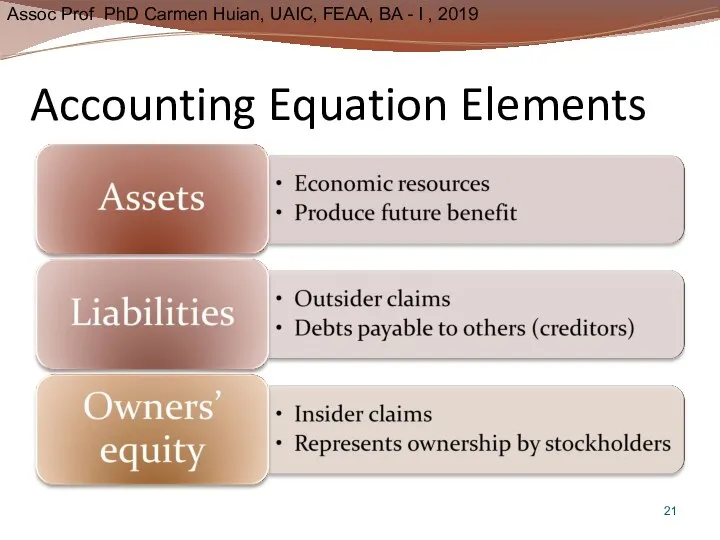
- 21. Accounting Equation Elements
- 22. ASSETS LIABILITIES Cash and cash equivalents Merchandise inventory Property, plant and equipment Accounts payable Income taxes
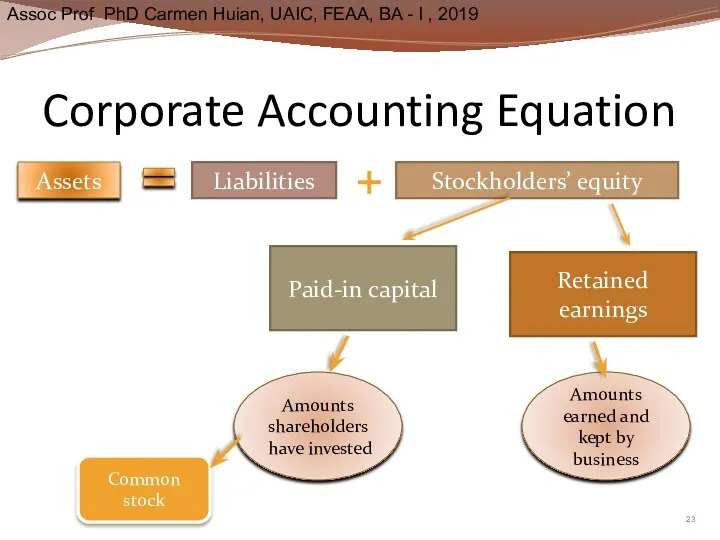
- 23. Corporate Accounting Equation Assets Liabilities Stockholders’ equity Paid-in capital Retained earnings Amounts shareholders have invested Common
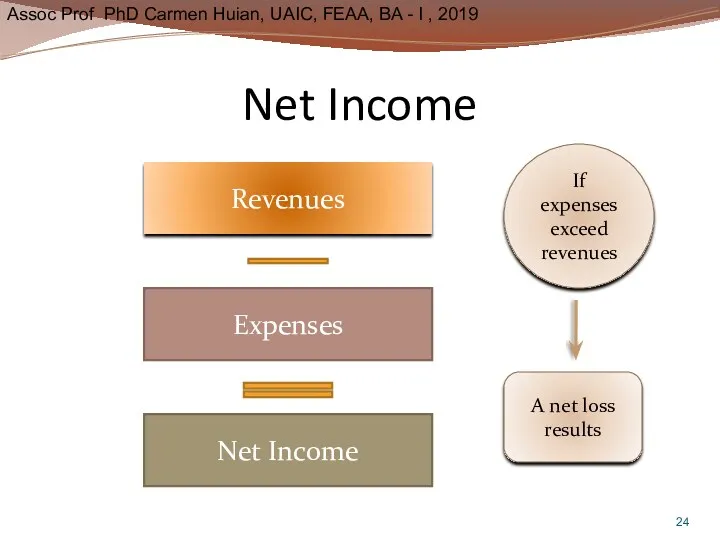
- 24. Net Income Revenues Expenses Net Income If expenses exceed revenues A net loss results
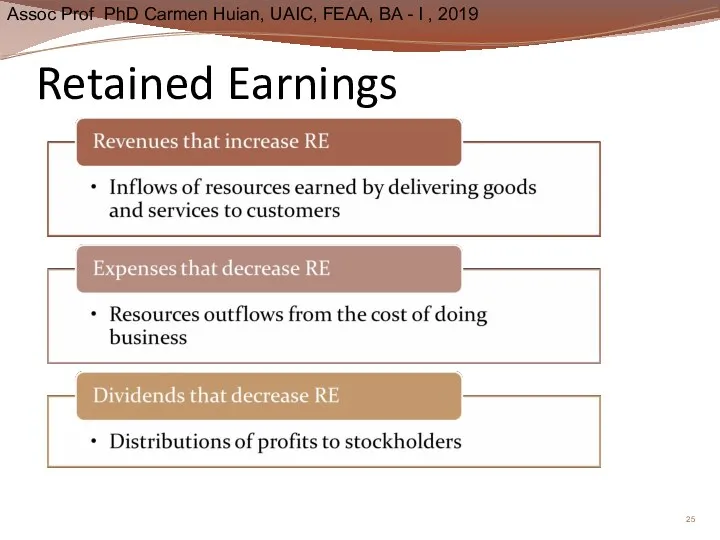
- 25. Retained Earnings
- 26. Exercise Hombran Doughnuts has: current assets of $290 million; property, plant, and equipment $490 million other
- 27. Exercise Requirements Use these data to write Hombran Doughnuts’ accounting equation. How much in resources does
