Содержание
- 2. Outline Introduction Main part 1. Alkaline earth metals: general characteristics, structure; properties and obtaining 2. Oxides
- 4. Electronic structure of atoms At the external energy level, the atoms of the IIA metals have
- 5. Minerals in nature Of the alkaline earth metals, calcium is the most abundant in nature, and
- 6. Physical properties of simple substances In the solid state of aggregation, the atoms are bound by
- 7. Chemical properties Alkaline earth metals have high chemical activity, react with oxygen, hydrogen, other non-metals, oxides,
- 8. acids, easily dissolving in their solutions with the formation of the corresponding salts: Ba + 2HCl
- 9. Obtaining Alkaline earth metals are obtained mainly by electrolysis of molten halides. Chlorides of metals are
- 10. 2. Oxides and hydroxides of alkaline earth metals Oxides Alkaline earth metals form oxides of the
- 11. Alkaline earth metal oxides react with: water: CaO + H2O = Ca (OH)2. Pay attention! Calcium
- 12. acid oxides: CaO + CO2 = CaCO3. acids: BaO + 2HCl = BaCl2 + H2O.
- 13. Barium sulphate Barium sulfate is used in medicine. It is used as an X-ray contrast agent
- 14. Hydroxides Alkaline earth metals, when they interact (or their oxides) with water, form basic hydroxides (bases).
- 15. Calcium hydroxide is a strong base, but slightly soluble in water. Its saturated solution is called
- 16. 3. Salts of alkaline earth metals Obtaning salts Salts of alkaline earth metals can be obtained
- 17. Salts of anoxic acids are formed by the direct interaction of simple substances: Ca + S
- 18. Chemical properties Salts of alkaline earth metals react with acids, salts. When heated, some salts decompose:
- 19. Qualitative analysis Calcium compounds color the flame a brick-red color. Barium ions can be detected in
- 20. 4. Application and biological role of alkaline earth metals and their compounds Calcium Metallic calcium is
- 21. The biological role of calcium The human body contains about 1% calcium, mainly in bones and
- 22. Calcium hydroxide Calcium hydroxide (slaked lime) is of great practical importance. It is used as a
- 23. Calcium carbonate Calcium carbonate (chalk, marble, limestone) is used in construction and agriculture, used in the
- 24. Gypsum and alabaster Gypsum and alabaster are used in construction and medicine. When mixing alabaster with
- 25. Quections for self control 1.Choose which of the listed elements belongs to alkaline earth metals? A)All
- 26. 3.Indicate which pairs of substances interact to form calcium hydroxide: A)all options are suitable B)Ca oxide