- 28. Learning Objective Four Evaluate business operations
- 29. The Financial Statements
- 30. The Income Statement Also called the Statement of Operations/Earnings Reports two main categories Revenues and gains
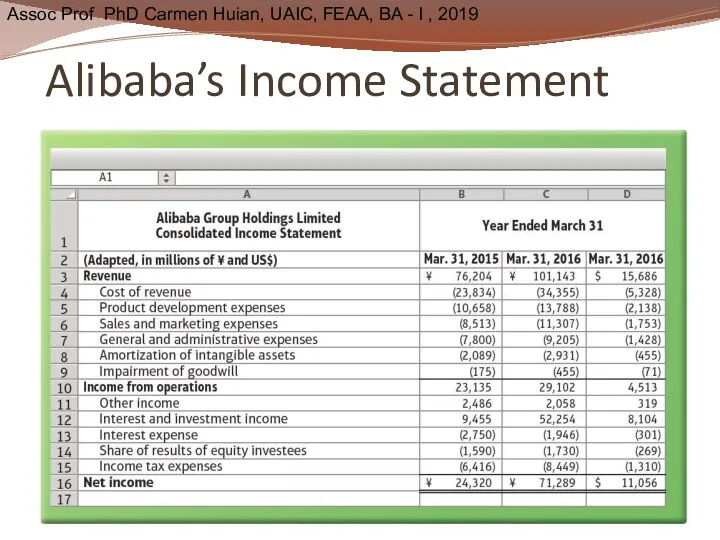
- 31. Alibaba’s Income Statement
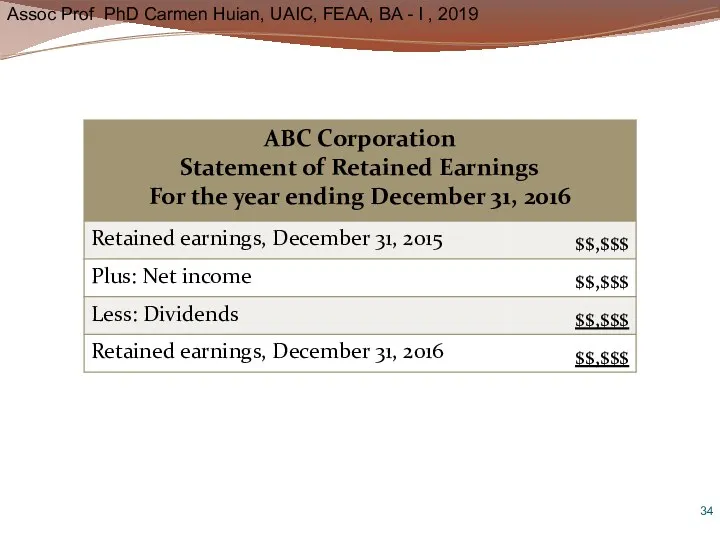
- 32. Statement of Retained Earnings Retained earnings is portion of net income company has kept Positive balance
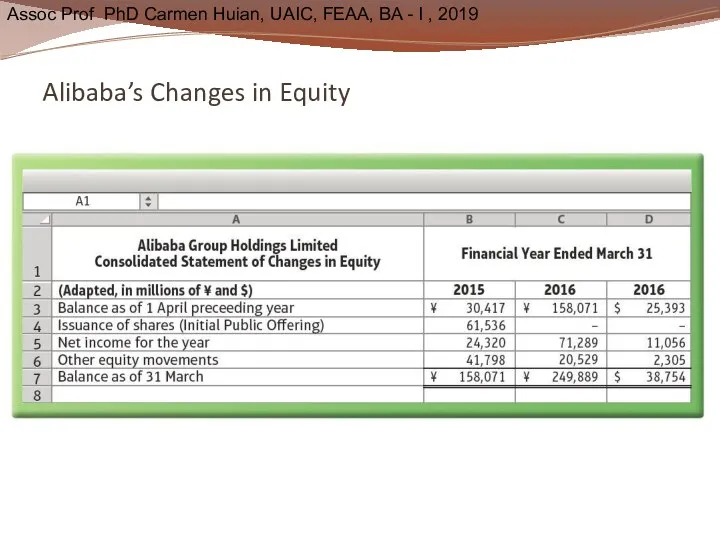
- 33. Alibaba’s Changes in Equity
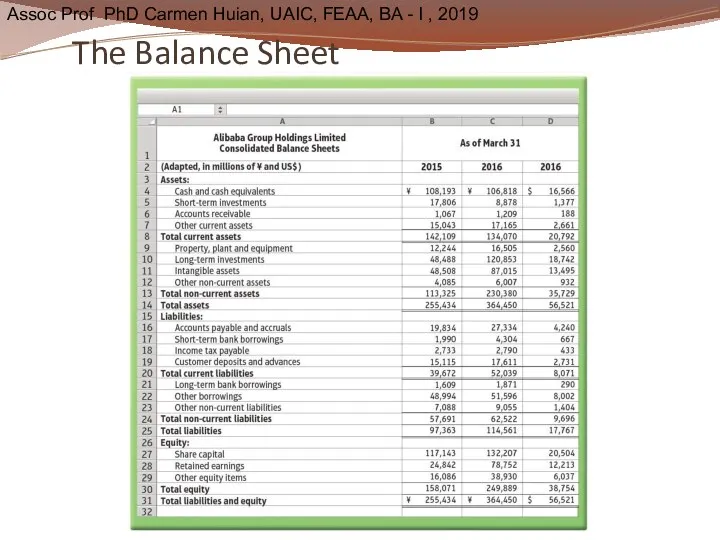
- 35. The Balance Sheet Also called the Statement of Financial Position Reports Assets Liabilities Stockholders’ equity
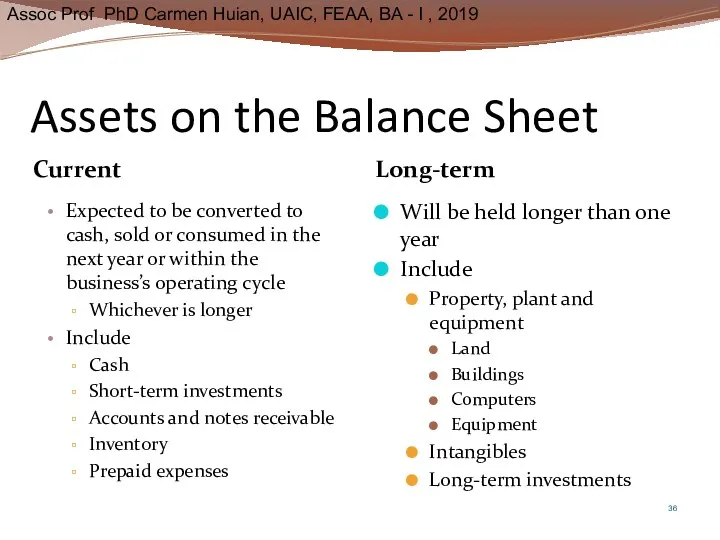
- 36. Assets on the Balance Sheet Current Long-term Expected to be converted to cash, sold or consumed
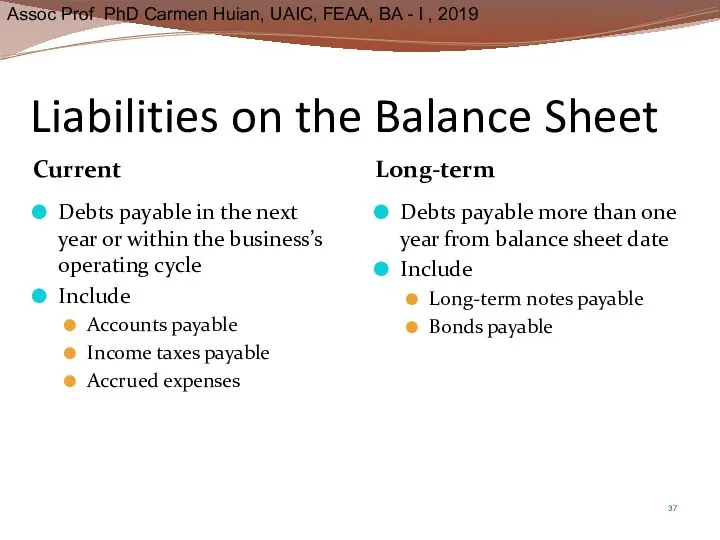