- 27. 5.Check all statements that are true of barium sulfate: A)insoluble in sulfuric acid B)used for canning
- 28. Literature 1.Basic literature : 1. Jenkins, Chemistry, ISBN 978-0-17-628930-0 2. Alberta Learning, Chemistry data booklet 2010,
- 29. 2.Additional literature : 1.Б.А.Мансуров «Химия» 10-11 кл., Атамура 2015 г 2.Б.Мансуров., Н.Торшина «Методика преподавания органической химии»
- 31. Скачать презентацию



























 Шкала рН. Лекция 03-1
Шкала рН. Лекция 03-1 Топливный элемент
Топливный элемент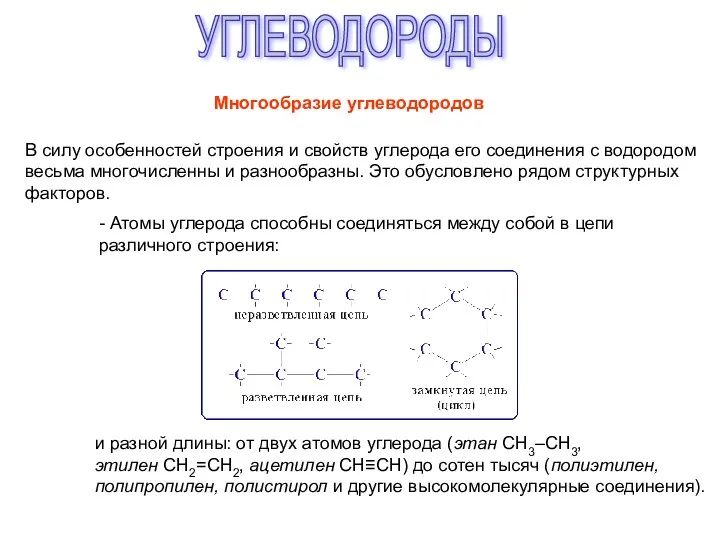 Углеводороды. Многообразие углеводородов
Углеводороды. Многообразие углеводородов Физико-химические методы анализа. Лекция 3
Физико-химические методы анализа. Лекция 3 Окислительно-восстановительные реакции
Окислительно-восстановительные реакции Вивчення властивостей полімерів і синтетичних волокон. Лабораторна робота
Вивчення властивостей полімерів і синтетичних волокон. Лабораторна робота Химические реакции в органической химии (10 класс)
Химические реакции в органической химии (10 класс) Поширення солей у природі
Поширення солей у природі Флотационные реагенты. Активаторы
Флотационные реагенты. Активаторы Нуклеиновые кислоты
Нуклеиновые кислоты Бейорганикалық заттар технологиясындағы жүйелерді термодинамикалық талдау
Бейорганикалық заттар технологиясындағы жүйелерді термодинамикалық талдау Фосфор. Открытие фосфора
Фосфор. Открытие фосфора Альдегиды и кетоны
Альдегиды и кетоны Биоорганическая химия
Биоорганическая химия Лекция 6. Растворы электролитов
Лекция 6. Растворы электролитов Железо. Строение атома, химические и физические свойства. Урок №1
Железо. Строение атома, химические и физические свойства. Урок №1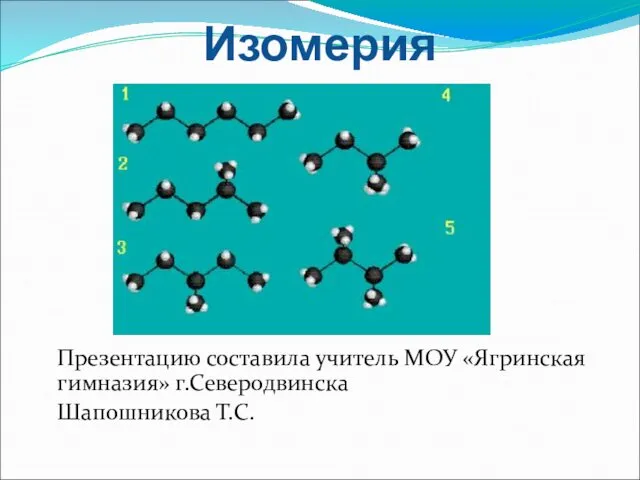 Изомерия и ее виды
Изомерия и ее виды Нұсқа талдау
Нұсқа талдау Классификация кристаллов по типу химической связи
Классификация кристаллов по типу химической связи Химический элемент V группы: сурьма
Химический элемент V группы: сурьма Introduction to Periodic Table
Introduction to Periodic Table Элементы группы галогенов
Элементы группы галогенов СЖЭ-ң жалпы сипаттамасы, ашылу тарихы, қолдану аумағы, минералдары
СЖЭ-ң жалпы сипаттамасы, ашылу тарихы, қолдану аумағы, минералдары Пищевые добавки
Пищевые добавки Виды химической связи
Виды химической связи Генетическая связь между классами неорганических соединений
Генетическая связь между классами неорганических соединений Химические свойства серной кислоты
Химические свойства серной кислоты Гидроксиды. Основания. Состав, классификация, свойства, получение
Гидроксиды. Основания. Состав, классификация, свойства, получение