- 37. Liabilities on the Balance Sheet Current Long-term Debts payable in the next year or within the
- 38. Stockholders’ Equity on the Balance Sheet Represents stockholders ownership of the business assets Consists of: Common
- 39. The Balance Sheet
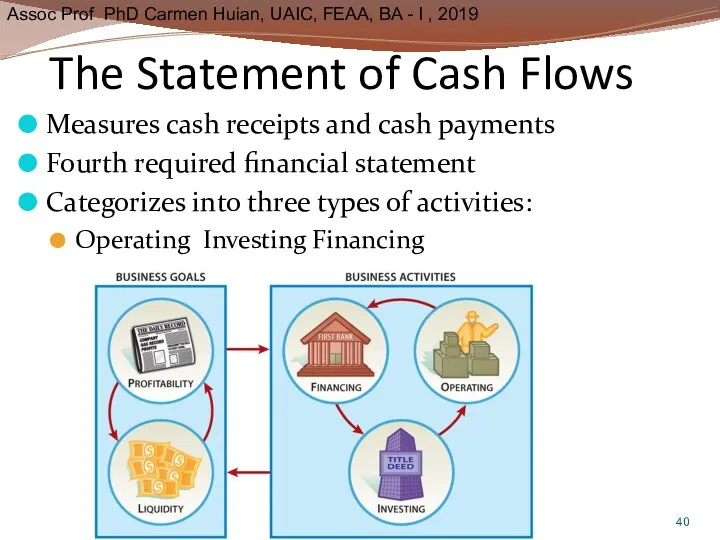
- 40. The Statement of Cash Flows Measures cash receipts and cash payments Fourth required financial statement Categorizes
- 41. Cash Flow Categories
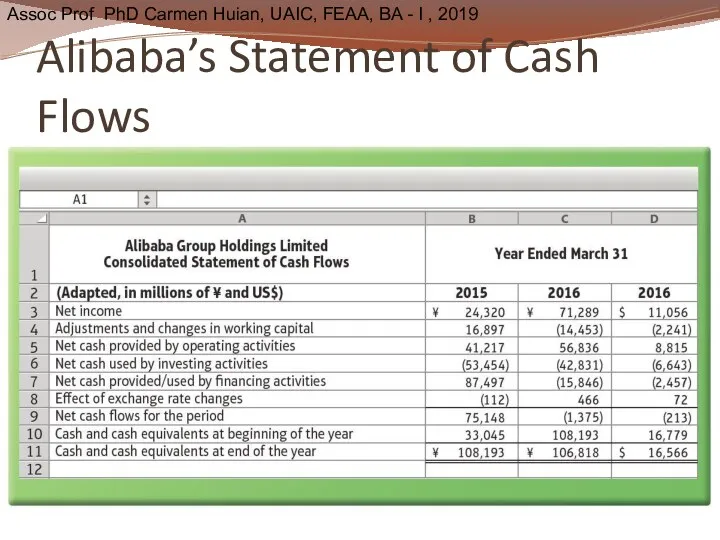
- 42. Alibaba’s Statement of Cash Flows
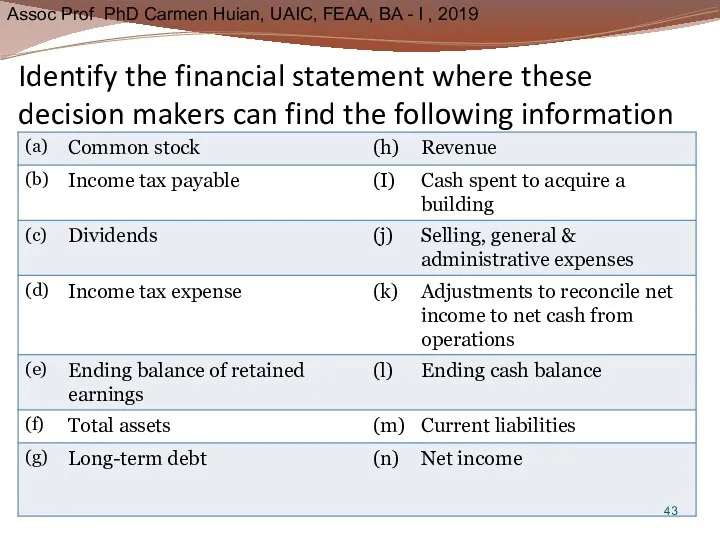
- 43. Identify the financial statement where these decision makers can find the following information
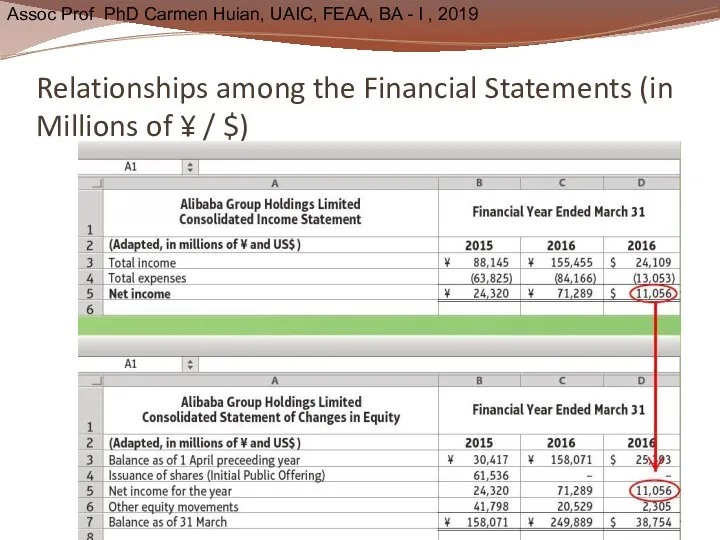
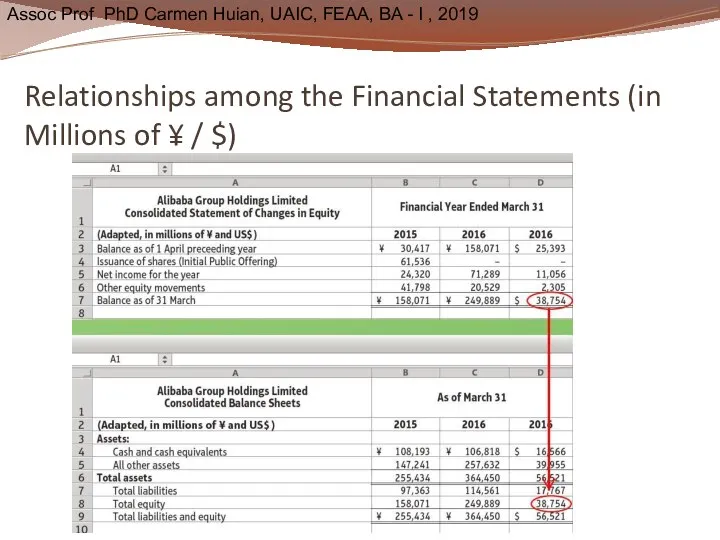
- 44. Relationships among the Financial Statements (in Millions of ¥ / $)
- 45. Relationships among the Financial Statements (in Millions of ¥ / $)
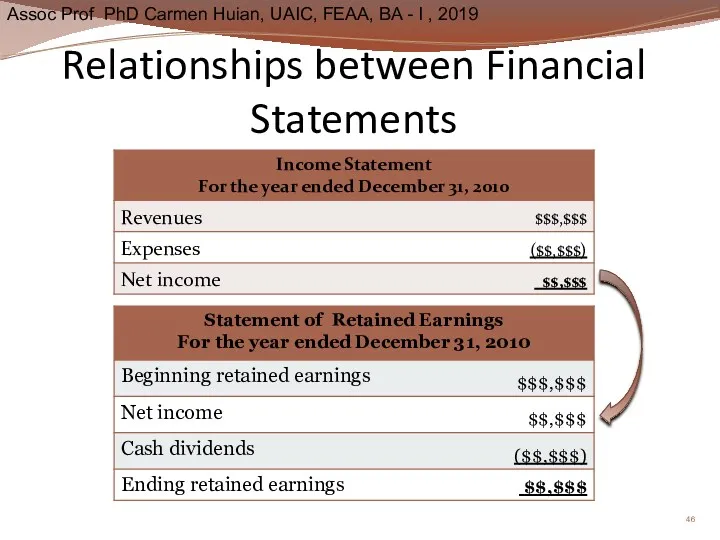
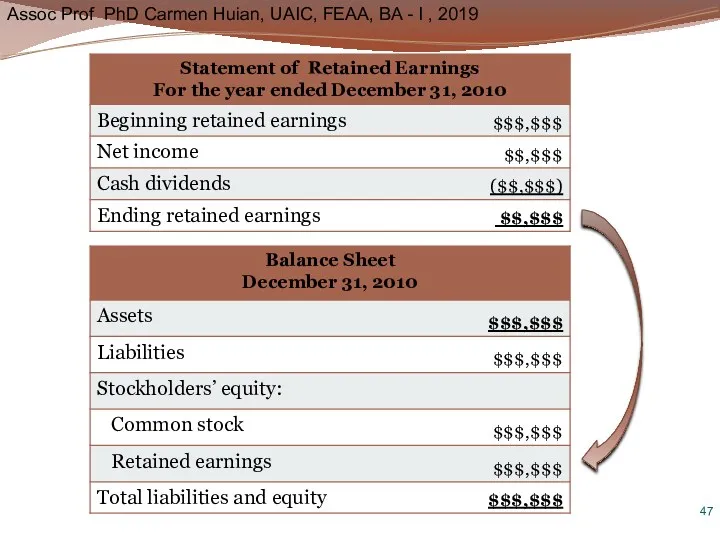
- 46. Relationships between Financial Statements
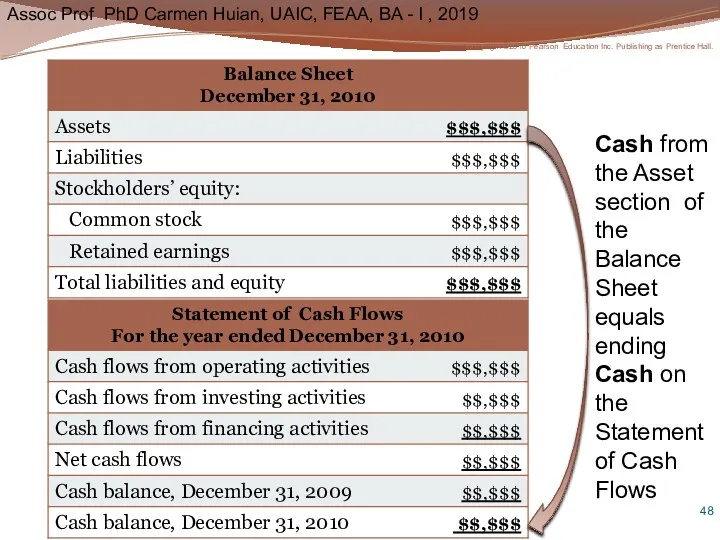
- 48. Cash from the Asset section of the Balance Sheet equals ending Cash on the Statement of
- 50. Скачать презентацию























 Рыночный подход к оценке бизнеса. Метод рынка капитала. Метод сделок. Метод отраслевых коэффициентов
Рыночный подход к оценке бизнеса. Метод рынка капитала. Метод сделок. Метод отраслевых коэффициентов Инвестициялық стратегия
Инвестициялық стратегия Фигуры технического анализа
Фигуры технического анализа Понятие, цели и организация оценки стоимости бизнеса. (Лекция 1)
Понятие, цели и организация оценки стоимости бизнеса. (Лекция 1) Asset Securitization in Russia
Asset Securitization in Russia Сопоставимость отчетных данных и принцип последовательности: МСФО (IAS) 8 Учетная политика, изменения в бухгалтерских
Сопоставимость отчетных данных и принцип последовательности: МСФО (IAS) 8 Учетная политика, изменения в бухгалтерских Отчетность за 9 месяцев 2018 года. Актуальные вопросы. Срок представления налоговой отчетности
Отчетность за 9 месяцев 2018 года. Актуальные вопросы. Срок представления налоговой отчетности Индивидуальный подоходный налог в Республике Казахстан и его учет
Индивидуальный подоходный налог в Республике Казахстан и его учет Налоги и налоговая система РФ
Налоги и налоговая система РФ Місцеві податки і збори
Місцеві податки і збори Доходность и убыточность операций с ценными бумагами
Доходность и убыточность операций с ценными бумагами Налоги. 7 класс
Налоги. 7 класс Инвестициялық жобалардың қаржылық механизмі және жобалық қаржыландыру
Инвестициялық жобалардың қаржылық механизмі және жобалық қаржыландыру Налог на прибыль организаций
Налог на прибыль организаций Relationship between liquidity ratios and profitability in Russian banks using regression analysis
Relationship between liquidity ratios and profitability in Russian banks using regression analysis Шығын айналымын болжау
Шығын айналымын болжау Бухгалтерские счета как элемент метода бухгалтерского учета
Бухгалтерские счета как элемент метода бухгалтерского учета Международные стандарты финансовой отчетности МСФО (IAS) 12 Налоги на прибыль
Международные стандарты финансовой отчетности МСФО (IAS) 12 Налоги на прибыль Тенденции развития современной финансовой науки
Тенденции развития современной финансовой науки Проведение операций по потребительскому кредитованию физических лиц
Проведение операций по потребительскому кредитованию физических лиц Криптовалюта. Доп. инструменты технического анализа
Криптовалюта. Доп. инструменты технического анализа Банки: чем они могут быть вам полезны в жизни
Банки: чем они могут быть вам полезны в жизни Қазақстанның қазіргі уақытта сыртқы қарызы қанша
Қазақстанның қазіргі уақытта сыртқы қарызы қанша Проект бюджета городского округа Судак на 2015 год
Проект бюджета городского округа Судак на 2015 год Финансовые инновации, финансовый инжиниринг. (Лекция 1)
Финансовые инновации, финансовый инжиниринг. (Лекция 1) Критерии оценки инвестиционных проектов
Критерии оценки инвестиционных проектов Планирование финансово-хозяйственной деятельности, как ключевой инструмент финансового менеджмента профсоюзной организации
Планирование финансово-хозяйственной деятельности, как ключевой инструмент финансового менеджмента профсоюзной организации Страхование жизни
Страхование жизни